Difference between revisions of "Mummies of Ancient Egypt"
From Londonhua WIKI
Mthatfalvi (talk | contribs) |
Mthatfalvi (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
==Ancient Egyptian Mummies at the British Museum== | ==Ancient Egyptian Mummies at the British Museum== | ||
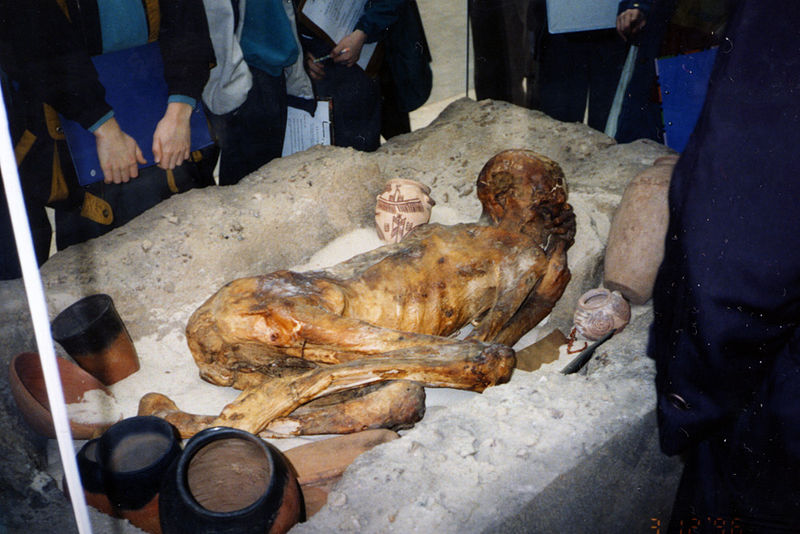
| − | The British Museum has the most Egyptian artifacts outside of Egypt, which include real mummies. The Ancient Egyptian Mummies exhibit includes coffins, mummies, funeral masks, and portraits used for burial of ancient Egyptians. <ref> Room 62-63: Egyptian death and afterlife: mummies. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/galleries/ancient_egypt/room_62-63_egyptian_mummies.aspx </ref> Within the exhibit are X-rays and CT scans of certain mummies. Below are pictures of some mummies that are on display in the [[British Museum]]. In total are 120 human mummies and 300 animal mummies that the [[British Museum]] has in its collection. <ref> Mummies in the Museum. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from https://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/family_visits/night_at_the_museum/mummies_in_the_museum.aspx </ref> | + | The British Museum has the most Egyptian artifacts outside of Egypt, which include real mummies. The Ancient Egyptian Mummies exhibit includes coffins, mummies, funeral masks, and portraits used for burial of ancient Egyptians.<ref name = "folly"> Room 62-63: Egyptian death and afterlife: mummies. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/galleries/ancient_egypt/room_62-63_egyptian_mummies.aspx </ref> Within the exhibit are X-rays and CT scans of certain mummies.<ref name = "folly"/> Below are pictures of some mummies that are on display in the [[British Museum]]. In total are 120 human mummies and 300 animal mummies that the [[British Museum]] has in its collection. <ref> Mummies in the Museum. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from https://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/family_visits/night_at_the_museum/mummies_in_the_museum.aspx </ref> |
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Mummy at British Museum.jpg|400px|thumb|Mummy on Display | File:Mummy at British Museum.jpg|400px|thumb|Mummy on Display | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 21 June 2017
Mummies of Ancient Egypt
 Mummy of Katebet | |
| Mummies of Ancient Egypt | |
|---|---|
| Artist | Attributed to emanuelle.laurent |
| Year | 2007 |
| Location | British Museum, London |
Overview
The history of making mummies started around 3500 B.C. Egyptians believed that death was not the end of their life but, a transition from one state to another. So they believed the body had to be preserved in order to be recognized when the Egyptian eventually awoke from the tomb. The art of mummification was practiced in Egypt until 30 B.C.
