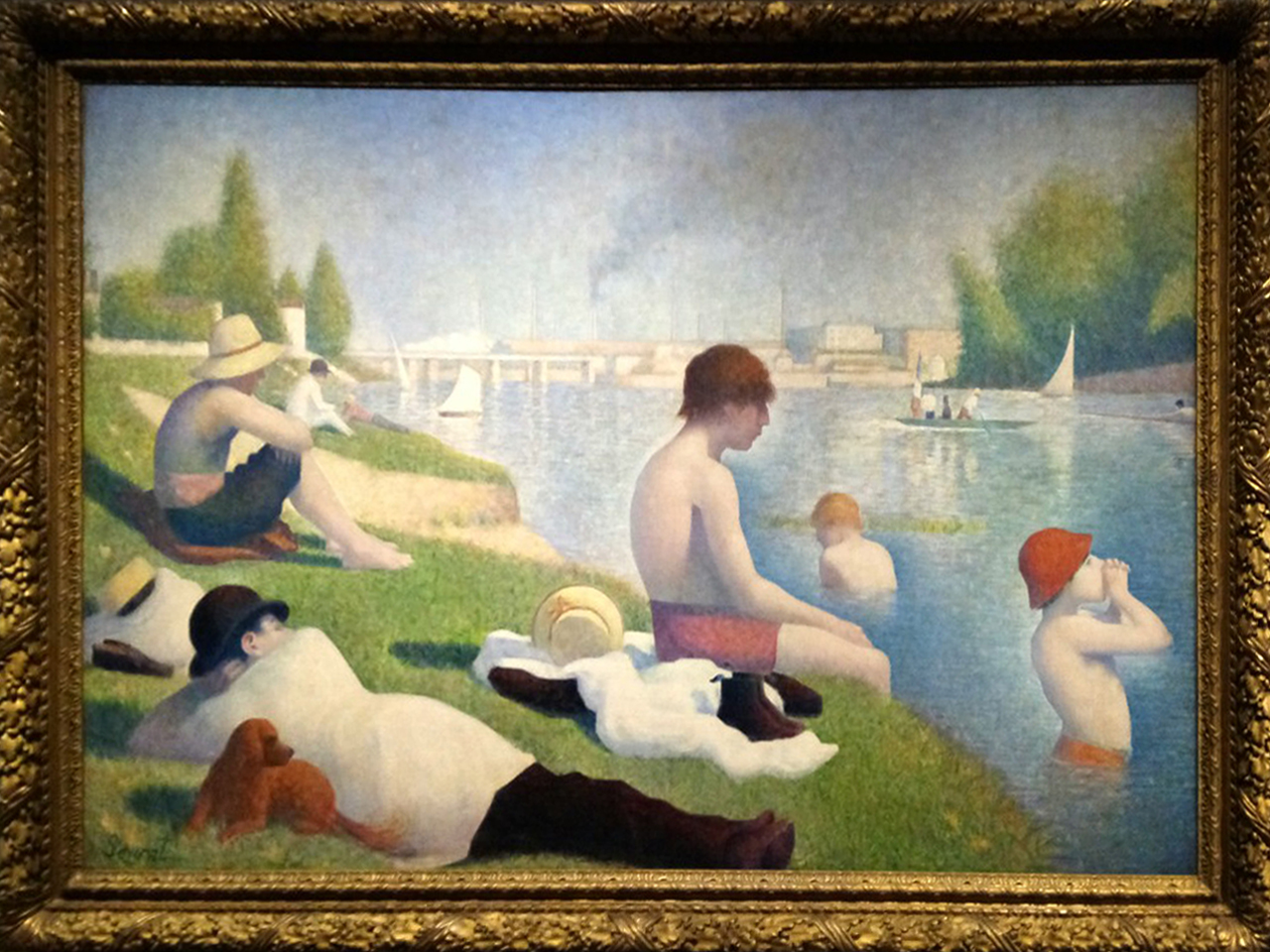Difference between revisions of "The National Gallery"
From Londonhua WIKI
Gczahorsky (talk | contribs) (Created page with "=Template Article= {{Infobox |title = Article Title |header1 = The Chandos Portrait of William Shakespeare |bodystyle = width:25em |image = File:National Gallery.jpg|400px...") |
Mthatfalvi (talk | contribs) |
||
| (128 intermediate revisions by 24 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{Infobox | {{Infobox | ||
| − | |title = | + | |title = National Gallery |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|bodystyle = width:25em | |bodystyle = width:25em | ||
|image = [[File:National Gallery.jpg|400px|alt=Article Image]] | |image = [[File:National Gallery.jpg|400px|alt=Article Image]] | ||
| − | |caption = | + | |caption = National Gallery, Trafalgar Square |
| − | |label2 = ''' | + | |label2 = '''Established''' |
| − | |data2 = | + | |data2 = 1824; 193 years ago |
| − | |label3 = ''' | + | |label3 = '''Location''' |
| − | |data3 = | + | |data3 = Trafalgar Square, London, WC2, United Kingdom |
| − | |label4 = ''' | + | |label4 = '''Director''' |
| − | |data4 = | + | |data4 = Gabriele Finaldi |
| − | |label5 = ''' | + | |label5 = '''Website''' |
| − | |data5 = | + | |data5 = www.nationalgallery.org.uk |
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
| − | The | + | The National Gallery is located in Central London and contains over 2,300 paintings that are free to view by the public. |
| + | The overall gallery is split into four main sections each consisting paintings within a certain period from early 12th century to early 19th century. Most of the pre 16th century paintings portrayed Greek mythology or the divinity of religion such as birth and death of Christ. Painting from late 14th to early 17th century transitioned from portraying mythical and religious senses to portraying objects in detail, landscapes, daily lives of common people and portraits of wealthy citizens. | ||
| + | Some notable artists displayed in the gallery are Leonardo da Vinci, Van Gogh, and Michelangelo. | ||
| + | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | =Background | + | =Background and Origin= |
| + | The National Collection started when the House of Commons bought the picture collection of John Julius Angerstein for £57,000. His collection contained 38 pictures and were kept at his house, 100 Pall Mall. In 1831 Parliment agreed to build a the National Gallery at Trafalgar Square as it was considered to be the very center of London. The building was completed in 1838. Over the years the Gallery has expanded and now spans 46,396 meters squared. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Painters and Works= | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ==Leonardo da Vinci== | ||
| + | [[File: Virgin of the Rocks.jpg|x350px|right|thumb|frame|The Virgin of the Rocks]]<br> | ||
| + | Leonardo da Vinci was a master painter, sculptor, architect, designer, theorist, engineer and scientist that created some of the most famous and respected pieces of art in the world. He has been named the "father of paleontology", the "father of ichonology", the "father of architecture", and one of the greatest painters of all time. As one of the greatest painters of all time, the National Gallery in London was lucky enough to acquire one of his paintings along with a mostly finished drawing. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The drawing located at the gallery is ''The Virgin and Child with St Anne and St John the Baptist''. This drawing is deeply intriguing because it was most likely a preparatory drawing for an upcoming at painting when it was first created. The reason this is so interesting is that it looks and seems almost completely finished as a charcoal drawing on a tinted canvas yet it still has some completely unfinished parts to it. This confusion lead Bernardino Luini to create the ''Holy Family with St Anne and the infant John the Baptist'', a painted replica of the drawing from Leonardo da Vinci | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The painting located at the National Gallery is one of two versions and is named the "Virgin on the Rocks". The other version of this painting is located at the Louvre. The ''Virgin of the Rocks'' in the Louvre is considered to be the older version dating from around 1483–1486 while the ''Virgin of the Rocks'' in the National Gallery is still ascribed to Leonardo da Vinci, but dates to before 1508. Originally, many thought that this painting was partially done by one of his assistants, further study from the gallery has determined that da Vinci did the greater portion of the work. Unfortunately, this is still highly under debate. The reason that there are two different versions is most likely because da Vinci created it to for a commission in Milan and sold the Louvre version privately. The London version was then created to fill the commission and given to the chapel of the Confraternity of the Immaculate Conception, a church in Milan. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | In 2005, the London painting was examined more closely by the National Gallery, using infrared and x-ray technology. This examination revealed that this painting was actually covering one of a different design. The original design pictured a woman on her knees with one hand outstretched and another on her heart and was most likely for the adoration of the infant Jesus. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | In 2009 and 2010, the painting was cleaned and had some conservative work. During this time, the gallery determined that da Vinci had done most, if not all, of the work on the painting as seen today in the National Gallery. | |
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Guido Cagnacci & the Repentant Magdalene== | ||
| + | [[File: 1044294.jpg|x350px|right|thumb|frame|The Repentant Magdalene]]<br> | ||
| + | Now on display in the National Gallery until the end of May is a great historical piece of art by Guido Cagnacci, an Italian painter in the 1600s. Cagnacci is not as widely known as da Vinci for example, but his work the Repentant Magdalene is considered priceless. This display at the Gallery is also the first time that a Cagnacci has been displayed in a public collection in the United Kingdom. Portraying Magdalene asking for forgiveness from her ways, the painting also shows the angel Virtue beating Vice, the devil. This painting is one of the only ones that shows Mary Magdalene as a sinner, crawling back for forgiveness, and is a turn away from Cagnacci's usual paintings of half dressed and seductive paintings. X-ray examination of the art has reviled two changes, notable to the servants and the Vice. An original servant was painted over, creating a more intimate environment with less of a crowd. The second change that Cagnacci had made was to change the Vice from standing at the feet of Mary Magdalene, to jumping in the air, giving it a more evil spirit look overall. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | == Johannes Vermeer == | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | <ref> Johannes Vermeer. (n.d.). Retrieved May 15, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/johannes-vermeer </ref> | |
