Difference between revisions of "Colourless London"
From Londonhua WIKI
Akgiacoman (talk | contribs) |
Akgiacoman (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
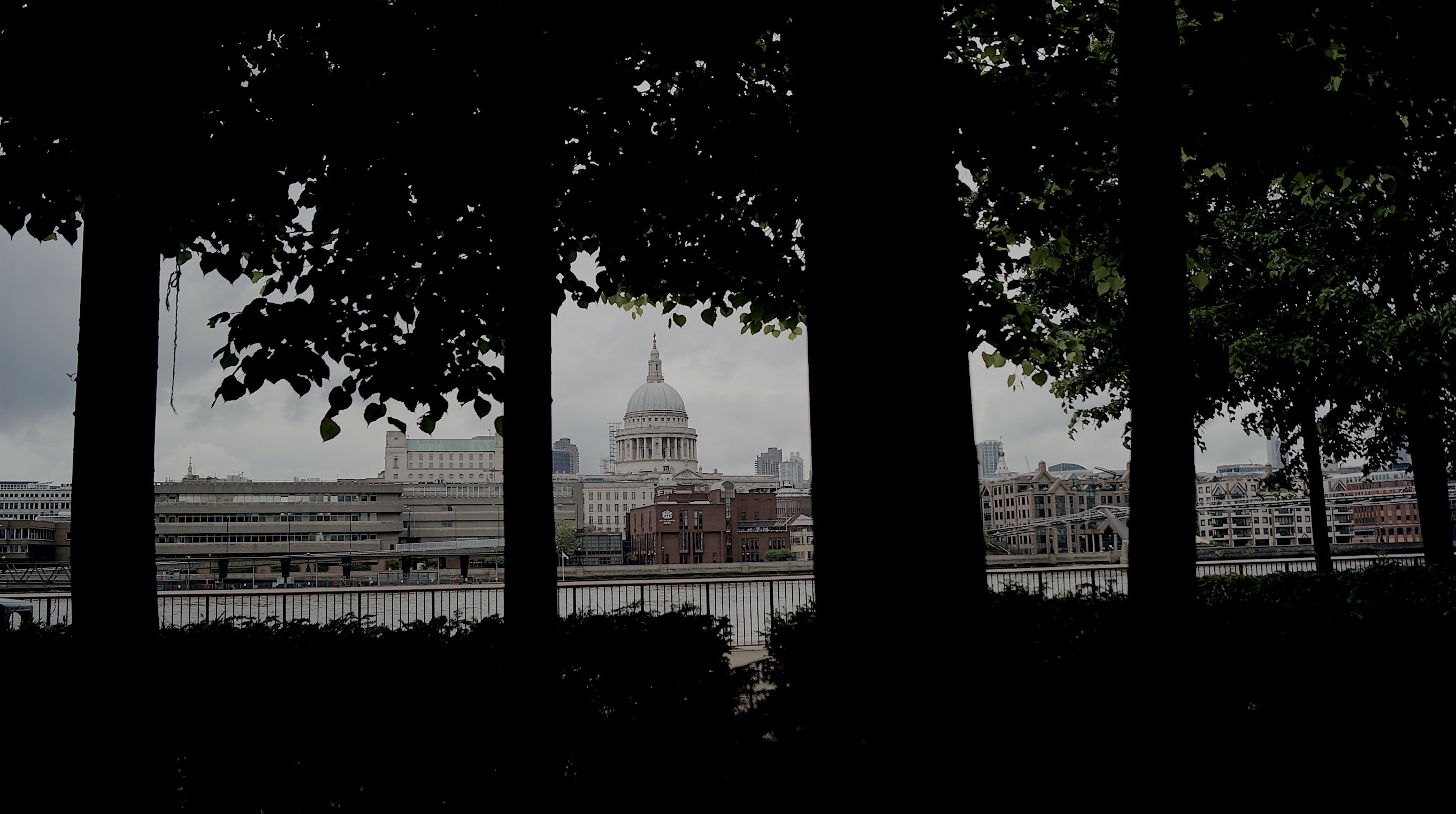
===St. Paul's Cathedral=== | ===St. Paul's Cathedral=== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | Being a place for Christian worship for over four hundred years, Sir Christopher Wren's St. Paul's Cathedral stands as the most iconic church in all Britain. The medieval Cathedral, with a tower and spire soaring above the city, was at the time one of the wonders of Europe. St Paul was built after the Fire of London of 1666, its dome with the ball and cross above it symbolic of London's steadfastness down the centuries and its endurance throughout the bombing of the Second World War. However, it was not until 1675 that a scheme for complete rebuilding was finally approved. Wren had made several other designs including that illustrated by the so-called Great Model still in the cathedral. When it came to the building of the Cathedral, he insisted on having a much freer hand, so the final product was just a resemblance of the original design.<ref>New, A. S. (1981). A guide to the cathedrals of Britain. London: Constable.</ref> It was completed in 1710, when Wren was seventy-eight years old, and by the final stages of construction, he was carried to the dome because he was unable to take the stairs. There are infinite features to be referenced about St. Paul's Cathedral; in fact several books have been filled with its history, however, it was chosen for this milestone not only for its physical beauty but because it conveys a higher message. | |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | [[St. Paul's Cathedral]] represents the change in beliefs of the whole country that generated much controversy all over Europe and took origin in this very city under the rule of Henry VIII and lead mainly by Cromwell. | + | [[St. Paul's Cathedral]] represents the change in beliefs of the whole country that generated much controversy all over Europe and took origin in this very city under the rule of Henry VIII and lead mainly by Cromwell. It represents the power that lies in all English people and the audacity of its governance, as well as the communion of all the religions of the world that lay in the hearts of all the newer generations of Londoners. From the outside St. Paul's stands with all its might and power and from the inside it is awe-inspiring, breathtaking, unlike any other cathedral or church built in Britain. Plus, this magnificent church has dominated the London skyline for hundreds of years, and has seen the city change without recognition. As the author Ann Saunders introduces one of her books, "the Cathedral lies at the heart of London and - in so many ways - in the heart of the nation". <ref>Sanders, A. (2001). St. Paul's (E. Drury, Ed.). London: Collins & Brown Limited.