Contents
Background or Origin of Article
History of Mummification
The history of mummification started around 3500 B.C. Mummification was first done naturally because of the dessert dry weather in Egypt and shallow graves. [1] This naturally preserved bodies. It was then thought by Egyptians that death was not the end to life and that they were just going to live another life. So it was then that mummification officially started being a regular practice around 2000 B.C. [1] Both men and women were mummified. A whole process was adopted and mummies started to have items buried with them such as clothing, jewelry, gold or anything they would need in the afterlife. When Christianity became the religion of practice, mummification ended.
Creation of Ancient Egyptian Mummies
Mummification was mainly done for wealthy people and royalty. According to a guide to Egyptian mummification, a chief embalmer who was closely involved with the process was a priest wearing a mask of Anubis. [2]
Process of Mummification
A step by step process of mummification according to the website is the following:
Insert a hook through a hole near the nose and pull out part of the brain
Make a cut on the left side of the body near the tummy
Remove all internal organs
Let the internal organs dry
Place the lungs, intestines, stomach and liver inside canopic jars
Place the heart back inside the body
Rinse inside of body with wine and spices
Cover the corpse with natron (salt) for 70 days
After 40 days stuff the body with linen or sand to give it a more human shape
After the 70 days wrap the body from head to toe in bandages
Place in a sarcophagus (a type of box like a coffin)
[2]
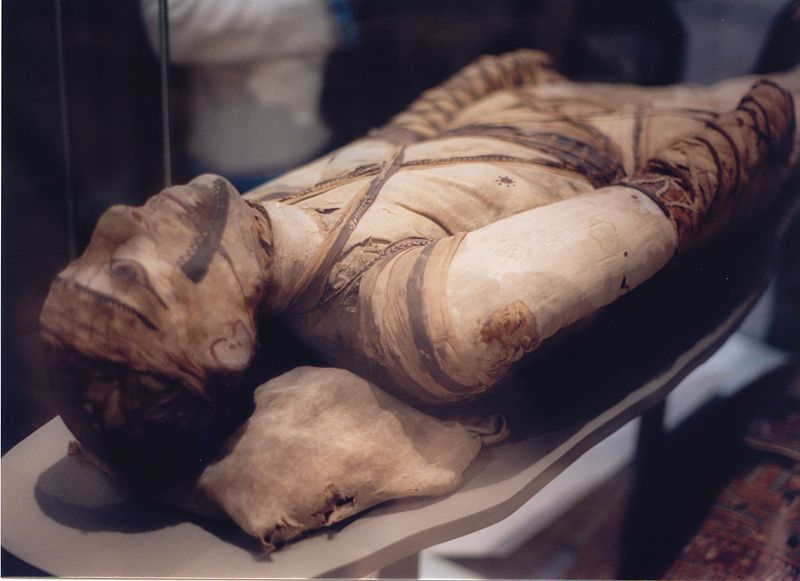
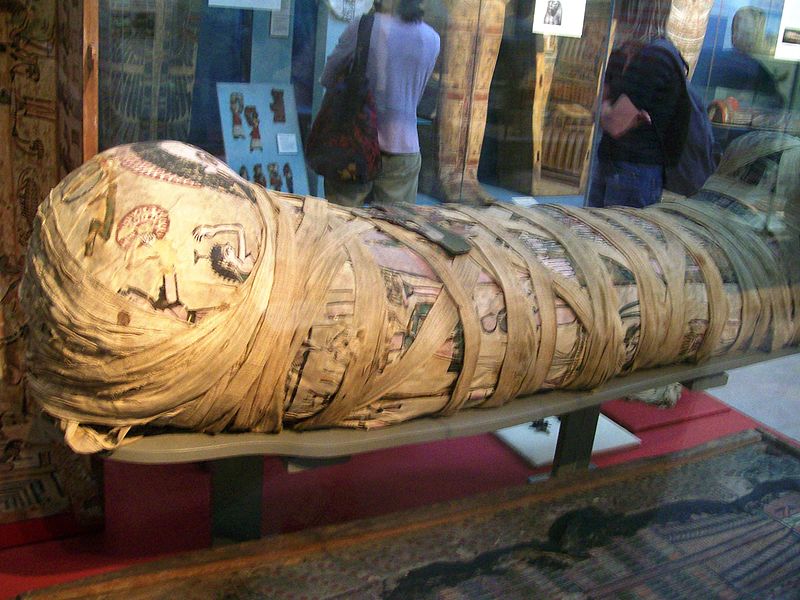
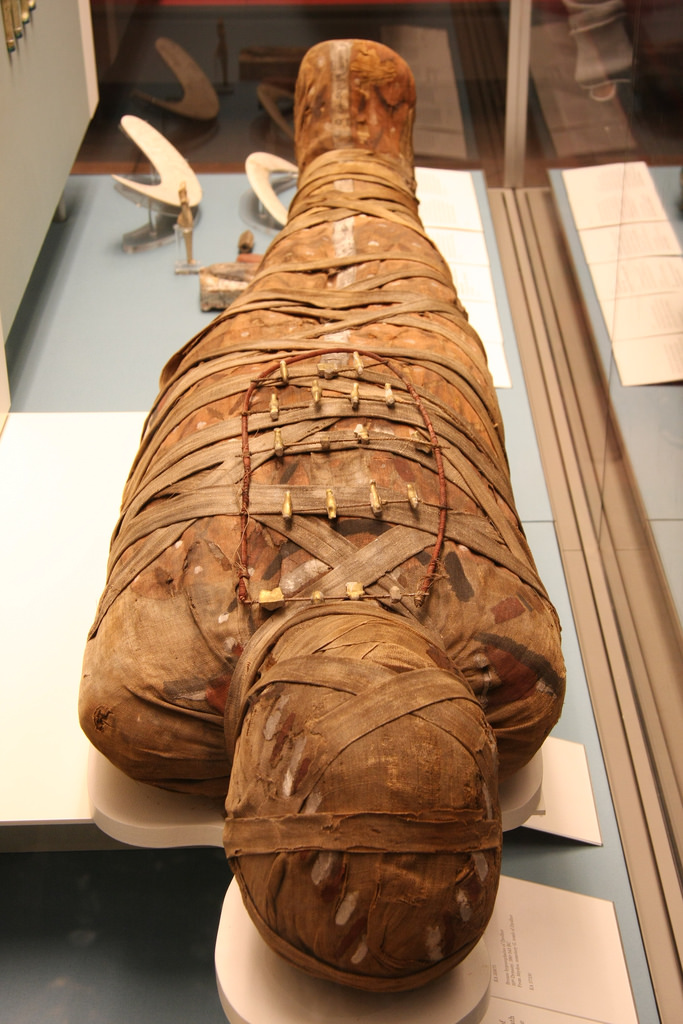
Ancient Egyptian Mummies at the British Museum
The British Museum has the most Egyptian artifacts outside of Egypt, which include real mummies. The Ancient Egyptian Mummies exhibit includes coffins, mummies, funeral masks, and portraits used for burial of ancient Egyptians.[3] Within the exhibit are X-rays and CT scans of certain mummies.[3] Below are pictures of some mummies that are on display in the British Museum. In total are 120 human mummies and 300 animal mummies that the British Museum has in its collection. [4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mark, J. J. (2017, February 14). Mummification in Ancient Egypt. Ancient History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from http://www.ancient.eu/article/44/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 A Step by Step guide to Egyptian Mummification. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://www.mylearning.org/a-step-by-step-guide-to-egyptian-mummification/p-1681/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Room 62-63: Egyptian death and afterlife: mummies. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from http://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/galleries/ancient_egypt/room_62-63_egyptian_mummies.aspx
- ↑ Mummies in the Museum. (n.d.). Retrieved May 20, 2017, from https://www.britishmuseum.org/visiting/family_visits/night_at_the_museum/mummies_in_the_museum.aspx