| + | Johannes Vermeer was a Dutch Painter born in 1632 and is known to be a great Dutch master. Although he only produced only 35 known paintings during his lifetime, Vermeer was known to produce truly detailed works. He became a master at Delft painters’ guild in 1653 when he got married. His works contain many symbols and have very well placed objects to convey messages. Many a time, there paintings inside of paintings that give the paintings a certain depth that is very symbolic. Even though he was a talented painter, Vermeer died leaving his family destitute. Some of his paintings included [[The National Gallery# A Young Woman Standing at a Virginal| ''A Young Woman Standing at a Virginal'']], the ''Girl with a Pearl Earring'', and ''The Milkmaid''. | ||
| + | |||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | === A Young Woman at a Virginal === | |
| + | [[File: N-1383-00-000052-wpu.jpg|x250px|right|thumb|frame| The Young Woman at the Virginal]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | In the painting contains a woman of status playing the virginal in a well-decorated room full of paintings and a tiled floor. The painting in the lid of the virginal is a pastoral setting, which could be a painting by a colleague Pieter Groenewegen. The second painting is inside of the painting is by Cesar van Everdingen and is of cupid. This painting can be seen as young woman’s choice between two paths: one of easy love or one of a more difficult love. She must make a decision and one can tell it’s about love due to the close association between music and love. <ref> A Young Woman standing at a Virginal. (n.d.). Retrieved May 15, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/johannes-vermeer-a-young-woman-standing-at-a-virginal </ref> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | ==Giovanni Antonio Canal== |
| − | + | [[File: IMG_0219.JPG|x350px|right|thumb|frame|Venice: The Basin of San Marco on Ascension Day]]<br> | |
| + | [[Giovanni Antonio Canal]], also known as Canaletto, lived from 1697-1768. He was an Italian painter who loved to paint Venetian landscapes of the city and the canals. Many of his more famous works are on display at The National Gallery in one room. The English people at the time loved traveling and exploring Venice, so Canaletto decided to bring Venice to them through his paintings. One painting, ''Eton College'', was painted around 1754. It is a painting of Eton College seen from the east across the River Thames. Canaletto traveled to England between 1746 and 1756, and during that time he painted many paintings for the English people. He wanted to give them a gift of a painting of something in their homeland. One of his most famous paintings, ''Venice: The Basin of San Marco on Ascension Day, 1740'', depicts an annual ceremony that symbolized the joining of Venice to the Adriatic Sea. The Doge would leave his palace on top of a golden state barge so he could travel out to where the city and the Adriatic meet and throw a golden ring into the Adriatic. Canaletto was a famous oil painter of his time and is remembered through both Italian and English history as a figure who combined the two cultures, showing one how the other lived. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | = | + | |
| − | + | ==Rembrandt van Rijn== | |
| + | [[File: 1542.png|x350px|right|thumb|frame|Self Portrait of Rembrandt]]<br> | ||
| + | The greatest visual artist to have ever lived is currently on display at the National Gallery. Born in 1606, Rembrandt is also considered the most important painter in dutch history, What makes Rembrandt unique is he did not have a particular style or scene. His works ranged from landscapes, to portraits (Portrait of Jacob Trip), to historical scenes (The Night Watch), to religious scenes, to science and anatomy (The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp), etc. His pieces often explored his close surroundings and the depths of human emotion. Since he rarely, if ever, traveled beyond the dutch border, he got most of his inspirations domestically. He is most well known for his narrative style. HIs biblical paintings have allow the audience to feel certain emotions while depicting a scene in uncanny detail. He is also known for painting Amsterdam's Jewish population. His contributions to the art world came at the perfect time, the Dutch Golden Age. This period had excess wealth and cultural achievements. His style was innovative in the way that he directly opposed the main style at the time, Baroque. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | = | + | |
| − | + | ==Raphael== | |
| + | Raphael Sanzio da Urbino, widely known as just Raphael, was an Italian painter, and later architect, who lived at the end of the of the 15th century and the beginning of the 16th century. His is considered to be part of the three great masters of this period along with Michelangelo and Leonardo Da Vinci, who also have paintings displayed in the Gallery. Many of Raphael's paintings depict religious scenes such as his painting of Jesus being put to death on the cross, titled ''The Mond Crucifixion''. He has many famous paintings featured in the National Gallery including his piece titled ''The Ansidei Madonna''. This piece was painted as an alter piece for the chapel of the Ansidei family in Perugia. Raphael used geometrical planning to obtain the result in "harmonious thirds". Another famous painting by Raphael was his piece titled ''Saint Catherine of Alexandria''. This painting shows Saint Catherine leaning against the wheel where she was supposed to be condemned to die, but the wheel miraculously broke. After his death in 1520 his paintings gained a lot of popularity in the 18th and 19th century. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | = | + | ==Diego Velasquez== |
| − | + | Diego Velasquez was an extremely important painter of the Spanish Golden age. He completed many portraits and was the head painter in the court of King Phillip IV. Some of his pieces were replicated and recreated by other famous painters later on including Salvador Dalí and Pablo Picasso. His portrait of Archbishop Fernando de Valdés in on display at the National Gallery. However the piece shown at the National Gallery is not the complete portrait, it is only a fragment and another fragment of the portrait is located at the Spanish Royal Collection. Velasquez's painting ''The immaculate Conception'' can also be seen at the museum. This painting shows The Virgin Mary standing on the moon with a circular crown of stars above her head and signifies that she is the immaculate conception, and therefore was conceived without original sin. Overall Velasquez's paintings had and still have a significant cultural and historical influence. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ...and ''' | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | ==Claude Lorrain== | |
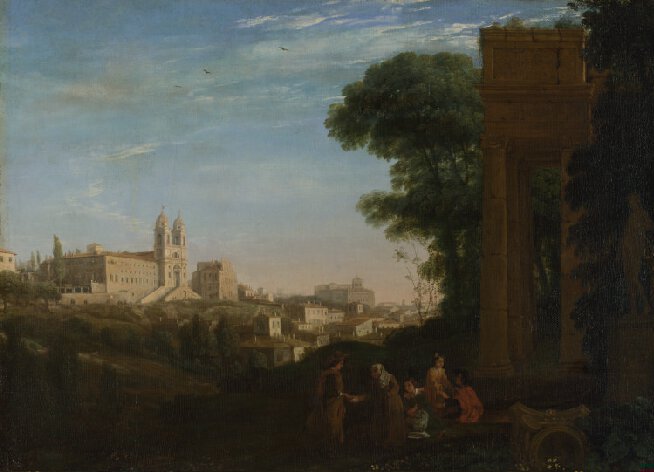
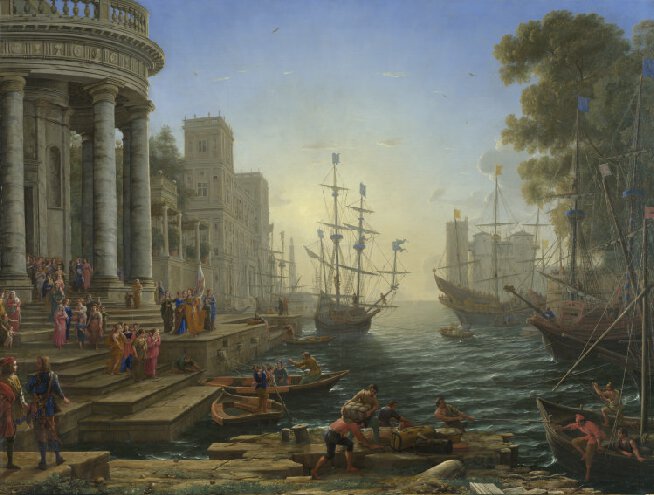