</ref> |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed"> | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 2 June 2017
Contents
Colourless London
by akgiacoman
 Your Project Page Picture Caption |
Abstract
"A London Full of Colour" is a project that aims to portray a different reality of the daily life of London citizens. By picturing different scenarios in their reality comparing them to the reality that I choose for each one of them, the audience will be able to admire the beauty and uniqueness of the city from a different perspective. I have gone to international poetry competitions and taken painting and photography courses before arriving to college. This project will combine my favorite forms of expression through art and hopefully brighten the days of the viewers. The main message I wish to convey is that every single one of us chooses the reality they want to live in, meaning that the same place could be seen as a prison for our souls or a wonderland for our imagination. The goal of this Milestone, however, is to display London as it is and to capture through pictures emotions displayed by people walking by or admiring the landscape. Pictures are taken from different perspectives and represent feelings of an average citizen living daily life. In the same way, this milestone explores the influence and relationship between the London weather and psiquis of the Londoners.
Introduction
London is a "world city" that encompasses many cultures, religions, forms of governance and mindsets distributed across the ages that complete its history. London is a marvelous place full of corners to discover, however, since ages ago, it has been covered by a sometimes unwanted and disturbing presence; the fog. Caused by the Thames, the fires, the pollution and the filth, the fog has become part of the identity of the city of London, England. Emerging in the early nineteen century and covering several nearby towns, the London fog was both, a source of inspiration and fear. As the artistic component of the city was being used to its full potential by geniuses like Monet and Dickens, the criminality rates were also rising due to the anonymity granted to many by the blurry fog. Whether it was an element of romanticism, mystery or terror, the weather in