| + | Born Claude Gellée in Duchy of Lorraine around the early 1600's before 1606.<ref name = "claud"> Claude. (n.d.). Retrieved May 12, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/claude</ref> He left around 1612 for Germany. He then went to Rome, where he became a studio assistant to a landscapist Agostino Tassi.<ref name = "claud"/> He then settled in Rome around 1628 where he started to sketch in the Roman countryside.<ref name = "claud"/> His works are all of landscapes and he is know for his style of landscape paintings.<ref name = "claud"/> Claude died in 1682. 14 of his paintings are shown in the Gallery. Pictured are three of his compositions; A View in Rome (1632), Seaport with the Embarkation of Saint Ursula (1641) and Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (1672). <br> | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File: aview.jpg|A View in Rome (1632)<br> <small> '''Attributed to''' Claude Lorrain via National Gallery - [https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/claude-a-view-in-rome Link] | ||
| + | File:landscape.jpeg|Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (1672) <br> <small> '''Attributed to''' Claude Lorrain [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons - [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AClaude_Lorrain_-_Landscape_with_Aeneas_at_Delos_-_WGA05015.jpg Link] | ||
| + | File: seaport.jpg|Seaport with the Embarkation of Saint Ursula (1641) <br> <small> '''Attributed to''' Claude Lorrain [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons - [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AClaude_Lorrain_-_Seaport_with_the_Embarkation_of_Saint_Ursula.jpg Link] | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| + | ==Claude Monet== | ||
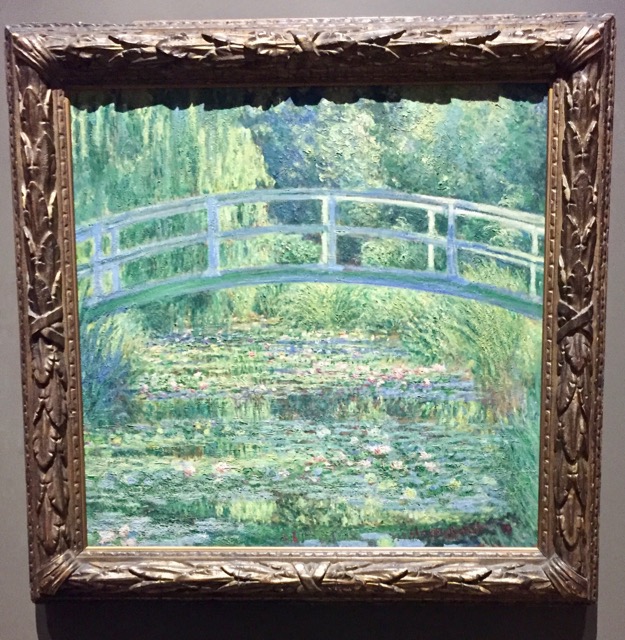
| + | [[File:EAWwater.jpg|x350px|right|thumb|frame|Water Lily Pond]]<br> | ||
| + | Claude Monet was born on November 14, 1840 in France. Monet studied at the Academie Suisse, he was close friends with Camille Pissarro, and you can see there work side by side in the National Gallery. Money and Camille eventually got married in June of 1870. Monet, with several other artists formed the Société Anonyme des Artistes, as an alternative way to showcase their works. Monet was very critical of his own work. He was known to destroy his own paintings by burning, cutting, or kicking them. His painting style was the start of Impressionism. They called it this because his work was more focused on form and light than realism. Monet and his fellow artist strayed away from the classical paintings and focused on more contemporary pieces of work. One of his more famous works of art was the Water Lily Pond. The arched bridge in the painting is actually one he built over his very own water garden. This painting was made in 1899 and it is oil on canvas. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Irises''=== | ||
| + | This painting, completed between 1914 and 1917, was made with thick, broad strokes and depicts the view from the Japanese bridge at Monet's studio at Giverny. The impressionistic effects of this painting may have been induced by the double cataracts that Monet had developed at the time of its painting. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Snow Scene at Argenteuil''=== | ||
| + | Monet spent much of the 1870s in Argenteuil, a town to the north-west of Paris. During the winter of 1874-1875, unusually heavy snows inspired a series of eighteen paintings of Argenteuil. Snow Scene at Argenteuil focuses on capturing the atmosphere of the wintery day, omitting many of the finer details. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''The Thames below Westminster''=== | ||
| + | This painting dates from 1871, when Money was living in London, England during the Franco-Prussian War. The painting shows the Houses of Parliament and Westminster Bridge through an atmospheric fog, sharply contrasting the soft shadows of the river with new foliage on the Embankment. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Irises.jpg | ||
| + | File:Snow Scene at Argenteuil.jpg | ||
| + | File:N-6399-00-000025-wpu.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | ==Jan van Eyke== | ||
| + | [[File: arnolfini1.jpeg|x350px|right|thumb|frame|The Arnolfini Portrait]]<br> | ||
| + | Jan van Eyke is a Flemish painter from the 15th century. The Ghent Altarpiece, located in the Stain Bavo Cathedral in Ghent, is van Eyke's most famous and recognizable work. He is known to have painted his signature as a pun on his name into his paintings, and has made that signature quite evident in some of his paintings. In his painting the Arnolfini Portrait, also know as the Portrait of Giovanni Arnolfini and His Wife, bears his signature directly in the middle of the portrait above a mirror that reflects back the image of him painting the couple. Jan van Eyke has painted both non secular and secular works, many of which were portraits. All of his non secular works but the Ghent Altarpiece include the Virgin Mary. He was also known to sign and date the frames of his paintings considering them a continuation of the art piece, this was considered unusual for the time. After his death in 1441, members of his workshop finished the paintings that he had started. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ==Vincent Van Gogh== | ||
| − | + | Vincent Van Gogh is a highly sought after Dutch Post- Impressionist artists who has created over 2,100 artworks before he committed suicide at the young age 37. Below are just a few of his oil paintings currently on display at The National Gallery. | |
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Sunflowers''=== | ||
| + | Created in 1888, ''Sunflowers'' was one of four works painted by Van Gogh to decorate his home. He associated the yellow with hope and friendship and expressed the work as an "idea symbolizing gratitude". This has been thought of as his favorite of the four canvasses because he hung it in his guest bedroom when anticipating a visit from friend and fellow painter, Paul Gauguin. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Chair''=== | ||
| + | Also created in 1888, ''Chair'' is a still work of everyday objects. These objects- the tobacco and pipe, the sprouting onions, and the chair itself- all follow the common theme of mundaneness throughout everyday life. Van Gogh wanted this work to represent his "direct and plain-speaking character". By contrasting of the yellow chair to the blue door and wall, he makes it clear the work is about this very plain chair in a very plain room. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Two Crabs''=== | ||
| + | ''Two Crabs'' was created in 1889, after his release from Arles hospital which began his embarkment on a series of still life. The left crab appears to be on its back while the forward right one is on it's back. It may very will be the same crab, just different perspectives. Also, the crabs are on a bright blue and green sea floor. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Farms near Auvers''=== | ||
| + | Created in 1890,a month before he died in his home town of Auvers, he painted ''Farms near Auvers'' which reflects on of his favorite things; the mossy patched rooftops. Some say this is an unfinished piece of work as seen by the rushed brushwork in the back. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===''Long Grass with Butterflies''=== | ||
| + | Also created the year he died in 1890, he painted ''Long Grass with Butterflies'' from what he observed "the grass grows tall and unkempt" in the garden of the assylum at St.Remy. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:VanGoghSunflowersTT.jpg|''Sunflowers'' | ||
| + | File:VanGoghChairTT.jpg|''Chair'' | ||
| + | File:OGNationalGalleryCrabs.jpg|''Two Crabs'' | ||
| + | File:OGNationalGalleryFarmsnearAuvers.jpg|''Farms near Auvers'' | ||
| + | File:OGNationalGalleryLongGrasswithButterflies.jpg|''Long Grass with Butterflies'' | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Georges Seurat== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ===Bathers at Asnières=== | ||
| + | {{Infobox | ||
| + | |title = Bathers at Asnières | ||
| + | |bodystyle = width:25em | ||
| + | |image = [[File:bathersatasnieres.jpg|400px|right]] | ||
| + | |label22 = '''Artist''' | ||
| + | |data22 = Georges Seurat | ||
| + | |label23 = '''Year''' | ||
| + | |data23 = 1884 | ||
| + | |label24 = '''Location''' | ||
| + | |data24 = National Gallery, London | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | Dated 1884, Georges Seurat's piece showing a scene next to the Seine river of several people relaxing and bathing. This piece is considered one of his masterpieces, and is one of the most prized paintings at the National Gallery. The painting and Seurat's other works only gained appreciation long after his death, and he has been lauded for its innovative brush techniques, including pointillism. This technique, which was his own invention, involved painting using small dots of color to create patterns that generated an image. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The piece was painted at Seurat's studio, on a canvas the same size as his more famous work, "A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte." When it was released, the painting garnered mixed reviews. However, as time passed, the piece became more respected. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | After X-ray imaging, an interesting theory emerged about some of the later additions to this painting. The skiff and ferry boat were added very late to the painting, and the theory suggests that these were added by Seurat to connect ''Bathers'' to ''A Sunday Afternoon''. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Carlo Crivelli== | ||
| + | This artist was born around 1430 in Venice, Italy and was most likely trained in Squarecione in Padua. He was cast out of Venice in 1457 for adultery and became more of an active artist. He was a master of alter pieces which usually depicted saints and the holy family, but deliberately created them to be artificial to draw the viewer to the fact that the painted pictures mystical. Crivelli had the ability to simulate marble architecture as well as incorporated coloured glass as jewels and guided work. His main influence was Giorgio Schiavone, who was a Croatian born painter who was active in Venice. Crivelli passed away around 1494 AD. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===La Madonna della Rondine=== | ||
| + | This is an alter piece that pictures Mary and Jesus surrounded by St Jerome and St Sebastian. The piece is called rondine (meaning swallow) because of the swallow perched above which is used as a symbol of the resurrection. In the predella, the tier below the alter, is St Jerome of the Wilderness, the Nativity and the Martyrdom of St Sebastian. Next to them are St Catherine, a martyr, and St George, who was in combat with a dragon. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ===The Immaculate Conception=== | ||
| + | The painting pictures the Virgin Mary, who miraculously conceived a child by the Holy Spirit. In the painting is a vase with a white lily to symbolize her purity. This piece was made for the Franciscan order's church at Pergola in the Italian Marches. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Francisco de Goya== | ||
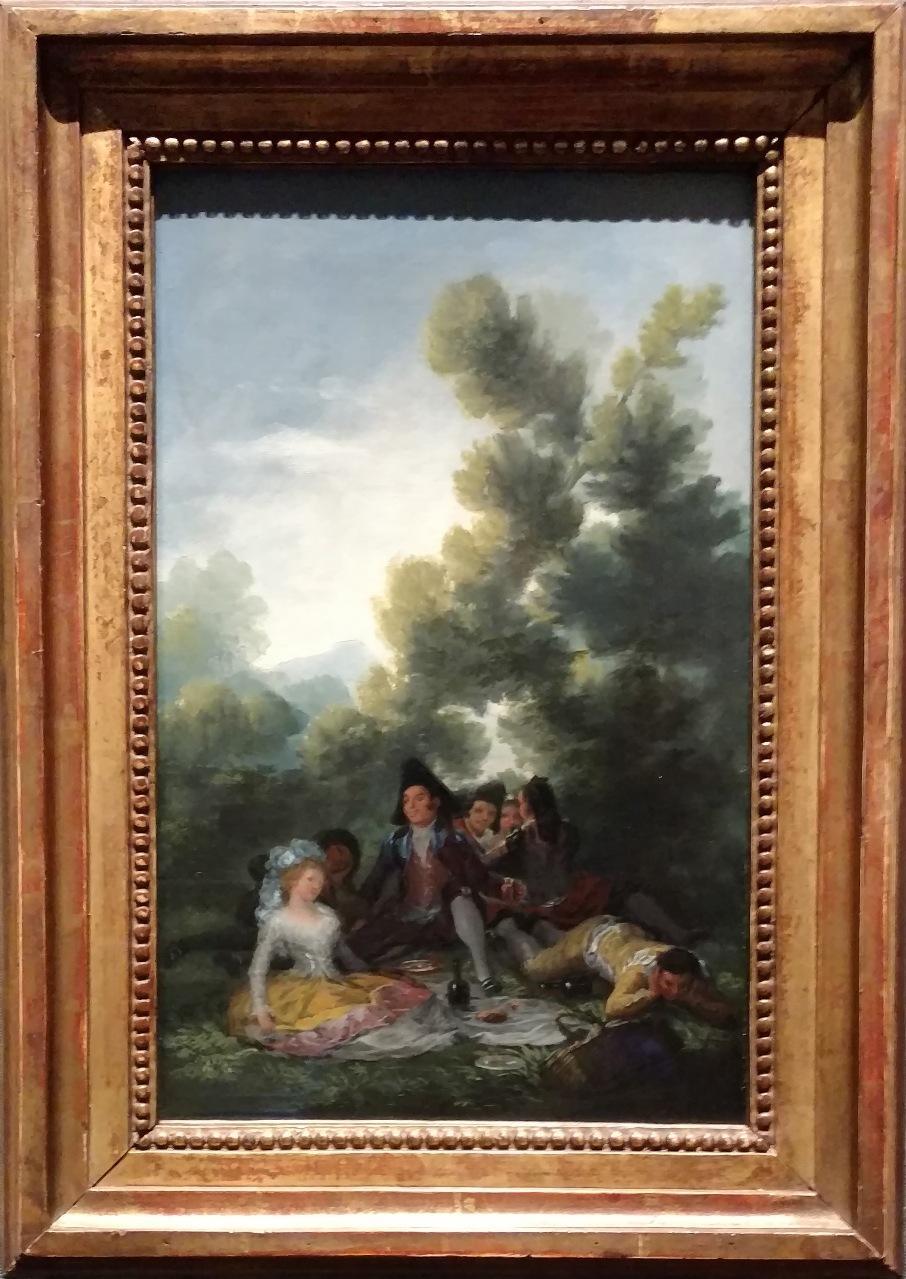
| + | Francisco de Goya is an artist of the Spanish Golden Age and one of the pioneers of the style of realism. The Golden age was an era of art, literature and science. It was a time of innovations and ideas, such as the idea of no more monarchy. The people of Spain preferred to have elections instead. This lead to wars. These political conditions inspired artists such as Goya. He was a painter for the king, Carlos IV. However, he painted the royal family with a brutal realism because he did not like how the monarchy would harm the people of Spain. In addition to royal portraits, Goya painted places that he visited. Common elements to his paintings include no distinct lines and dark tones. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed" heights=450p> | ||
| + | Image:Goya- Doña Isabel de Porcel- sm- JR.jpg|'''Doña Isabel de Porcel''' <br> Doña Isabel is painted wearing the fashion of the time, the lace headdress. However, this portrait has more to it than what meets the eye, literally. Beneath Doña Isabel there is another painting of a man in a waistcoat. Some portions of it can be seen through parts of the portrait of Doña Isabel. While credited to Goya as one of his finest portraits, some scholars question if he painted it. | ||
| + | Image: Goya- The Duke of Wellington- sm- JR.jpg|'''The Duke of Wellington''' <br> Arthur Wellesley is depicted after freeing Spain from French occupation. The Peninsular Gold Cross, rosette and badge of the Order of the Golden Fleece were not originally included in the painting but added in at a later time. | ||
| + | Image: Goya- A Picnic- sm- JR.jpg|'''A Picnic''' <br> This painting depicts a group of men and women eating outside under a tree. It is believed that this painting served as a sketch for a tapestry cartoon that Goya made for King Charles III of Spain. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =The National Gallery in Media= | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The National Gallery is one of the most iconic buildings in London located in Trafalgar Square. Because of its importance the National Gallery can be seen in many television shows and movies. One example is in the popular British television show Doctor Who, where the 50th anniversary special opens in the National Gallery. The National Gallery was also used as a meeting point for James Bond and his quartermaster in the 2012 film Skyfall. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | + | [[File:BondGallery.jpg|thumb|left|James Bond at the National Gallery]] | |
| − | + | [[File:DoctorGallery.png|thumb|right|Clara and The Doctor at The National Gallery]] | |
| + | Image:BondGallery.jpg|''James Bond at the National Gallery'' | ||
| + | Image:DoctorGallery.jpg|''Clara and The Doctor at The National Gallery'' | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Hidden Art= | ||
| + | The purpose of visiting an art gallery is to view all the pieces that they have on display but what about the art that is hidden in plain sight. Most spend so much time looking at the paintings hanging on the walls that the beauty of the surrounding area is missed. In 1831 the National Gallery was constructed at Trafalgar Square comprising of just six rooms with the remaining space used by the Royal Academy of Arts. 31 years laters the Royal Academy moved into it's own building opening up more space for the Gallery. From then on there have been 4 more extensions to the building. This building now has several beautifully designed rooms that can be found on the upper levels. Many of the entrance ways are elaborate pieces of art with corinthian columns surrounding doors and gold plated reliefs just above. The ceilings also can be admired with their many carvings and large windows bringing in much natural light. The floors are also worth a look between the mosaics by the main entrance, the patterned metal air grates, and the different designs made from the hard wood floor. | ||