London is an iconic representation of the relationship of how these kinds of conditions sometimes determine the identity of a city and the behavior of its population. In this Milestone this relationship and its social, cultural, and psychological repercussions are exposed through the background as the reader is invited to explore the history of the fog, to better understand the later creative component that is captured in the pictures taken of some of the most iconic and well-known sites in the city.
Section 1: Background
Weather in London
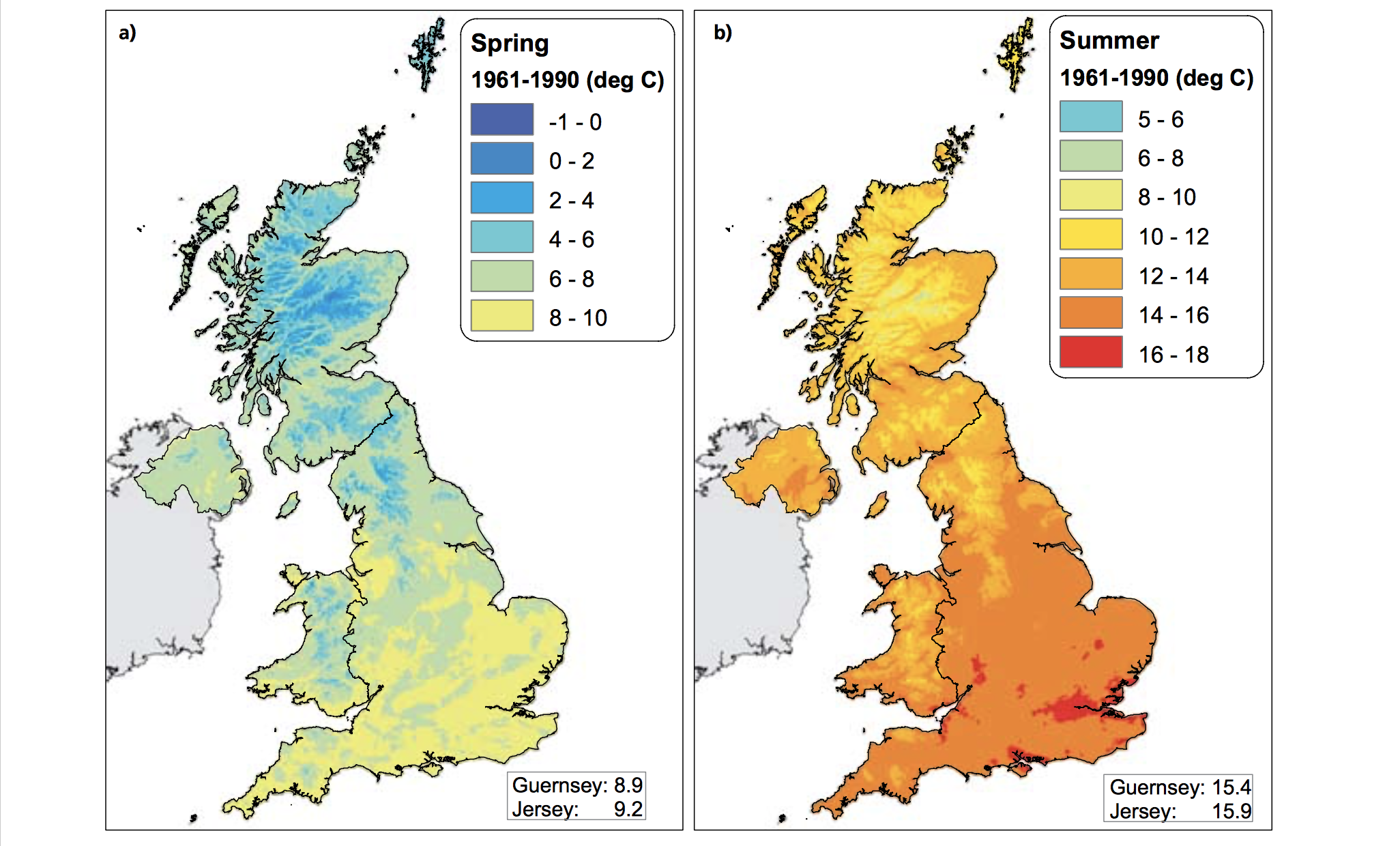
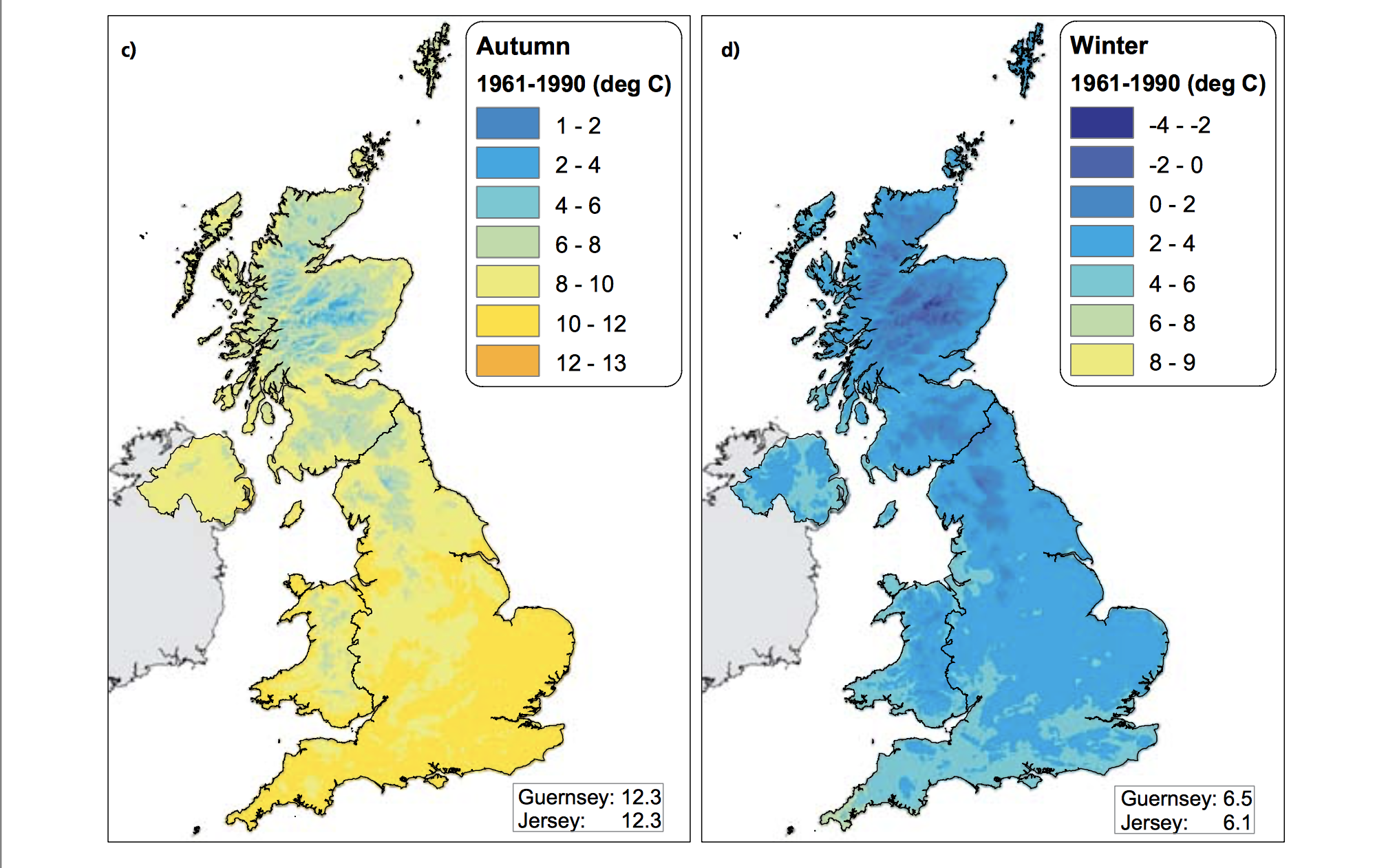
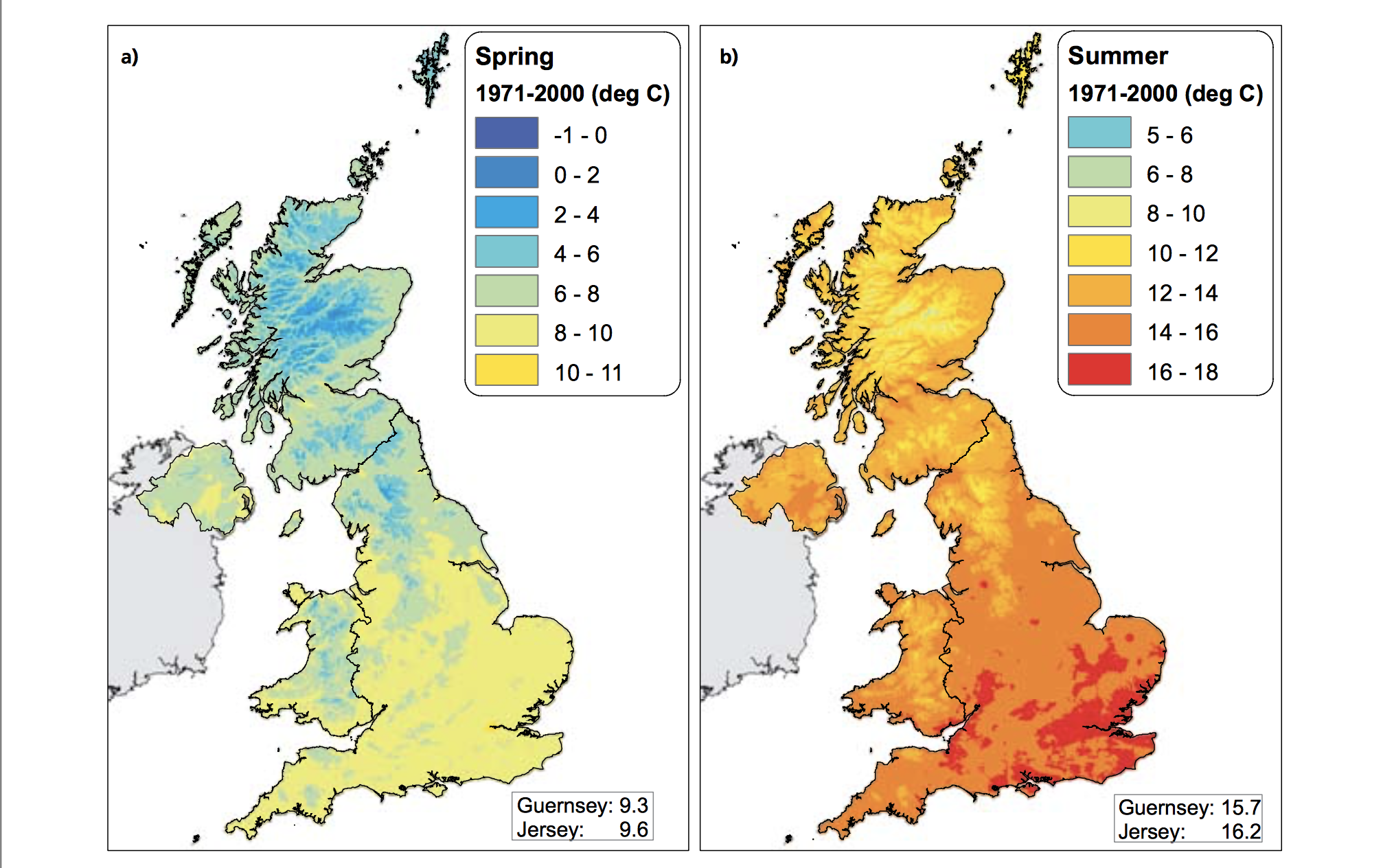
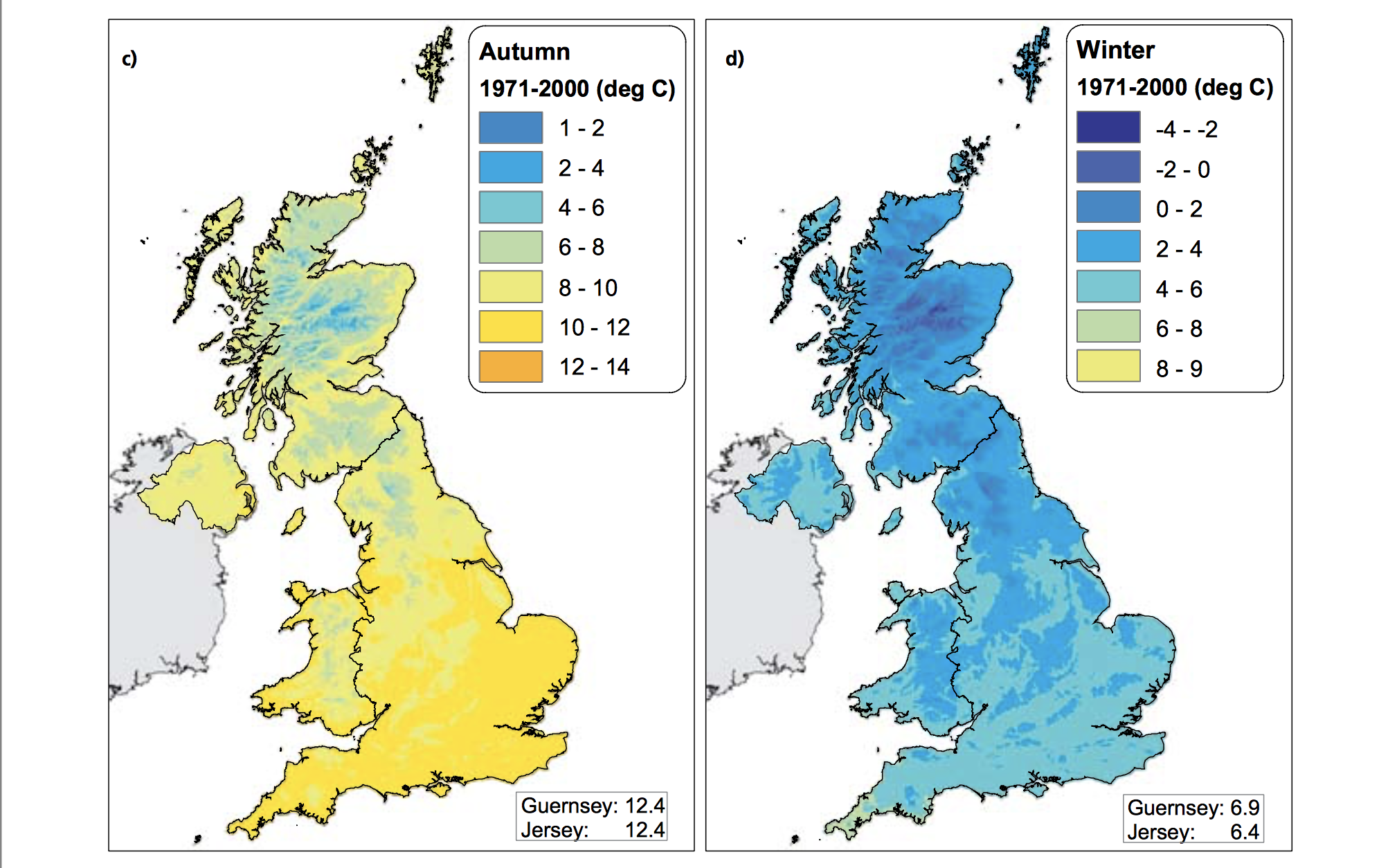
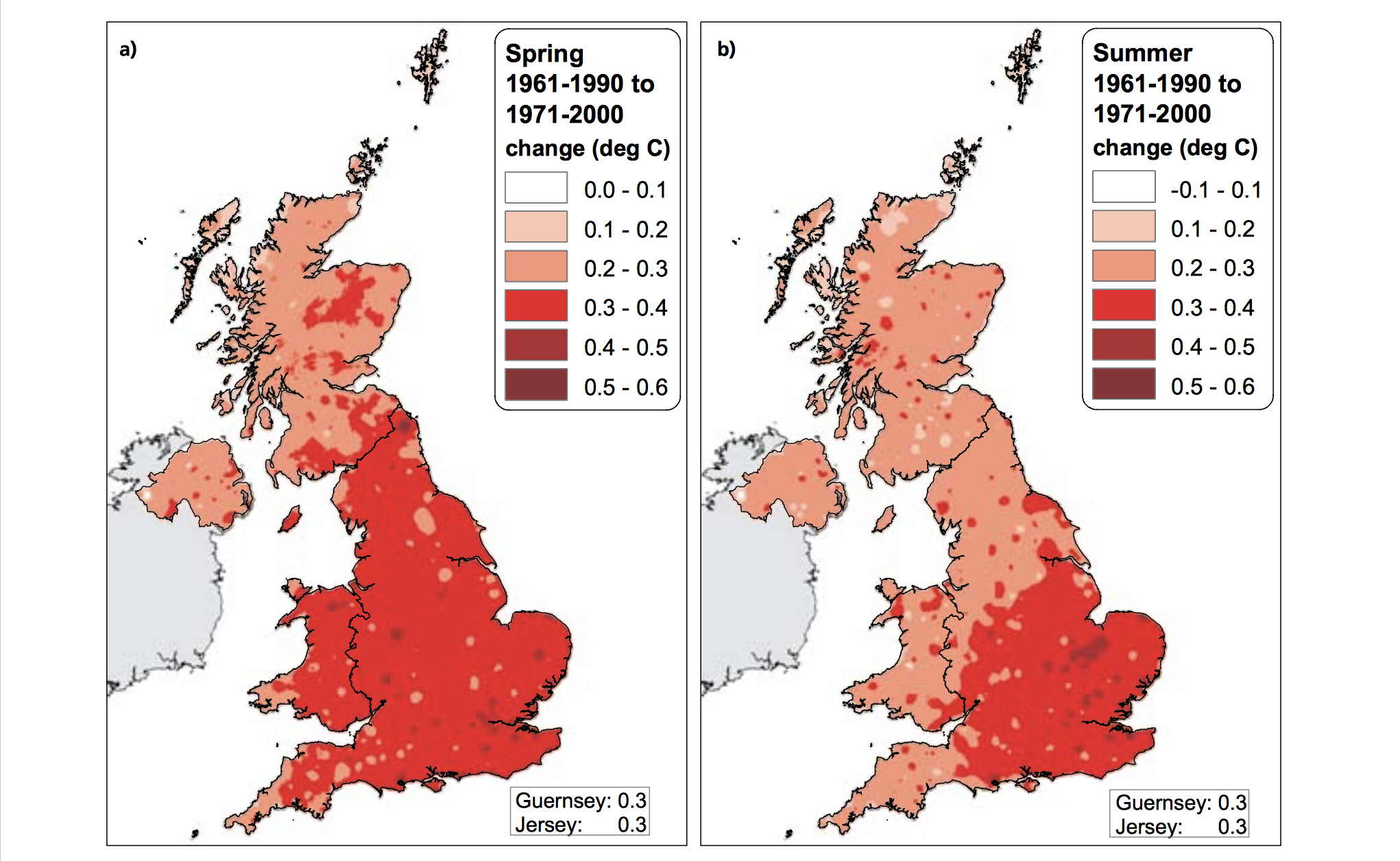
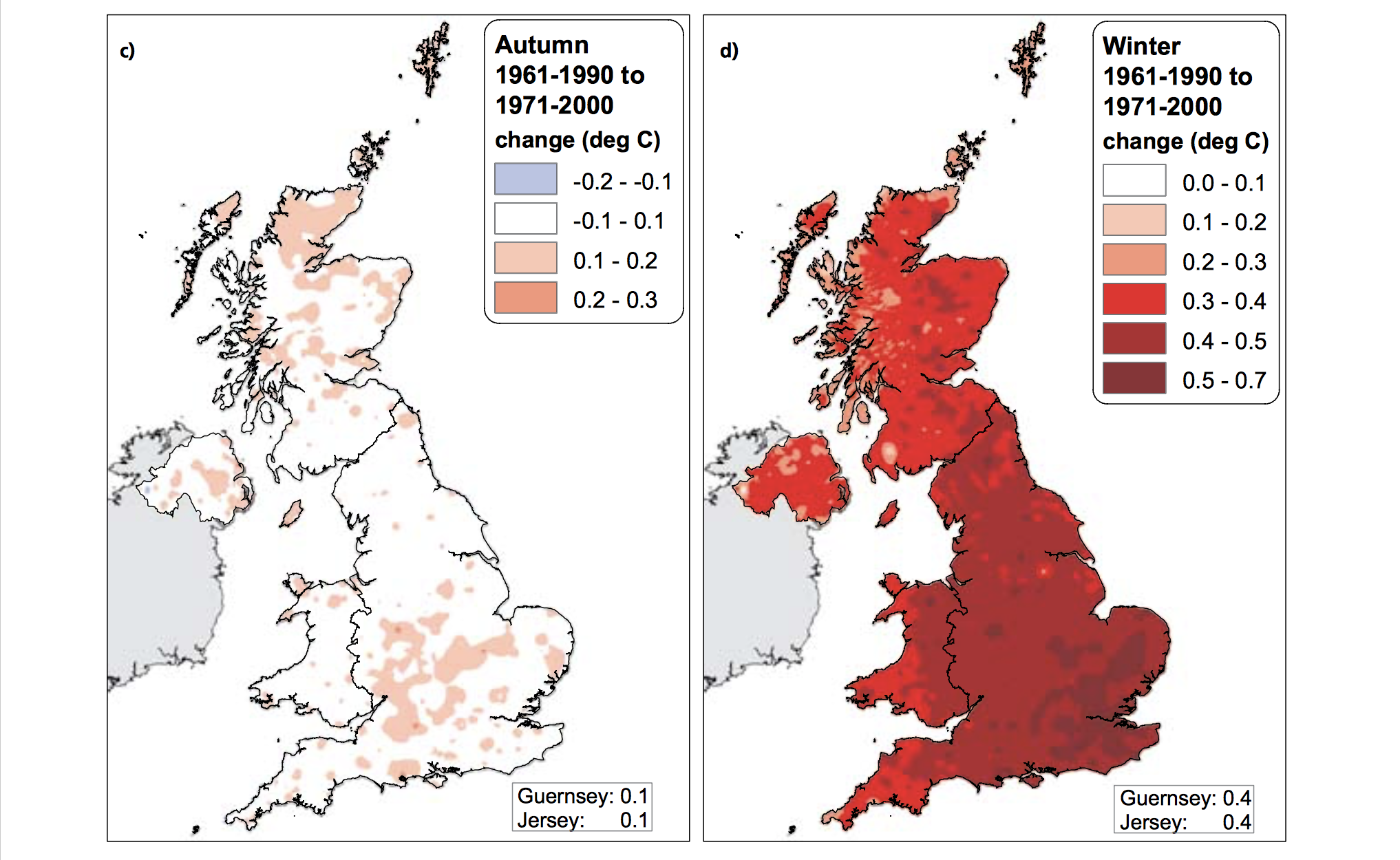
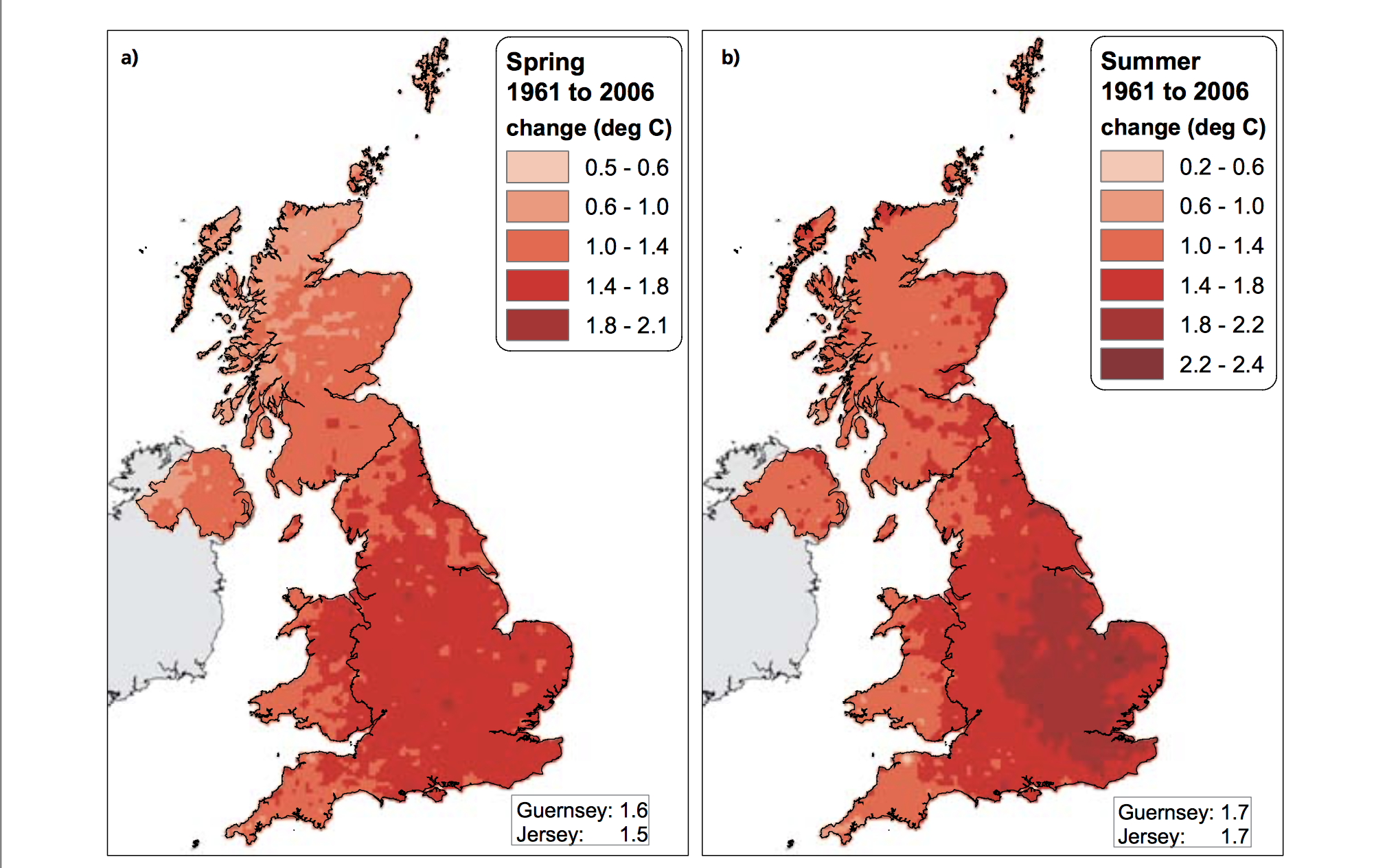
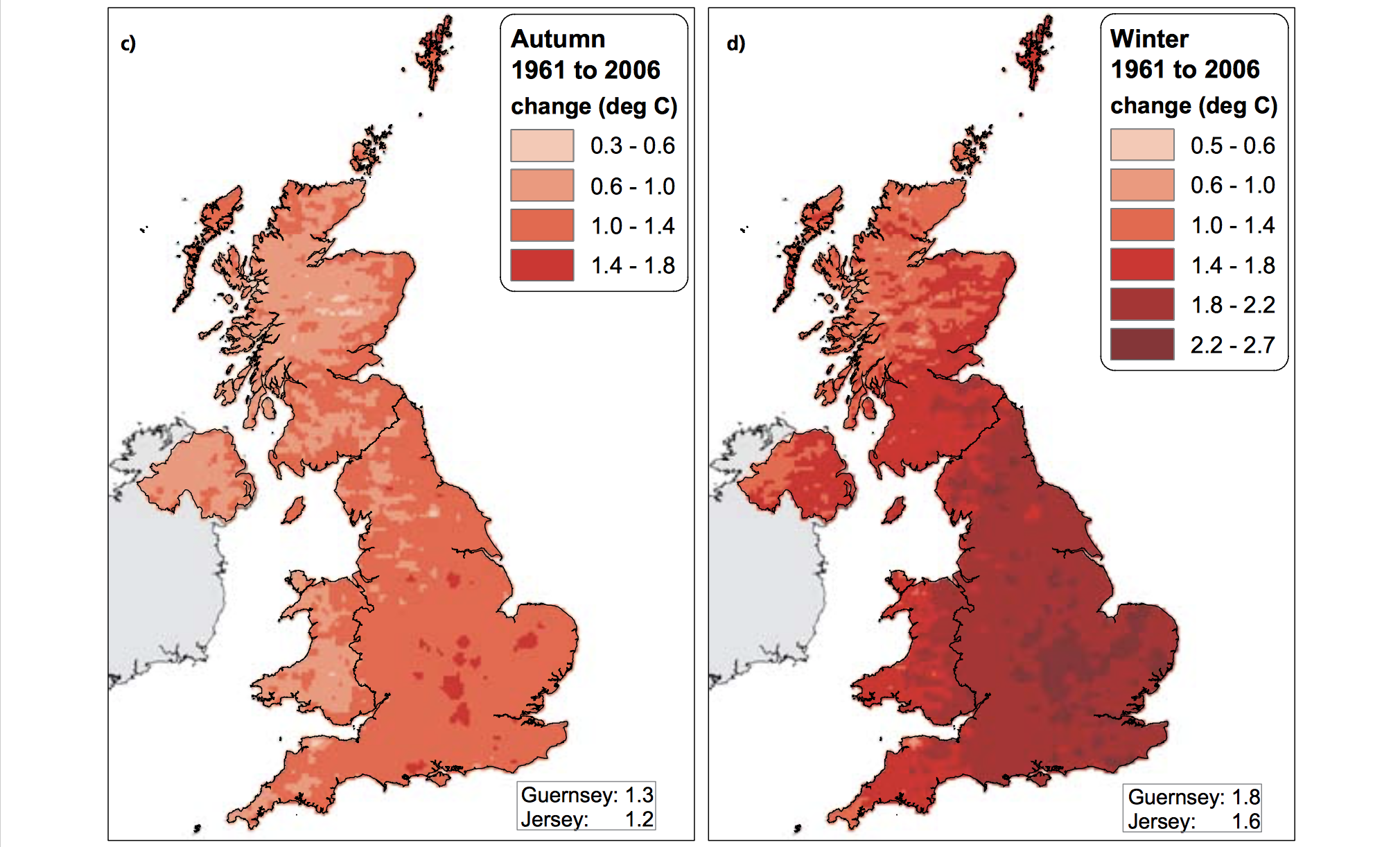
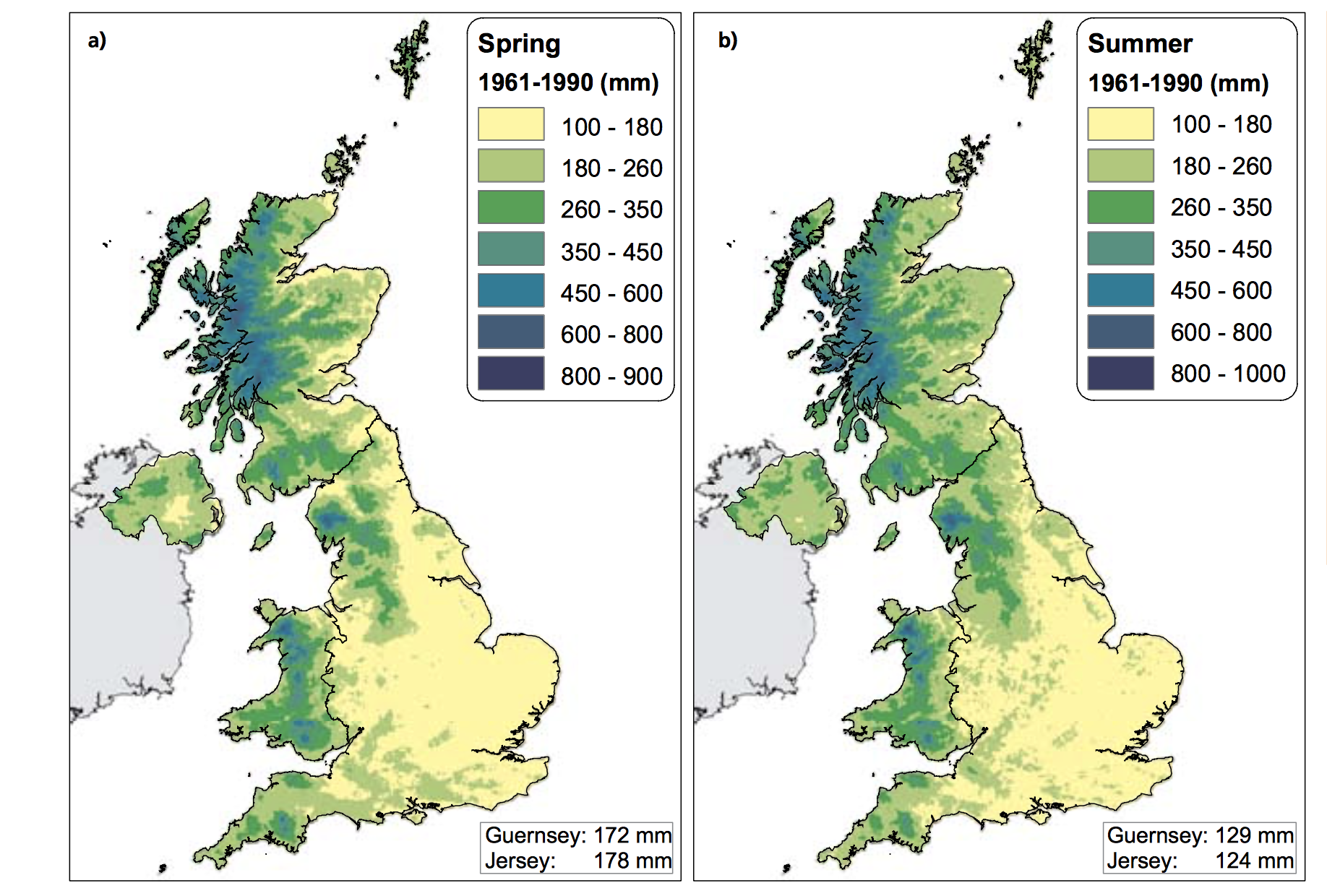
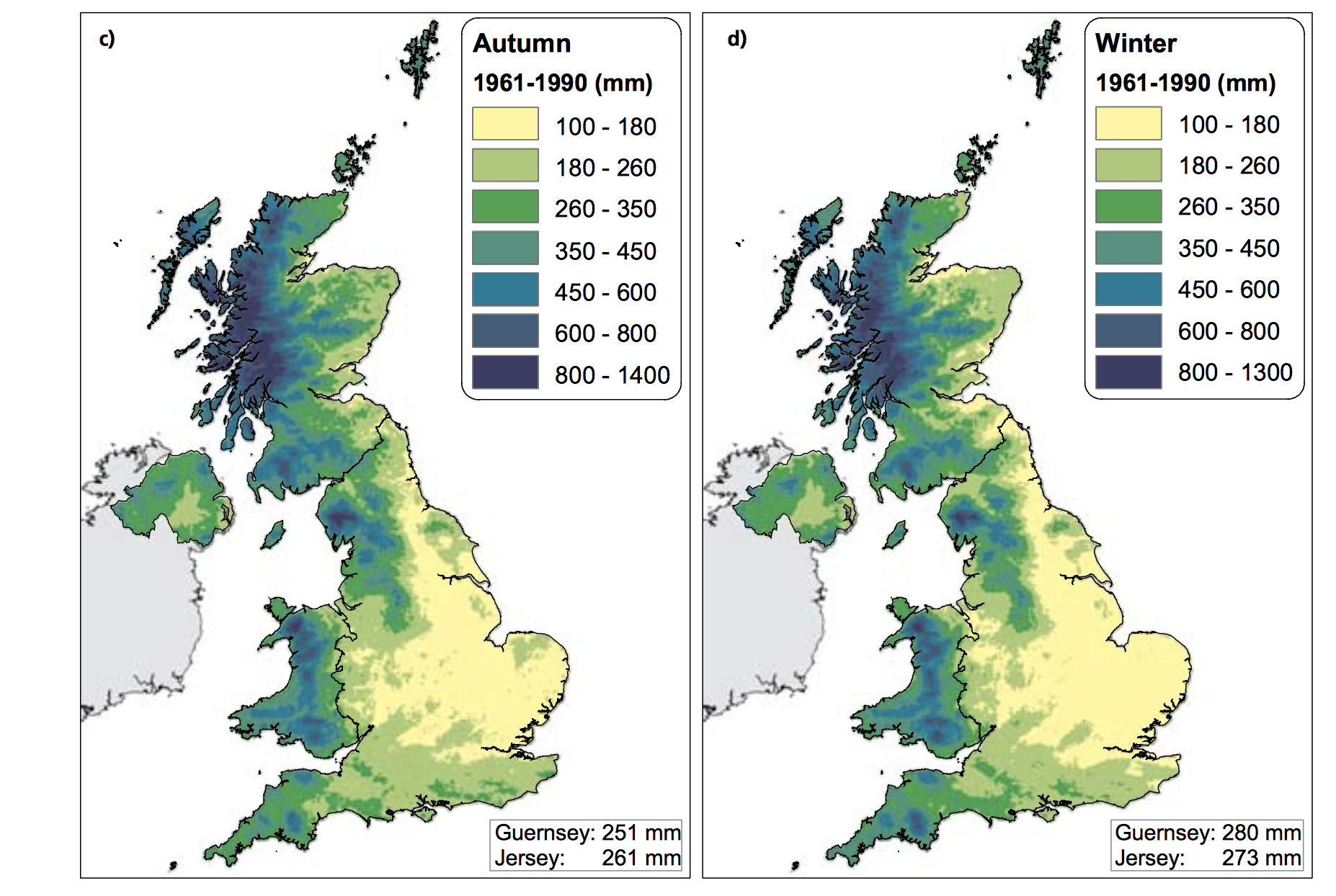
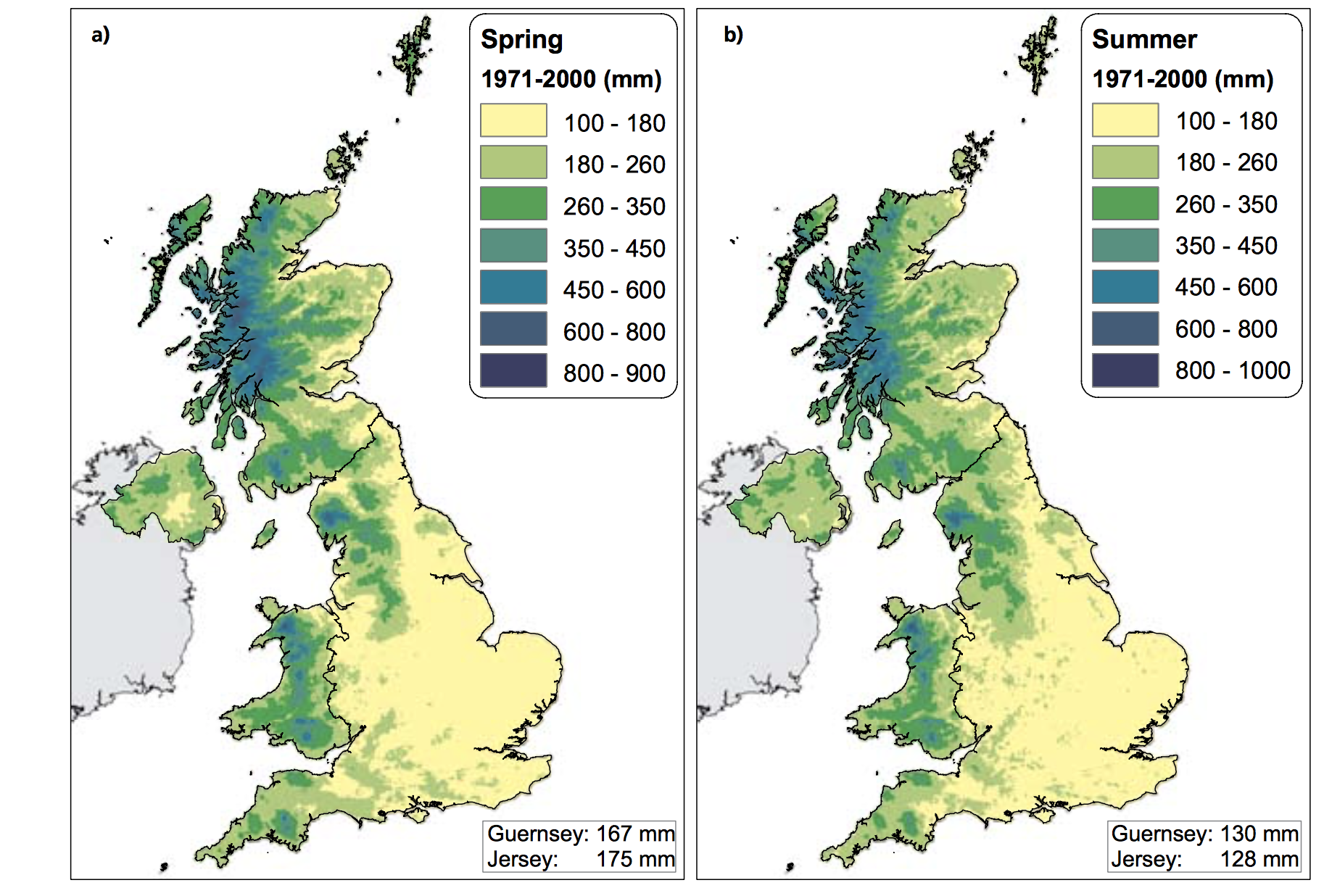
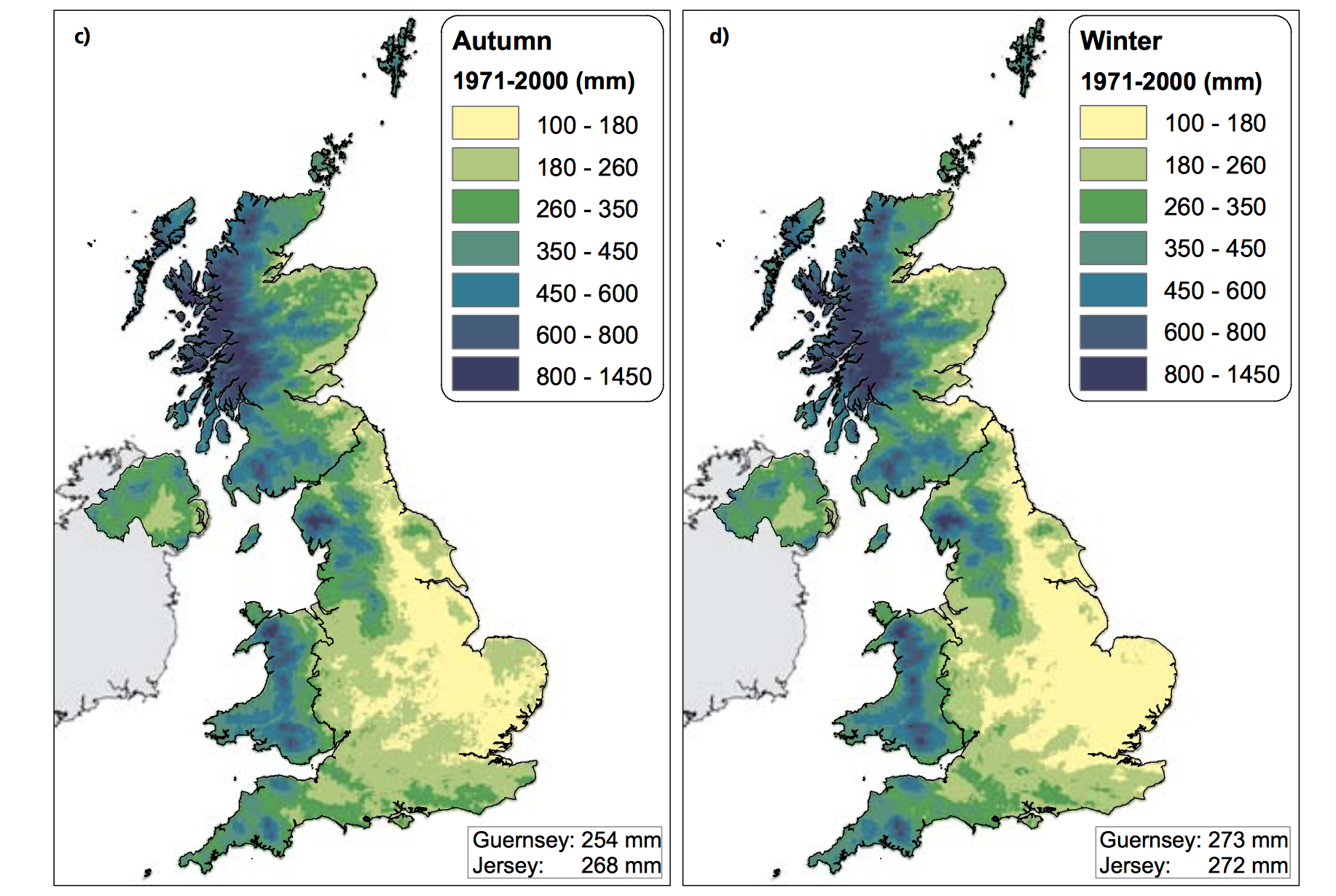
The Central England Temperature (CET) monthly series, beginning in 1659, is the longest continuous temperature record in existence [1]. The following pictures show the average temperature on the different seasons of the year of the UK since the sixties, this information was taken from a report published in 2009 titled "The climate of the United Kingdom and recent trends". The report took information mainly from the CET to construct the graphics. In terms of record warm individual days, 10 August 2003 saw the hottest ever maximum temperature in the UK; 38.5 oC at Faversham, Kent, exceeding the previous record in 1990 by 1.4 degrees Celsius. Though the temperature record does not go that far back, the growing of grapes in the medieval period has been used to imply that current warm temperatures in England have been experienced before. However, Jones and Mann note in their article that “past vine growing in England reflects little, if any, on the relative climate changes in the region since medieval times”.[2] As seen in the images, there has been an increase in the temperature of the United Kingdom overall. Now, in terms of rain, annual mean precipitation over England and Wales has not changed significantly since 1766. Seasonal rainfall is highly variable, but appears to have decreased in summer and increased in winter, although with little change in the latter over the last 50 years. Severe windstorms around the UK have become more frequent in the past few decades, although not above that seen in the 1920s. The graphics that go from yellow to navy blue, show the degrees of precipitation (rain) all across the UK in the same period of time. In the Images it can be seen how much the temperatures varies from season to season as well as how it changes as years pass. [3]