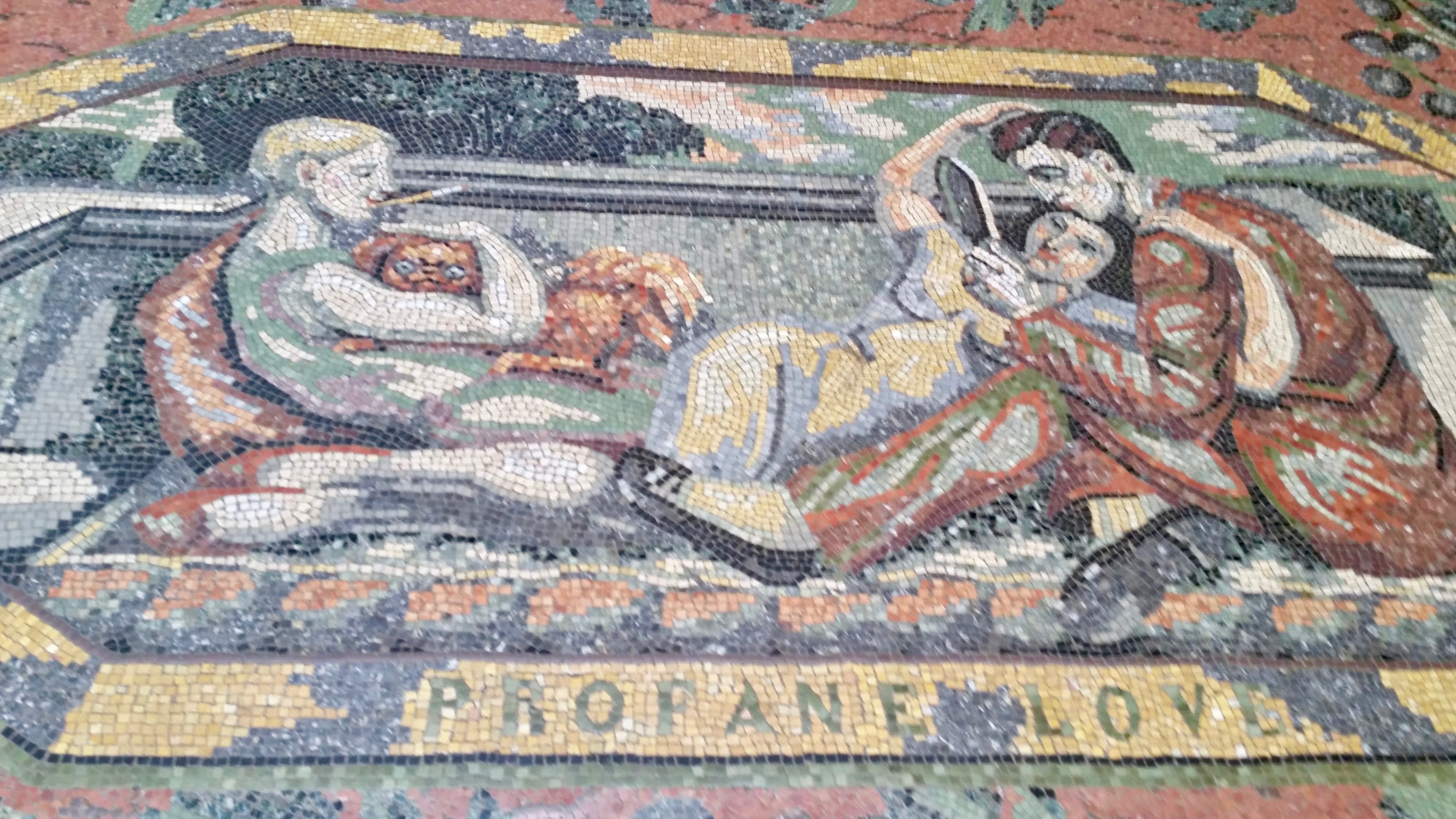
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | + | File: National Gallery Bench.jpg|A decorative bench | |
| − | + | File: Gallery Column.jpg|One of the many corinthian columns | |
| − | + | File: Gallery Floor Grate 1.jpg|A decorative grate | |
| − | + | File: Gallery Mosaic.jpg|A mosaic located on the floor near the main entrance | |
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | # National Gallery History retrieved from [http://www.nationalgallery.org.uk www.nationalgallery.org.uk] | ||
| + | # Rembrandt. (n.d.). Retrieved May 10, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/rembrandt | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Art]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:38, 21 June 2017
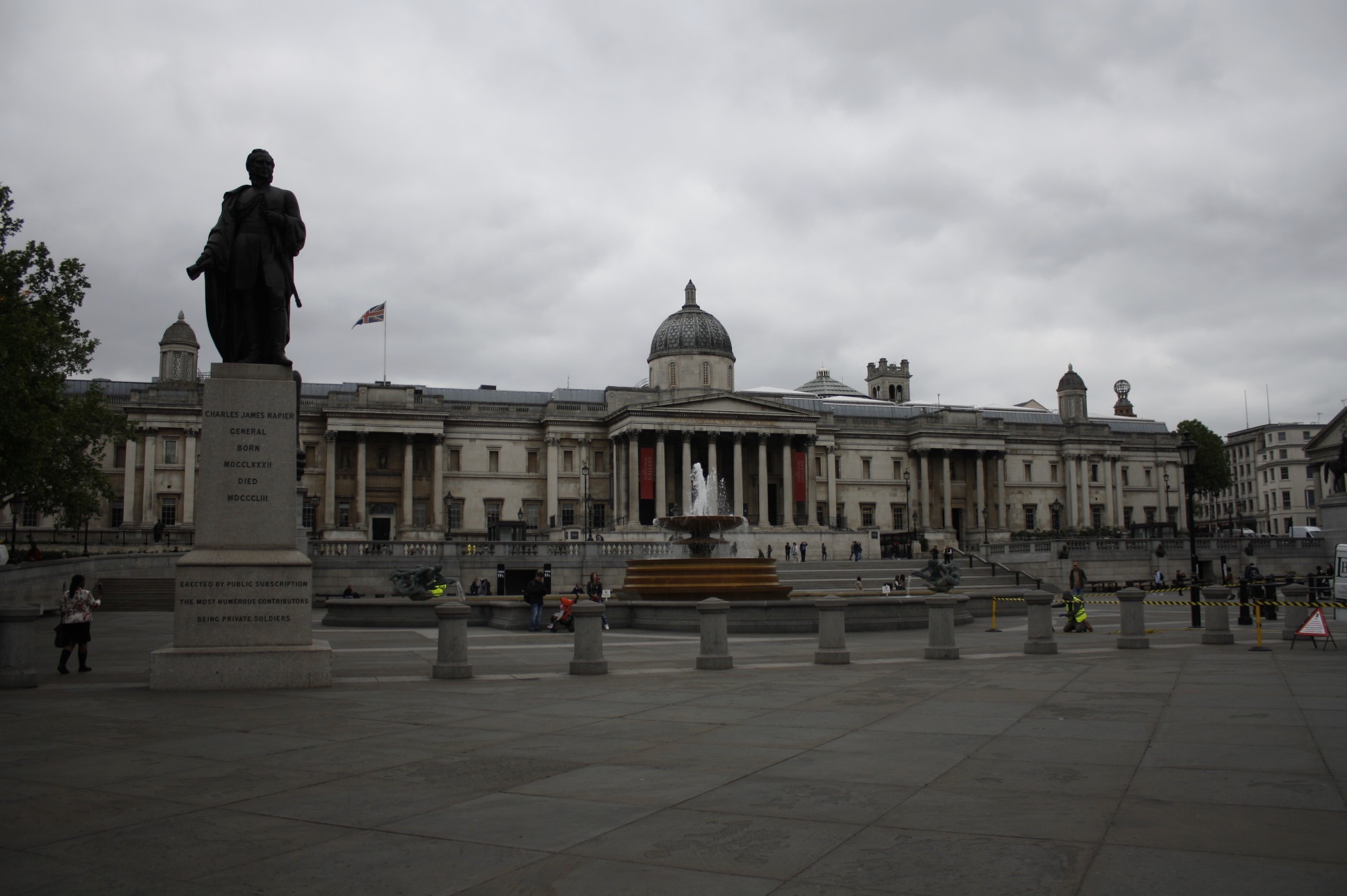 National Gallery, Trafalgar Square | |
| Established | 1824; 193 years ago |
|---|---|
| Location | Trafalgar Square, London, WC2, United Kingdom |
| Director | Gabriele Finaldi |
| Website | www.nationalgallery.org.uk |
Overview
The National Gallery is located in Central London and contains over 2,300 paintings that are free to view by the public. The overall gallery is split into four main sections each consisting paintings within a certain period from early 12th century to early 19th century. Most of the pre 16th century paintings portrayed Greek mythology or the divinity of religion such as birth and death of Christ. Painting from late 14th to early 17th century transitioned from portraying mythical and religious senses to portraying objects in detail, landscapes, daily lives of common people and portraits of wealthy citizens. Some notable artists displayed in the gallery are Leonardo da Vinci, Van Gogh, and Michelangelo.
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Background and Origin
- 3 Painters and Works
- 3.1 Leonardo da Vinci
- 3.2 Guido Cagnacci & the Repentant Magdalene
- 3.3 Johannes Vermeer
- 3.4 Giovanni Antonio Canal
- 3.5 Rembrandt van Rijn
- 3.6 Raphael
- 3.7 Diego Velasquez
- 3.8 Claude Lorrain
- 3.9 Claude Monet
- 3.10 Jan van Eyke
- 3.11 Vincent Van Gogh
- 3.12 Georges Seurat
- 3.13 Carlo Crivelli
- 3.14 Francisco de Goya
- 4 The National Gallery in Media
- 5 Hidden Art
- 6 References
Background and Origin
The National Collection started when the House of Commons bought the picture collection of John Julius Angerstein for £57,000. His collection contained 38 pictures and were kept at his house, 100 Pall Mall. In 1831 Parliment agreed to build a the National Gallery at Trafalgar Square as it was considered to be the very center of London. The building was completed in 1838. Over the years the Gallery has expanded and now spans 46,396 meters squared.
Painters and Works
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci was a master painter, sculptor, architect, designer, theorist, engineer and scientist that created some of the most famous and respected pieces of art in the world. He has been named the "father of paleontology", the "father of ichonology", the "father of architecture", and one of the greatest painters of all time. As one of the greatest painters of all time, the National Gallery in London was lucky enough to acquire one of his paintings along with a mostly finished drawing.
The drawing located at the gallery is The Virgin and Child with St Anne and St John the Baptist. This drawing is deeply intriguing because it was most likely a preparatory drawing for an upcoming at painting when it was first created. The reason this is so interesting is that it looks and seems almost completely finished as a charcoal drawing on a tinted canvas yet it still has some completely unfinished parts to it. This confusion lead Bernardino Luini to create the Holy Family with St Anne and the infant John the Baptist, a painted replica of the drawing from Leonardo da Vinci
The painting located at the National Gallery is one of two versions and is named the "Virgin on the Rocks". The other version of this painting is located at the Louvre. The Virgin of the Rocks in the Louvre is considered to be the older version dating from around 1483–1486 while the Virgin of the Rocks in the National Gallery is still ascribed to Leonardo da Vinci, but dates to before 1508. Originally, many thought that this painting was partially done by one of his assistants, further study from the gallery has determined that da Vinci did the greater portion of the work. Unfortunately, this is still highly under debate. The reason that there are two different versions is most likely because da Vinci created it to for a commission in Milan and sold the Louvre version privately. The London version was then created to fill the commission and given to the chapel of the Confraternity of the Immaculate Conception, a church in Milan.
In 2005, the London painting was examined more closely by the National Gallery, using infrared and x-ray technology. This examination revealed that this painting was actually covering one of a different design. The original design pictured a woman on her knees with one hand outstretched and another on her heart and was most likely for the adoration of the infant Jesus.
In 2009 and 2010, the painting was cleaned and had some conservative work. During this time, the gallery determined that da Vinci had done most, if not all, of the work on the painting as seen today in the National Gallery.
Guido Cagnacci & the Repentant Magdalene
Now on display in the National Gallery until the end of May is a great historical piece of art by Guido Cagnacci, an Italian painter in the 1600s. Cagnacci is not as widely known as da Vinci for example, but his work the Repentant Magdalene is considered priceless. This display at the Gallery is also the first time that a Cagnacci has been displayed in a public collection in the United Kingdom. Portraying Magdalene asking for forgiveness from her ways, the painting also shows the angel Virtue beating Vice, the devil. This painting is one of the only ones that shows Mary Magdalene as a sinner, crawling back for forgiveness, and is a turn away from Cagnacci's usual paintings of half dressed and seductive paintings. X-ray examination of the art has reviled two changes, notable to the servants and the Vice. An original servant was painted over, creating a more intimate environment with less of a crowd. The second change that Cagnacci had made was to change the Vice from standing at the feet of Mary Magdalene, to jumping in the air, giving it a more evil spirit look overall.
Johannes Vermeer
[1]
Johannes Vermeer was a Dutch Painter born in 1632 and is known to be a great Dutch master. Although he only produced only 35 known paintings during his lifetime, Vermeer was known to produce truly detailed works. He became a master at Delft painters’ guild in 1653 when he got married. His works contain many symbols and have very well placed objects to convey messages. Many a time, there paintings inside of paintings that give the paintings a certain depth that is very symbolic. Even though he was a talented painter, Vermeer died leaving his family destitute. Some of his paintings included A Young Woman Standing at a Virginal, the Girl with a Pearl Earring, and The Milkmaid.
A Young Woman at a Virginal
In the painting contains a woman of status playing the virginal in a well-decorated room full of paintings and a tiled floor. The painting in the lid of the virginal is a pastoral setting, which could be a painting by a colleague Pieter Groenewegen. The second painting is inside of the painting is by Cesar van Everdingen and is of cupid. This painting can be seen as young woman’s choice between two paths: one of easy love or one of a more difficult love. She must make a decision and one can tell it’s about love due to the close association between music and love. [2]
Giovanni Antonio Canal
Giovanni Antonio Canal, also known as Canaletto, lived from 1697-1768. He was an Italian painter who loved to paint Venetian landscapes of the city and the canals. Many of his more famous works are on display at The National Gallery in one room. The English people at the time loved traveling and exploring Venice, so Canaletto decided to bring Venice to them through his paintings. One painting, Eton College, was painted around 1754. It is a painting of Eton College seen from the east across the River Thames. Canaletto traveled to England between 1746 and 1756, and during that time he painted many paintings for the English people. He wanted to give them a gift of a painting of something in their homeland. One of his most famous paintings, Venice: The Basin of San Marco on Ascension Day, 1740, depicts an annual ceremony that symbolized the joining of Venice to the Adriatic Sea. The Doge would leave his palace on top of a golden state barge so he could travel out to where the city and the Adriatic meet and throw a golden ring into the Adriatic. Canaletto was a famous oil painter of his time and is remembered through both Italian and English history as a figure who combined the two cultures, showing one how the other lived.
Rembrandt van Rijn
The greatest visual artist to have ever lived is currently on display at the National Gallery. Born in 1606, Rembrandt is also considered the most important painter in dutch history, What makes Rembrandt unique is he did not have a particular style or scene. His works ranged from landscapes, to portraits (Portrait of Jacob Trip), to historical scenes (The Night Watch), to religious scenes, to science and anatomy (The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp), etc. His pieces often explored his close surroundings and the depths of human emotion. Since he rarely, if ever, traveled beyond the dutch border, he got most of his inspirations domestically. He is most well known for his narrative style. HIs biblical paintings have allow the audience to feel certain emotions while depicting a scene in uncanny detail. He is also known for painting Amsterdam's Jewish population. His contributions to the art world came at the perfect time, the Dutch Golden Age. This period had excess wealth and cultural achievements. His style was innovative in the way that he directly opposed the main style at the time, Baroque.
Raphael
Raphael Sanzio da Urbino, widely known as just Raphael, was an Italian painter, and later architect, who lived at the end of the of the 15th century and the beginning of the 16th century. His is considered to be part of the three great masters of this period along with Michelangelo and Leonardo Da Vinci, who also have paintings displayed in the Gallery. Many of Raphael's paintings depict religious scenes such as his painting of Jesus being put to death on the cross, titled The Mond Crucifixion. He has many famous paintings featured in the National Gallery including his piece titled The Ansidei Madonna. This piece was painted as an alter piece for the chapel of the Ansidei family in Perugia. Raphael used geometrical planning to obtain the result in "harmonious thirds". Another famous painting by Raphael was his piece titled Saint Catherine of Alexandria. This painting shows Saint Catherine leaning against the wheel where she was supposed to be condemned to die, but the wheel miraculously broke. After his death in 1520 his paintings gained a lot of popularity in the 18th and 19th century.
Diego Velasquez
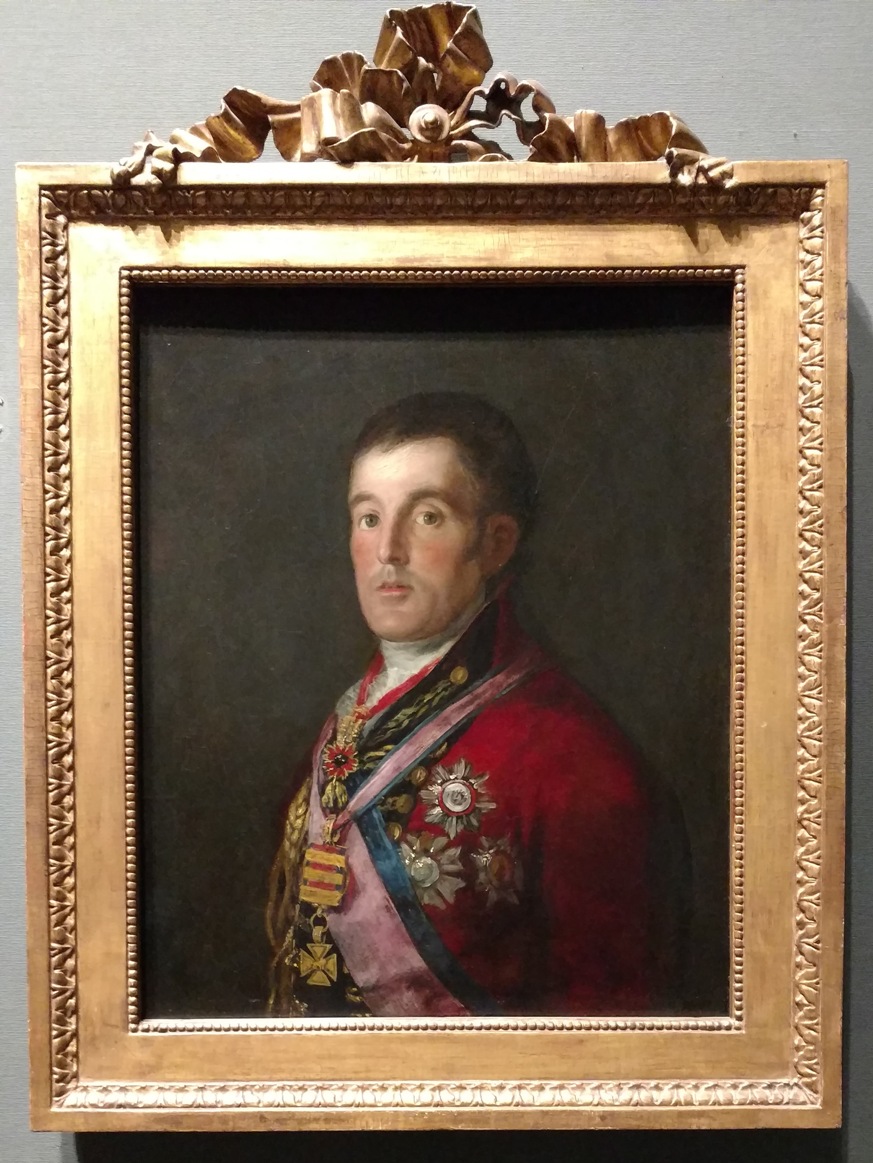
Diego Velasquez was an extremely important painter of the Spanish Golden age. He completed many portraits and was the head painter in the court of King Phillip IV. Some of his pieces were replicated and recreated by other famous painters later on including Salvador Dalí and Pablo Picasso. His portrait of Archbishop Fernando de Valdés in on display at the National Gallery. However the piece shown at the National Gallery is not the complete portrait, it is only a fragment and another fragment of the portrait is located at the Spanish Royal Collection. Velasquez's painting The immaculate Conception can also be seen at the museum. This painting shows The Virgin Mary standing on the moon with a circular crown of stars above her head and signifies that she is the immaculate conception, and therefore was conceived without original sin. Overall Velasquez's paintings had and still have a significant cultural and historical influence.
Claude Lorrain
Born Claude Gellée in Duchy of Lorraine around the early 1600's before 1606.[3] He left around 1612 for Germany. He then went to Rome, where he became a studio assistant to a landscapist Agostino Tassi.[3] He then settled in Rome around 1628 where he started to sketch in the Roman countryside.[3] His works are all of landscapes and he is know for his style of landscape paintings.[3] Claude died in 1682. 14 of his paintings are shown in the Gallery. Pictured are three of his compositions; A View in Rome (1632), Seaport with the Embarkation of Saint Ursula (1641) and Landscape with Aeneas at Delos (1672).
A View in Rome (1632)
Attributed to Claude Lorrain via National Gallery - LinkLandscape with Aeneas at Delos (1672)
Attributed to Claude Lorrain [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons - LinkSeaport with the Embarkation of Saint Ursula (1641)
Attributed to Claude Lorrain [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons - Link
Claude Monet
Claude Monet was born on November 14, 1840 in France. Monet studied at the Academie Suisse, he was close friends with Camille Pissarro, and you can see there work side by side in the National Gallery. Money and Camille eventually got married in June of 1870. Monet, with several other artists formed the Société Anonyme des Artistes, as an alternative way to showcase their works. Monet was very critical of his own work. He was known to destroy his own paintings by burning, cutting, or kicking them. His painting style was the start of Impressionism. They called it this because his work was more focused on form and light than realism. Monet and his fellow artist strayed away from the classical paintings and focused on more contemporary pieces of work. One of his more famous works of art was the Water Lily Pond. The arched bridge in the painting is actually one he built over his very own water garden. This painting was made in 1899 and it is oil on canvas.
Irises
This painting, completed between 1914 and 1917, was made with thick, broad strokes and depicts the view from the Japanese bridge at Monet's studio at Giverny. The impressionistic effects of this painting may have been induced by the double cataracts that Monet had developed at the time of its painting.