The London Fog
The Source of the Issue
In most parts of the world, fog is seen as just a natural phenomenon, "clouding the air with small particles when the natural conditions are right". The London fog was born by the early 1800s, because of the increasing pollution of the air caused by the smoke coming out of the wood fires used for burning sea coal. [4] . Small manufactories were all around the city and larger polluters accumulated near the rivers. Glass makers, breweries, potteries, tanneries and domestic coal fires, all contributed to the atmosphere of noxious fumes."The city's rapid expansion multiplied the number of domestic coal fires and mingled their smoke as it poured out into the atmosphere with the noxious emissions of factory chimneys and workshops in the early stages of the industrial revolution in the capital."[5] So then a battle to remove the fog began when in 1819, Michael Angelo Taylor, MP of Durham, demanded the Parliament to take action to mitigate the issue. In response to this, a select committee was formed to discuss if smoke was dangerous to health and if there was anything that could be done about it. Taylor put a lot of effort into his cause and brought to the sessions arguments that now are logical to us but, in that time, were absurd. Arguments like that factory owners should make adaptations and buy new machines and that tis would not only be beneficial to the city to to them as well, in a long term of course. He was also amongst the first to suggest that the black fog was harmful to public health and it carried diseases. However, there were dissenting voices; manufacturers argued that smoke only represented a minor inconvenience. Some even dared to claim that smoke "disinfected" the air from the smell of the drains. Even Robert Angus Smith, who discovered acid rain in 1859 strongly believed that tough the sulfurous acid contained in the smoke was capable of damaging buildings, it treated miasma. As a result of these popular believes, Taylor had very little success in the parliament, however, he set a precedent and his claims were later supported by scientific data and medical evidence.[6]