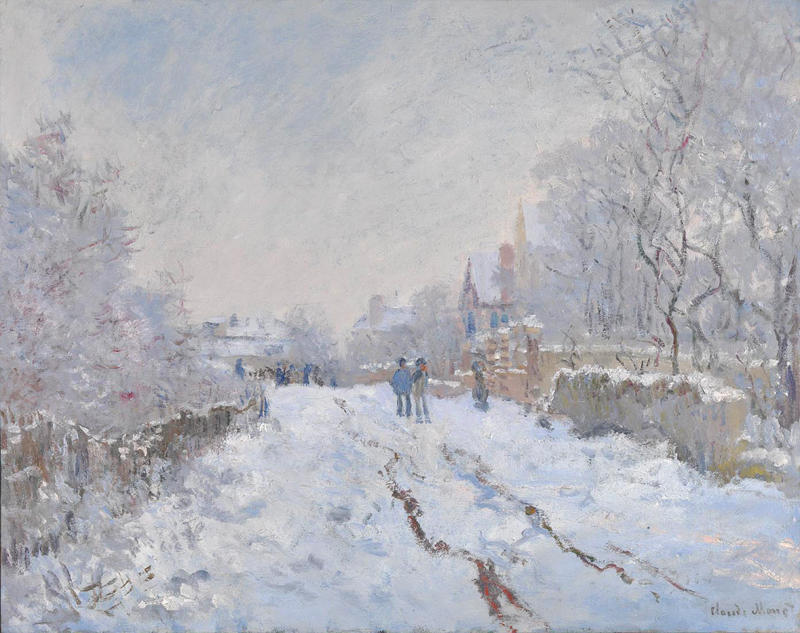
Snow Scene at Argenteuil
Monet spent much of the 1870s in Argenteuil, a town to the north-west of Paris. During the winter of 1874-1875, unusually heavy snows inspired a series of eighteen paintings of Argenteuil. Snow Scene at Argenteuil focuses on capturing the atmosphere of the wintery day, omitting many of the finer details.
The Thames below Westminster
This painting dates from 1871, when Money was living in London, England during the Franco-Prussian War. The painting shows the Houses of Parliament and Westminster Bridge through an atmospheric fog, sharply contrasting the soft shadows of the river with new foliage on the Embankment.
Jan van Eyke
Jan van Eyke is a Flemish painter from the 15th century. The Ghent Altarpiece, located in the Stain Bavo Cathedral in Ghent, is van Eyke's most famous and recognizable work. He is known to have painted his signature as a pun on his name into his paintings, and has made that signature quite evident in some of his paintings. In his painting the Arnolfini Portrait, also know as the Portrait of Giovanni Arnolfini and His Wife, bears his signature directly in the middle of the portrait above a mirror that reflects back the image of him painting the couple. Jan van Eyke has painted both non secular and secular works, many of which were portraits. All of his non secular works but the Ghent Altarpiece include the Virgin Mary. He was also known to sign and date the frames of his paintings considering them a continuation of the art piece, this was considered unusual for the time. After his death in 1441, members of his workshop finished the paintings that he had started.
Vincent Van Gogh
Vincent Van Gogh is a highly sought after Dutch Post- Impressionist artists who has created over 2,100 artworks before he committed suicide at the young age 37. Below are just a few of his oil paintings currently on display at The National Gallery.
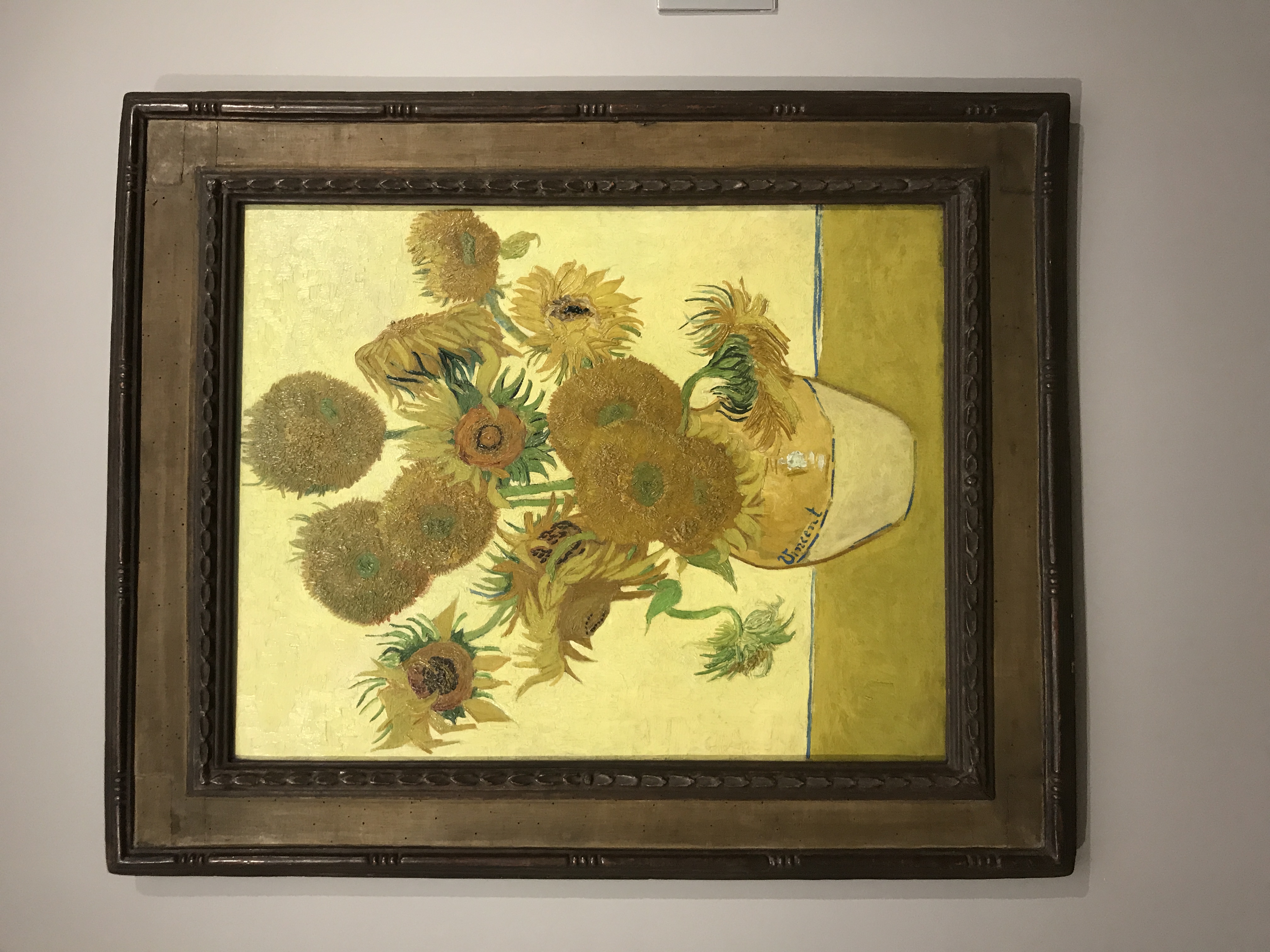
Sunflowers
Created in 1888, Sunflowers was one of four works painted by Van Gogh to decorate his home. He associated the yellow with hope and friendship and expressed the work as an "idea symbolizing gratitude". This has been thought of as his favorite of the four canvasses because he hung it in his guest bedroom when anticipating a visit from friend and fellow painter, Paul Gauguin.
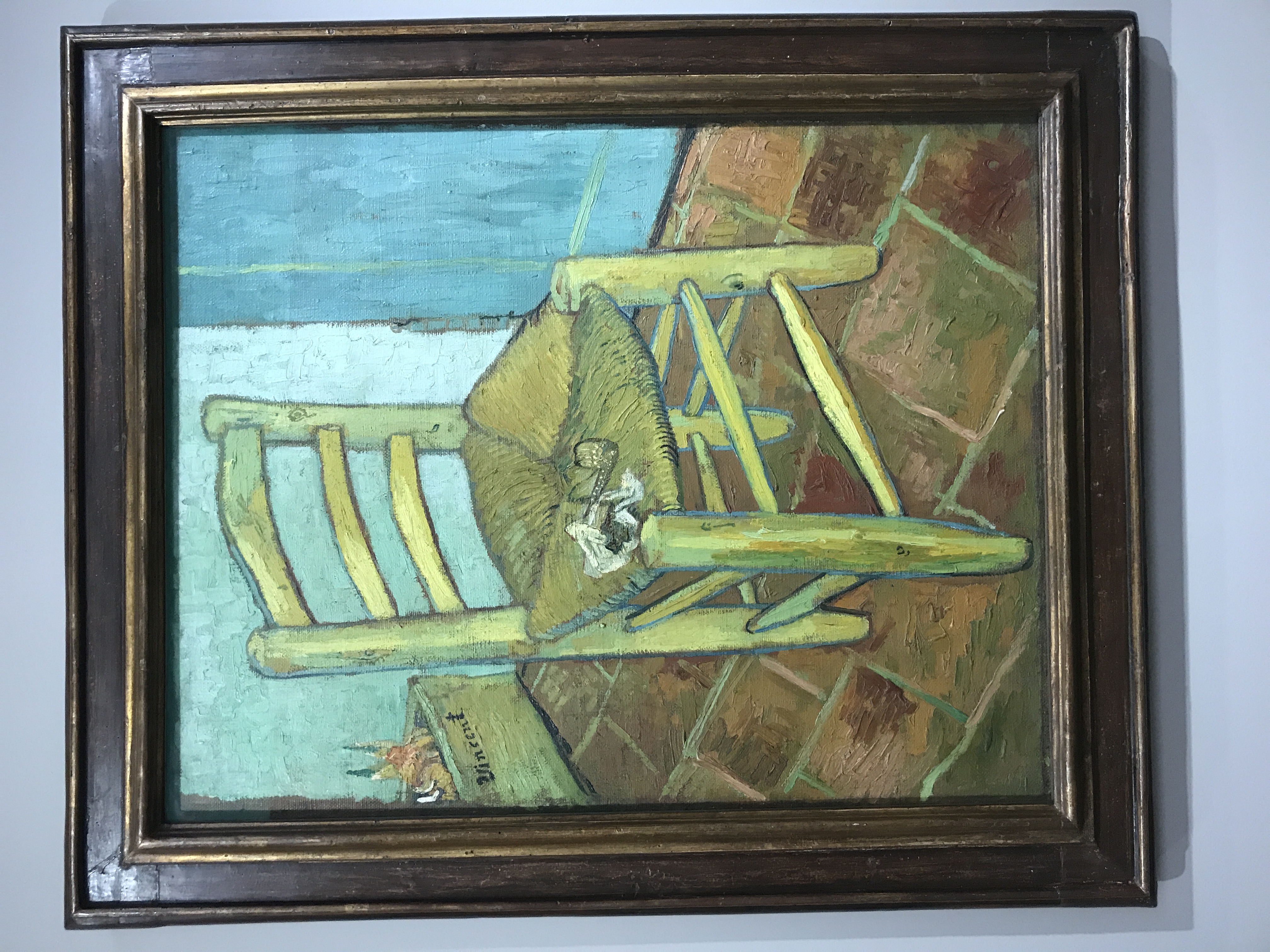
Chair
Also created in 1888, Chair is a still work of everyday objects. These objects- the tobacco and pipe, the sprouting onions, and the chair itself- all follow the common theme of mundaneness throughout everyday life. Van Gogh wanted this work to represent his "direct and plain-speaking character". By contrasting of the yellow chair to the blue door and wall, he makes it clear the work is about this very plain chair in a very plain room.