Several others followed Taylor's steps with almost no success at all until the Clean Air Act finally killed the fog in 1962.[7] According to an article published by the American Lung Association, thanks to the Clean Air Act, this year's "State of the Air" report found that the percentage of people that live in locations with high risk to their health due to air pollution decreased from 52 percent to 40 percent. We should all be alarmed about potential rollbacks of Clean Air Act regulations and proposed cuts to EPA's budget. "The progress in public health protections brought to us with the Clean Air Act have saved hundreds of thousands of lives." [8] However, even though the deathly London fog "died" with the Clean Air Act, it is something to take care of still today, because development and growth have not stopped and nobody would want them to. By the beginning of the year 2017, the news agency CNN released an article where they announced; "London breached its annual air pollution limits five days into the new year, Mayor Sadiq Khan said Friday.". Nitrogen dioxide is a gas emitted by diesel engines that causes lung disease and respiratory problems. European Union law stipulates that a maximum nitrogen dioxide concentration of 200 micrograms per cubic meter must not be exceeded for more than 18 hours over the year. Despite this, Brixton Road exceeded this limit since the first week of the year. This only shows that the struggle that Londoners dealt with back in the nineteen century is still somewhat present today. [9]
Severity
In the book "Dirty Old London", it is emphasized how severe the problem of the fog started to become by the end of the nineteenth century. "The most wretched poor were passing on an ever-accumulating collection of physical and mental defects to their rickety children. This dark parody of Darwinian evolution gained great credence when thousands of young men new turned away for service in the Boer War on grounds of their poor physical condition. Smoke and fog were high amongst the possible culprits for what seemed a disturbing decline in physical strength."[10] Judging from the author's perspective, it is visible how the fog, besides causing physical damage to the citizens of London, became as well a social issue. As mentioned later in the book, in the diary of George Gissing, for January 1888, he complains about the fog in a most depressing way of manifesting his misery.
"Mond. Jan. 9. Hideous fog; bad cold...
Tuesday. Jan. 10. Fog still; cold worse...
Wed. Jan. 11. Fog denser than ever. Cold so much worse, had to lie up in house...
Thursd. Jan. 12. A terrible day; the fourth that we have not seen the sky.
Frid. Jan 13. Fog hanging about still, until 3 in afternoon. Then clearing...
Sat. Jan. 14. Black fog at noon, then cleared, and at night tanked heaven for showing its stars once more...
Thursd. Jan. 19. Cold and cloudy. Must be several weeks since it was a single gleam of sunlight." [11]
The queen Elizabeth I herself complained about the hideous fog saying that she found "herself greatly grieved and annoyed with the taste and smoke of sea coals".[12] And though in the economical side, London was the very source of development for England and "a financial and mercantile hub for the world"[13], it was, at the same time, one of the most filthy capital cities the world has ever come to know, even today. This is often attributed to the rapid population growth between the eighteen and the nineteen hundreds. The population in London increased from about a million to over six million citizens, "suburbia replaced green fields, crushing up the country in its concrete grasp"[14]. As a result, the filth increased and with it, the diseases spread more rapidly and the fog turned the city into complete darkness for days during the winter times, which, at the same time, increased the criminality rates."The capital ended the century with the nickname of "The Smoke"- a city named after its most enduring pollutant." [15]
"The Doom of the Great City", a book published in 1880, also describes in great detail how the majority of central London was "choked to death" by toxic fog, and even further, how people cared very little about solving the problem. "Londoners were well accustomed to the inconvenience of fogs, and looked upon them in the light of a regular institution, not caring to investigate their cause with a view to some means of mitigating them." However, in that time, very little was known about the terrible consequences of long term exposure to the contamination in the fog. It was not until about the 1840's when the sanitary movement started tackling the smoke issue. [16]
From a Londoner's Perspective
It is not hard to understand how tired some Londoners must have been of the filthiness and the fog, seeing such an impotent city swallowed by the mirk of the smoke. "By the end of the (19th) century, the pall of smoke and fog over the metropolis seemed inescapable, and Londoners were designated to its presence. Parliament would not act; householders were apathetic. Late-Victorian "degenerationists" argued that vitiated air and lack of sunlight were creating an underclass of slum-dwellers, atrophying in the darkness." [17] However, it was often commented by tourists that Londoners had grown used to living among the infamous filth and had learned to adapt to their circumstances, tolerating the presence of the fog, the, hideous rotting smell and the mud of the river. "An American town-bred lady would as soon think of swimming up the Thames against tide as walking far in such ankle-deep mud." [18]
Even the ladies of the upperclass were advised to wash their faces several times a day to remove the layer of soot that accumulated in the skin "if one lives in dear, dirty old London, or in any smoky city, three times a day is none too often"[19]. However just as Jack London said in 1903, "The color of life is grey and drab. everything is helpless, hopeless unrelieved, and dirty. The people themselves are dirty, while any attempt at cleanliness becomes howling farce, when it is not pitiful and tragic. Strange, vagrant odours come drifting along the greasy wind, and the rain, when it falls, is more like grease than water from the heavens."[20].
Weather's Influence
People have always wondered how exactly does weather impact someone's mood. Is it possible that heat makes people more aggressive? Does rain makes people sad? Or is it just another of Hollywood's tools? How about cold temperatures? Some professors and psychologists claim to have the answer for some of these inquiries. An article published in 2008 states that several contributors found that weather’s daily influence has more of an impact on a person’s negative mood, rather than helping one’s positive mood. "Higher temperatures raise a person with a low mood up, while things like wind or not enough sun made a low person feel even lower.". [21] This means that people are more heavily influenced in a negative way by weather than in a positive way. Likewise, researcher Marie Connolly found that women who were interviewed on days “with more rain and higher temperatures [reported] statistically and substantively decreasing life satisfaction, consistent with the affect results.” [22] This claim is something The Epoch Times agrees with, as it published "Humidity tends to make people more tired and irritable.
Barometric pressure fluctuations can alter moods and trigger headaches, some studies finding a link between low pressure and suicide. On rainy days, people report lower satisfaction with their lives.".[23]
Though the results of studies on the links between depression and rain are not entirely attributed to weather, because of all the factors that may influence, the relationship between weather and a person's mood should not be completely discarded either. This being said because there is a study from the same year that analyzed six weather parameters: temperature, wind power, sunlight, precipitation, air pressure, and photoperiod and compared them to mood. Combining these weather parameters, they found no general tie to rainy or sunny days; however, they did find a slight correlation of the intensity of mood reported by each individual.[24] Which means that people tend to had their emotions feeling more intensified in extreme weather conditions such as too much sunlight or too much rain. Also, the rain often means that a person is more likely to stay in more and socialize less. Socializing is actually one of the most powerful antidepressants of all, as is sunlight as discussed before. Thus if someone is staying in he or she can often start to feel tired and low in terms of mood, and furthermore the lack of stimulation can arouse feelings of 'cabin fever' and frustration and even a further deficiency of vitamin D in extreme cases.[25]
 As provided by the Seasonal Affective Disorder Association in the United Kingdom |
And even though short term relationships between the weather and someone's emotions couldn't be stated, it has been proven that Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is real and it affects people in the United Kingdom and Ireland because they are situated in the higher latitudes of the northern hemisphere."Without sufficient levels of morning light our bodies circadian rhythms are not triggered and our body fails to produce the hormones required to feel wide awake. During the day if we do not receive enough sunlight we feel sluggish, lethargic and low in energy and at night we stay awake long after darkness which can result in lack of sleep, disrupted sleep patterns and mood swings." [26] In summary, if a person does not receive sunlight at the correct times and in sufficient quantities, the symptoms of SAD ensue. The symptoms of SAD recur regularly each winter and usually start between September and November, continuing until March or April and are as displayed in the image to the right.[27]
Just in the same way researchers have come to the conclusion that excessive rain is linked with feelings of discomfort and depression, it also has had to do with violent behaviors. Researchers from the University of California at Berkeley analyzed 60 previous studies on U.S. violent crime rates, historical uprisings and empire collapses, recent wars and lab simulations testing police decisions of when to shoot — and what they found was a link between violence and heat, as well as extreme rainfall. For every standard deviation of change, occurrences of “intergroup conflict” rose by a whopping 14 percent, while instances of “interpersonal violence,” which includes rape and domestic violence, increased by four percent.[28] It has also been object of study the fact that crime rates increase during the summer months; according to the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) "A DOJ study revealed rates of serious violent crimes, household larceny and household property victimization are significantly higher in summer months.". [29]
Section 2: Deliverable
The Setting
In this Milestone, a variety of photographs were taken in order to illustrate the claims made in the background about the weather in London, England. As it is a great and enormous city, five places were chosen to represent it. Each one of these places represents in some way an aspect of the capital city and are explained in this section of the Milestone, followed by a gallery with the pictures taken in each place.
The Tower Bridge
 |
With a Victorian Neo-Gothic style, the Tower Bridge is a bascule and suspension bridge on River Thames, located near the Tower of London from where it got its name. In the late nineteenth century, East End of London reached so high commercial development that in the 1876, a “Special Bridge or Subway Committee” was formed to build a new crossing bridge over the Thames. About fifty designs were received, however, because a conflicts of interests, a design took eight years to be approved by the committee. The chosen design had been submitted by Sir Horace Jones in collaboration with John Wolfe Barry. The construction of the Tower Bridge began in 1886 and was completely done in 1894. Prince and Princess of Wales officially opened the bridge on 30th of June 1894. The bridge connected Horselydown Lane, today Tower Bridge Road, with Iron Gate, today Tower Bridge Approach. "Five companies and 432 workers worked on it. It has 70,000 tons of concrete in foundations only and some 10,000 tons of steel and is covered in Cornish granite and Portland stone as means of protection for steel structure and as an esthetic element." [30]
When it was built, Tower Bridge was the largest and most sophisticated bascule bridge ever completed ("bascule" comes from the French for "see-saw"). These bascules were operated by hydraulics, using steam to power the enormous pumping engines. The energy created was stored in six massive accumulators, as soon as power was required to lift the Bridge, it was always readily available. The accumulators fed the driving engines, which drove the bascules up and down. Despite the complexity of the system, the bascules only took about a minute to raise to their maximum angle of 86 degrees. [31] A masterpiece of engineering and architecture, the Tower Bridge was chosen as one of the five most representative landmarks in London for various reasons. The Tower Bridge represents the development and continuous growth of the city, adapting to new technologies to satisfy the needs of its population "the city's dynamic economy generates a high level of development activity"[32]. Also, this landmark is not only a very important touristic spot in the city but also an icon for its citizens; people that grew up in London since the late eighteen hundreds have seen its birth and development and it has stood firm through all these years as a majestic and working superstructure.
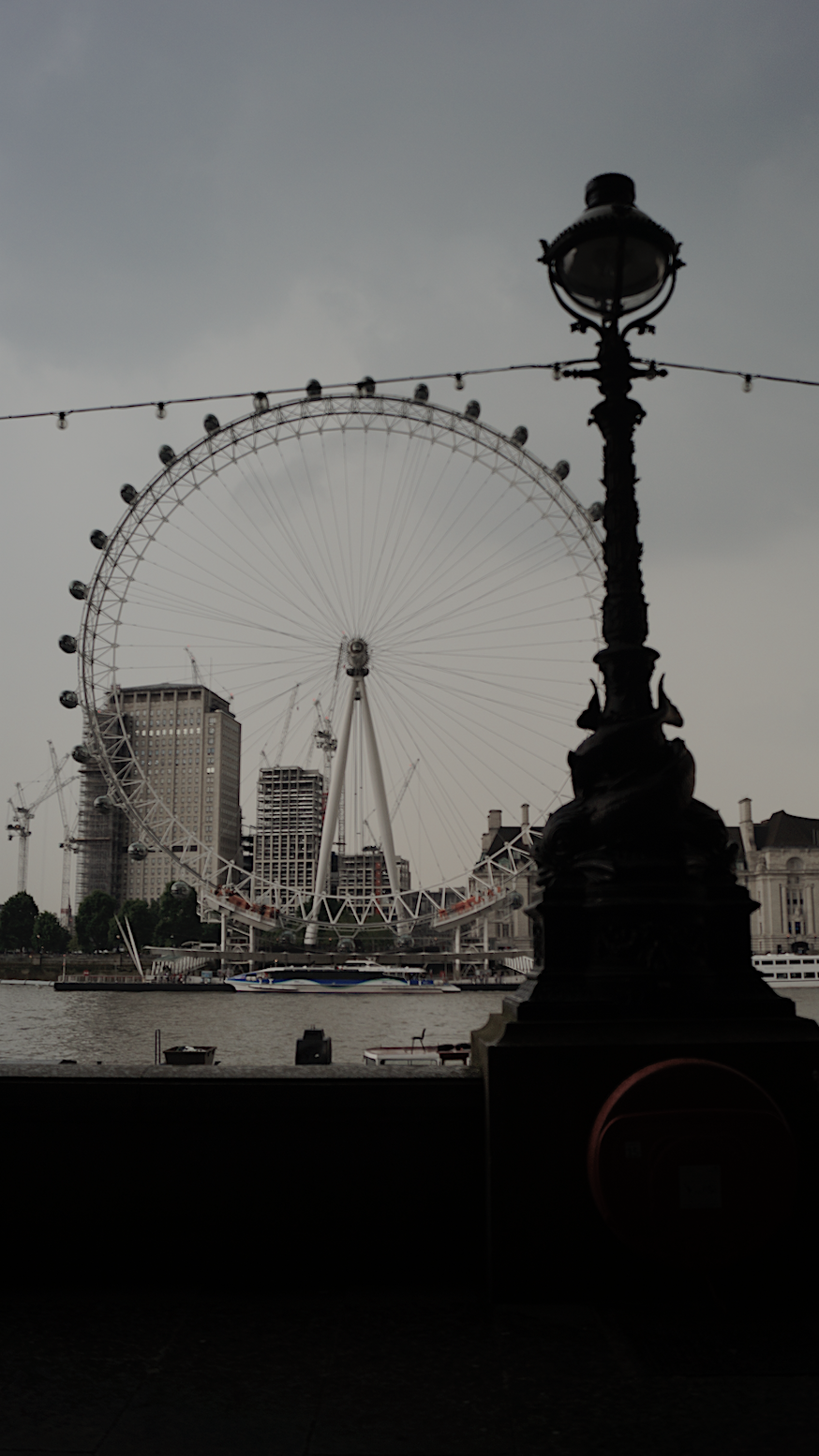
The London Eye
The London Eye, also known as the Millennium Wheel, is located on London’s Southbank, and holds the title of the world’s largest observation wheel and most popular paid tourist attraction in the whole country. The wheel itself has a diameter of 120 meters and offers some of the greatest panoramic views of the city, stretching as far as 25 miles. It has 32 capsules, each symbolizes London’s 32 boroughs and they are numbered 1 to 33, eliminating the thirteenth carriage for good luck. The London Eye attracts approximately 15,000 visitors a day and has won more than 40 awards for "its significant contribution to London’s tourism and architectural landscape".[33] The architectural design process of the London Eye was a collaborative work between several minds and talents; different architects are credited with the design of the London Eye. The primary individuals cited as the architects of the London Eye are Frank Anatole, Julia Barfield, Steven Chilton, Nic Bailey, Malcolm Cook, Mark Sparrowhawk, and David Marks.For its construction, the individual components for the wheel were floated up the River Thames and were assembled flat on the ground before being raised. Then the pieces were lifted up by using a strand jack system and once the wheel was constructed, there were varying stages of lift undertaken. The first stage brought the wheel up to only a 65 degree position and left the wheel like that for over a week. This allowed the engineers to prepare the foundation in a more durable fashion. The total weight of the entire London Eye is 1,700 tonnes and was created out of materials that were manufactured by European Union members. [34]
This site was chosen because it represents London as a top touristic destination for people all around the globe. A great people for people to visit and even stay, the city of London is home for a blend on many cultures and ideologies and is viewed as a world city. The iconic nature of the attraction makes most tourists flock to the wheel when they visit London for the first time. This landmark attracts visitors from all around the world and has transformed London’s landscape standing today as "a national symbol that celebrates Britain’s innovation and technological success in the 21st century".[35] The London Eye is not only the largest, and arguably the most famous, observation wheel in the world, but also maintains an important role in maintaining the touristic flow in London. It is an icon of the importance of tourism to this country's economy rather than merely being a "commemorative structure to celebrate the new millennium", as it was originally conceived. Even BBC News considers how it to represent one of the UK capital's major symbols.[36]
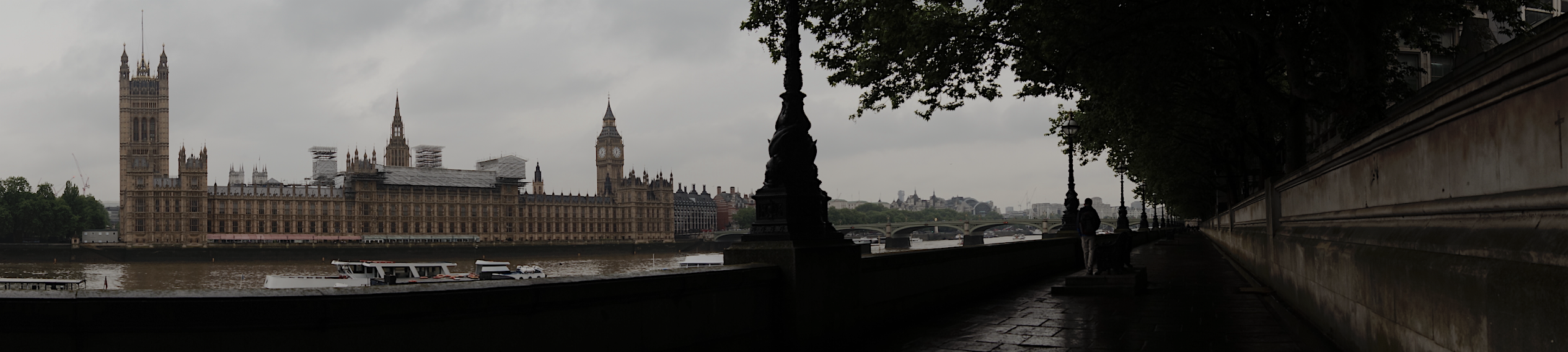
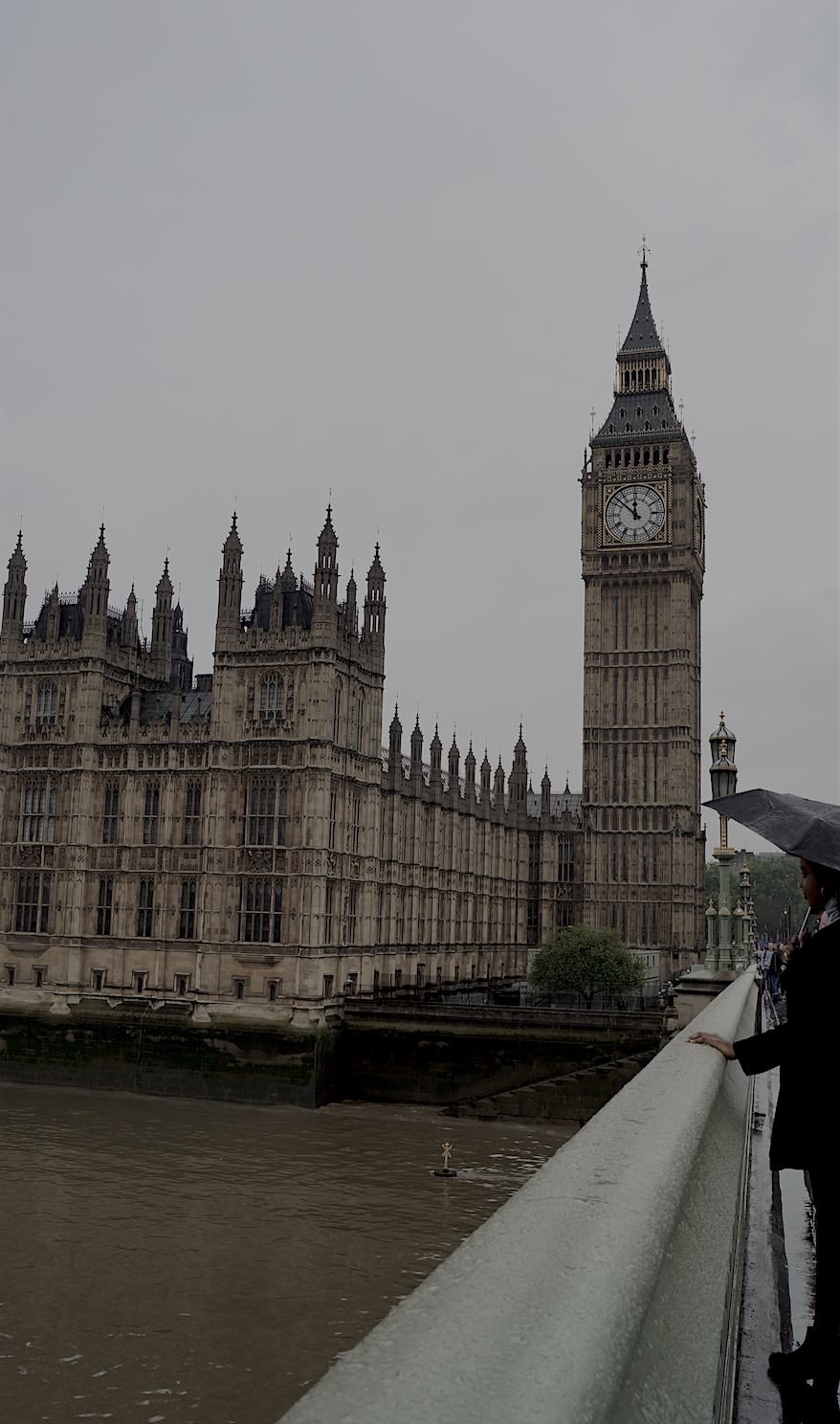
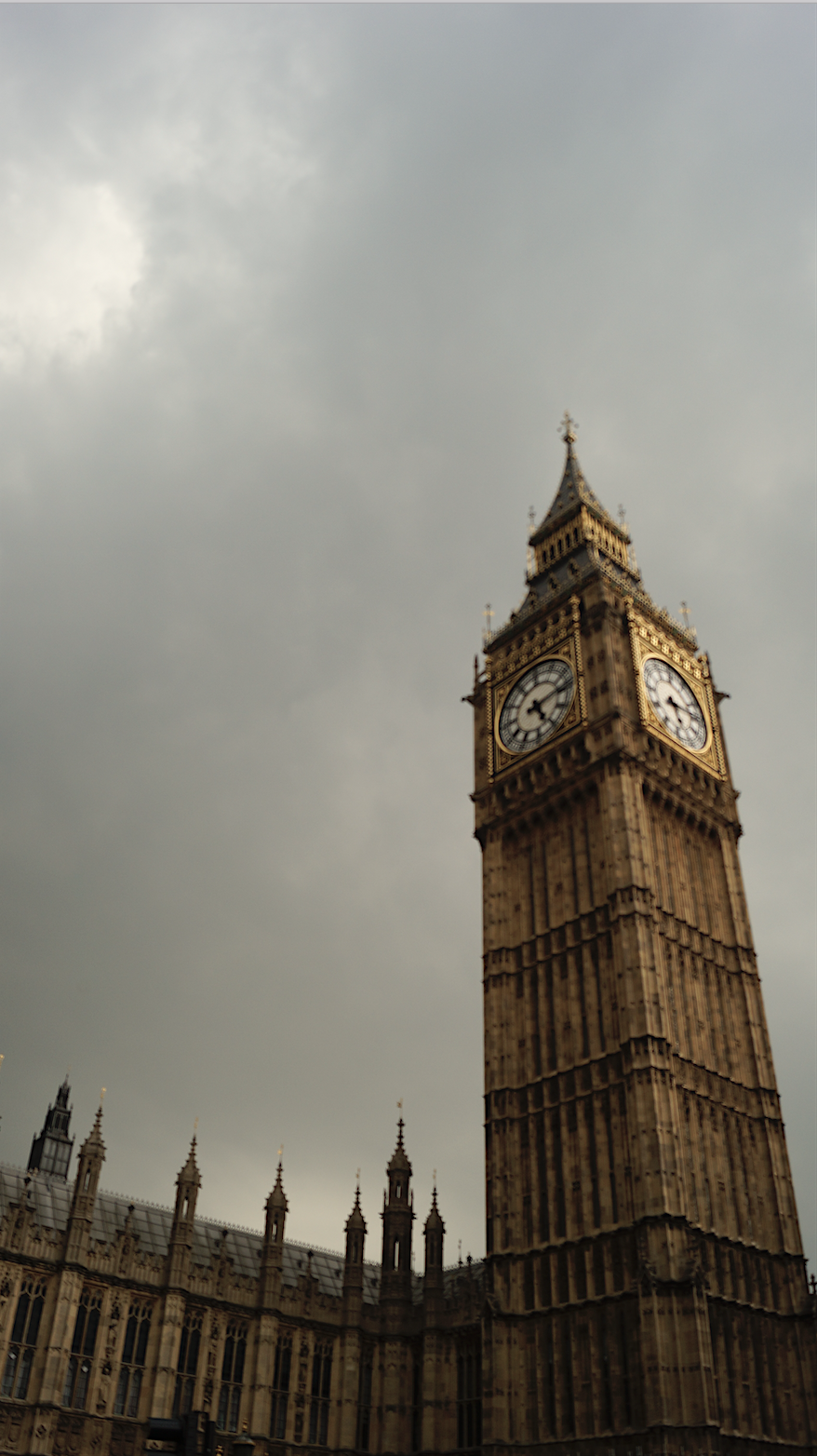
The Big Ben
Big Ben is the nickname given to the Great Bell of the clock at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London. It’s often extended to refer to the Great Clock and the Clock Tower, which was officially renamed Elizabeth Tower to celebrate the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II in 2012. When the original Palace of Westminster was destroyed in 1834 by a terrible fire, several architects and designers were invited to submit proposals for the new palace. More than 400 designs were submitted by more than 90 architects and Sir Charles Barry was chosen by a committee set up specifically for this issue. However, his design did not feature a clock tower. Barry turned to Augustus Pugin for the design of the tower and it was added to the plan later in 1836. But as he was not a professional clockmaker, Edward John Dent was appointed to build the clock following the design of clock maker Edmund Beckett Denison. When Dent died, his stepson Frederick completed the clock in 1854. The Parliament was built in a Neo-Gothic style and the foundation stone for the Elizabeth Tower was laid on 28 September 1843. Due to construction work falling five years behind the schedule, and the bell cracking, the tower was completed in 1859. A short time later in September 1859 the bell broke again, and was fixed and reinstalled in 1863 costing £22,000. Apart from occasional halts, it has struck ever since and in 2009, Big Ben celebrated its 150th anniversary.[37] [38]
The Big Ben represents the parliament, and the parliament represents the government and all the forms of governance this city has gone through since being a roman city at its beginnings. In the development of any city the most relevant and influential component is its government, which is why this Milestone had to represent the one of London through the Big Ben. Besides, the Big Ben is, without a doubt, one of the most famous symbols of the city and people can be seen everyday at any time taking "the Big Ben selfie" all across the bridge.
The Gherkin
30 St. Mary Axe, better known as "the Gherkin" or "the cucumber" is London’s most instantly recognisable tower after the Big Ben, of course. Totalling 500,000 sq ft, The Gherkin is an iconic structure housing a flourishing community and it deserves its reputation for being ‘the most civilised skyscraper in the world’.[39] Besides its use for business, it is an astonishing piece of art and a gem of modern architecture. During the early stages of construction of the building, the grave of a young Roman girl was discovered. The girl was preserved at The Museum of London while the building was constructed and then re-buried at the base of the tower on completion. The triangular panels create a complex of colour and shade and at the bottom of the skyscraper, stone benches carved with classical epitaphs remind us that this, as much as the World Trade Centre site for which Foster failed to get the commission, is a place of memorial and pain, devastated by an IRA bomb. "Norman Foster and Partners' Swiss Re building is, as well as defiantly modern, resonantly classical." [40] And though it's architect regrets his design, Londoners and tourists find the contrast it makes with the rest or the city's architecture, fascinating. The Gherkin didn't win the Stirling Prize, the London Region Award, and the Emporis Skyscraper Award for nothing;
The Gherkin is recognised as one of the more distinctive skyscrapers in the financial district of London and it stands on the former site of the Baltic Exchange building.The UK's financial services sector as a whole made a total tax contribution of £71.4bn in the taxes in the year to March 2016, equivalent to 11.5% of total UK government tax receipts. This figure includes taxes paid, as well as taxes collected, by the sector. The financial services sector employs over 1.1 million people, representing 3.4% of the UK's total workforce.[41] Nearly half of London’s finance and insurance output is derived from the City of London. Taken together with professional services, financial services contributed £245bn to the UK economy in 2015 [42] The Gherkin represents the city's economic growth and workforce, which continues to lift the United Kingdom as one of the most influential countries in the world. It is a monument and a mirror that makes tourists and locals see London in a new way.
St. Paul's Cathedral
Being a place for Christian worship for over four hundred years, Sir Christopher Wren's St. Paul's Cathedral stands as the most iconic church in all Britain. The medieval Cathedral, with a tower and spire soaring above the city, was at the time one of the wonders of Europe. St Paul was built after the Fire of London of 1666, its dome with the ball and cross above it symbolic of London's steadfastness down the centuries and its endurance throughout the bombing of the Second World War. However, it was not until 1675 that a scheme for complete rebuilding was finally approved. Wren had made several other designs including that illustrated by the so-called Great Model still in the cathedral. When it came to the building of the Cathedral, he insisted on having a much freer hand, so the final product was just a resemblance of the original design.[43] It was completed in 1710, when Wren was seventy-eight years old, and by the final stages of construction, he was carried to the dome because he was unable to take the stairs. There are infinite features to be referenced about St. Paul's Cathedral; in fact several books have been filled with its history, however, it was chosen for this milestone not only for its physical beauty but because it conveys a higher message.
St. Paul's Cathedral represents the change in beliefs of the whole country that generated much controversy all over Europe and took origin in this very city under the rule of Henry VIII and lead mainly by Cromwell. It represents the power that lies in all English people and the audacity of its governance, as well as the communion of all the religions of the world that lay in the hearts of all the newer generations of Londoners. From the outside St. Paul's stands with all its might and power and from the inside it is awe-inspiring, breathtaking, unlike any other cathedral or church built in Britain. Plus, this magnificent church has dominated the London skyline for hundreds of years, and has seen the city change without recognition. As the author Ann Saunders introduces one of her books, "the Cathedral lies at the heart of London and - in so many ways - in the heart of the nation". [44]
Conclusion
In this section, provide a summary or recap of your work, as well as potential areas of further inquiry (for yourself, future students, or other researchers).
References
- ↑ Manley, G., 1974: Central England Temperatures: monthly means 1659 to 1973. QJR Meteorol Soc, p. 100, 389-405.
- ↑ Jones, P.D. and Mann, M.E., 2004: Climate over past millennia. Rev Geophys, 42, RG2002.
- ↑ Jenkins, G.J., Perry, M.C., and Prior, M.J. (2008). The climate of the United Kingdom and recent trends. Met Of ce Hadley Centre, Exeter, UK.
- ↑ CORTON, C. L. (2015). LONDON FOG: the biography. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. p. 1.
- ↑ CORTON, C. L. (2015). LONDON FOG: the biography. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. p. 1.
- ↑ Jackson, L. (2014). Dirty Old London. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 212-237
- ↑ CORTON, C. L. (2015). LONDON FOG: the biography. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. p. 1.
- ↑ Kim Lacina | April 21, 2017 (Last Updated: May 3, 2017). (n.d.). The Air We Breathe. Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://www.lung.org/about-us/blog/2017/04/the-air-we-breathe.html
- ↑ Cullen, S., & Roberts, E. (2017, January 6). London breaches annual air pollution limits in first week of 2017 (CNN, Ed.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://edition.cnn.com/2017/01/06/health/london-air-pollution/index.html
- ↑ Jackson, L. (2014). Dirty Old London. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 212-237
- ↑ George Gissing's Diary, quoted in Pierre Coustillas, London and the life of literature in Late Victorian England, Hassocks: Harvester Press, 1978, p. 19.
- ↑ Brimblecombe, P. "Writing on smoke", Writings on the History and Culture of Pollution, ed. Hannah Bradby (London: Earthscan, 1990), p. 93-113.
- ↑ Jackson, L. (2014). Dirty Old London. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 1.
- ↑ [George Sala], The great invasion, Household Words (April 1852), p.73.
- ↑ Jackson, L. (2014). Dirty Old London. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 4.
- ↑ Hay, W. D. (1880). The Doom of the Great City, London: Newman & Co, being a narrative of a survivor, written A.D. 1942.
- ↑ Jackson, L. (2014). Dirty Old London. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 212-237
- ↑ David W. Bartlett, London by day and night, [London}, 1852.
- ↑ "The Face and Complexion", Weekly Standard and Express, April 2 1898
- ↑ London, J. (1903). The People of the Abyss. New York.
- ↑ Denissen, J.J.A.; Butalid, Ligaya; Penke, Lars; van Aken, Marcel A. G. (2008). The effects of weather on daily mood: A multilevel approach. Emotion, 8, 662-667.
- ↑ Connolly, M. (2013). Some like it mild and not too wet: The influence of weather on subjective well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 14, 457-473..
- ↑ Haslam, N., & University of Melbourne. (2016, March 17). Here Comes the Sun: How the Weather Affects Our Mood. Retrieved May 21, 2017, from http://www.theepochtimes.com/n3/1989415-here-comes-the-sun-how-the-weather-affects-our-mood/
- ↑ J. D.; L. P.; L. B.; M. A. The Effects of Weather on Daily Mood: A Multilevel Approach. The Effects of Weather on Daily Mood: A Multilevel Approach, https://www.psychologie.hu-berlin.de/de/prof/perdev/pdf/2008/denissen_weather_mood_2008.pdf.
- ↑ Loewen, S. C. (n.d.). Effects of Weather on Human Emotions. Retrieved May 21, 2017, from http://www.healthguidance.org/entry/15843/1/Effects-of-Weather-on-Human-Emotions.html
- ↑ What is SAD? (n.d.). Retrieved May 21, 2017, from http://www.sad.org.uk/
- ↑ The Seasonal Affective Disorder Association in the United Kingdom. (2016, September 1). Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder. Retrieved May 21, 2017, from http://www.sada.org.uk/symptoms_2.php
- ↑ Gregoire, C. (2014, January 14). The Surprising Ways The Weather Affects Your Health And Well-Being. Retrieved May 21, 2017, from http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2014/01/14/climate-health_n_4568505.html
- ↑ Lauritsen, J. L., & White, N. (2014). U.S. Department of Justice Of ce of Justice Programs. Seasonal Patterns in Criminal Victimization Trends. Retrieved May 21, 2017, from https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/spcvt.pdf.
- ↑ "Facts and History of Tower Bridge in London." Tower Bridge - Facts and History of Tower Bridge in London. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 May 2017. <http://www.bridgesdb.com/bridge-list/tower-bridge/>
- ↑ "Tower Bridge Exhibition." Tower Bridge History | Historic Bridges London. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 May 2017. <http://www.towerbridge.org.uk/bridge-history/>
- ↑ "Development." Development - Development and population information - City of London. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 May 2017. <https://www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/services/environment-and-planning/planning/development-and-population-information/Pages/development.aspx>
- ↑ Hill, M. (2016, April 13). The History Of The London Eye In 1 Minute. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from https://theculturetrip.com/europe/united-kingdom/england/london/articles/the-history-of-the-london-eye-in-1-minute/
- ↑ Design Book Magazine. (n.d.). London Eye. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from http://www.designbookmag.com/londoneye.htm
- ↑ Hill, M. (2016, April 13). The History Of The London Eye In 1 Minute. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from https://theculturetrip.com/europe/united-kingdom/england/london/articles/the-history-of-the-london-eye-in-1-minute/
- ↑ Akwagyiram, A. (2005, May 21). UK | England | London | The history of the London Eye. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/4569123.stm
- ↑ Gill, J. (2016, March 22). The History Of Big Ben In 1 Minute. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from https://theculturetrip.com/europe/united-kingdom/england/london/articles/the-history-of-big-ben-in-1-minute/
- ↑ London News. (n.d.). THE BIG BEN STORY. Retrieved May 30, 2017, from http://bigbenfacts.co.uk/story/index.html
- ↑ The Gherkin, London. (n.d.). Retrieved May 31, 2017, from http://www.thegherkinlondon.com/
- ↑ Jones, J. (2004, October 18). The Gherkin is a triumph of architecture as sculpture. Retrieved May 31, 2017, from https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2004/oct/18/architecture.regeneration
- ↑ PwC and City of London, Total Tax Contribution of UK Financial Services (ninth edition), December 2016
- ↑ Office for National Statistics, Regional Gross Value Added (Income Approach), December 2016, and GLA Economics, Regional Gross Value Added estimates for London by different regional geographies, July 2016
- ↑ New, A. S. (1981). A guide to the cathedrals of Britain. London: Constable.
- ↑ Sanders, A. (2001). St. Paul's (E. Drury, Ed.). London: Collins & Brown Limited.