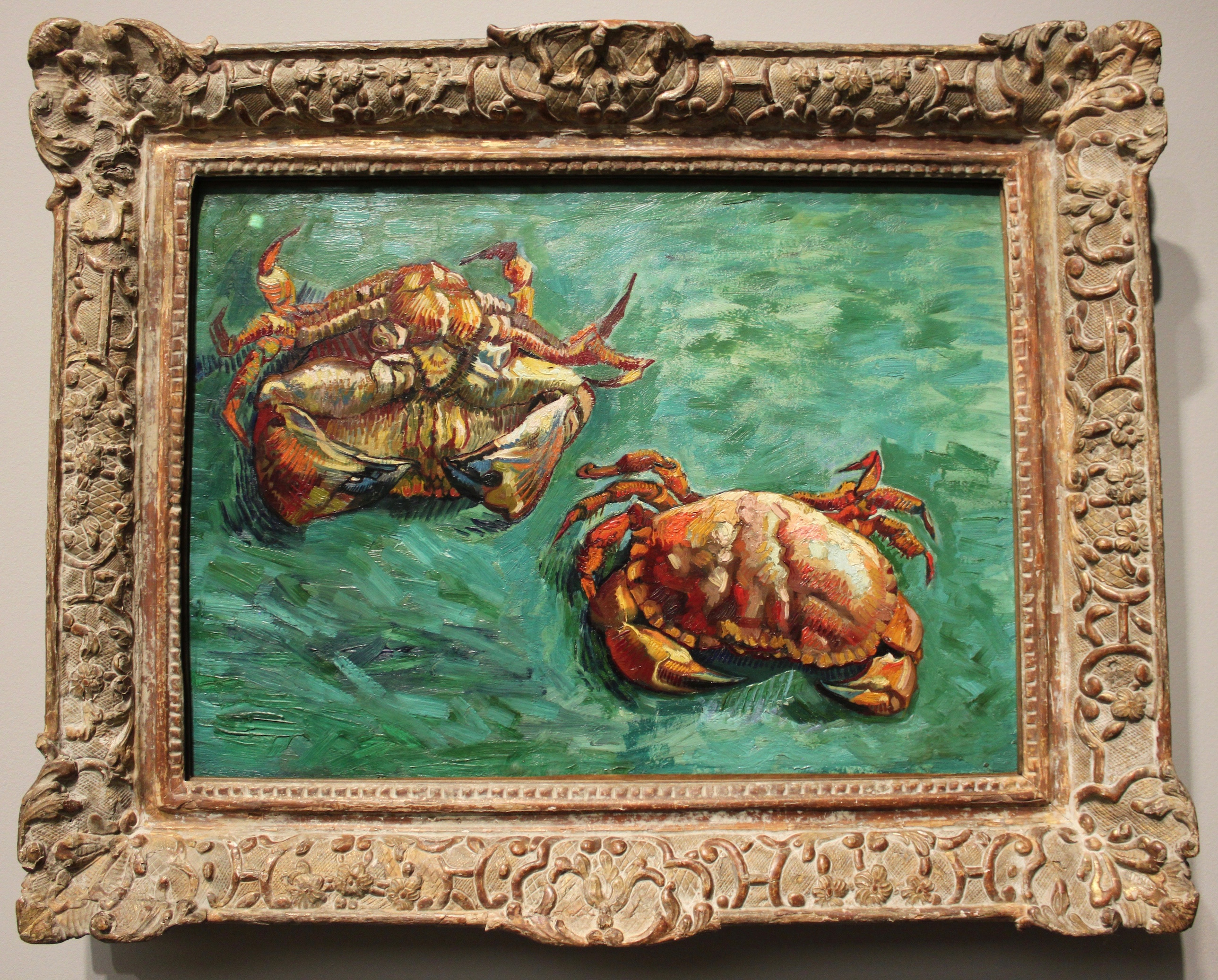
Two Crabs
Two Crabs was created in 1889, after his release from Arles hospital which began his embarkment on a series of still life. The left crab appears to be on its back while the forward right one is on it's back. It may very will be the same crab, just different perspectives. Also, the crabs are on a bright blue and green sea floor.
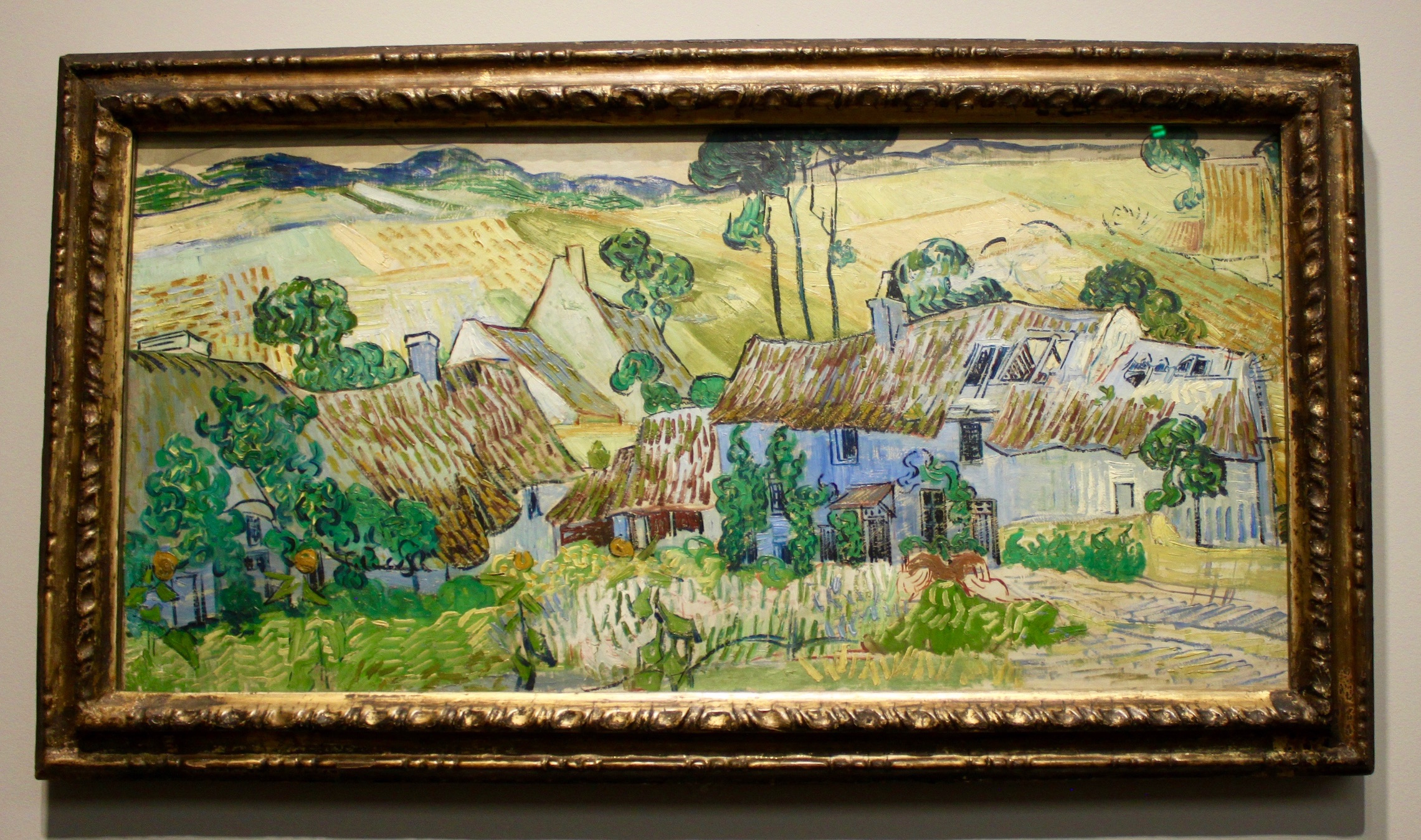
Farms near Auvers
Created in 1890,a month before he died in his home town of Auvers, he painted Farms near Auvers which reflects on of his favorite things; the mossy patched rooftops. Some say this is an unfinished piece of work as seen by the rushed brushwork in the back.
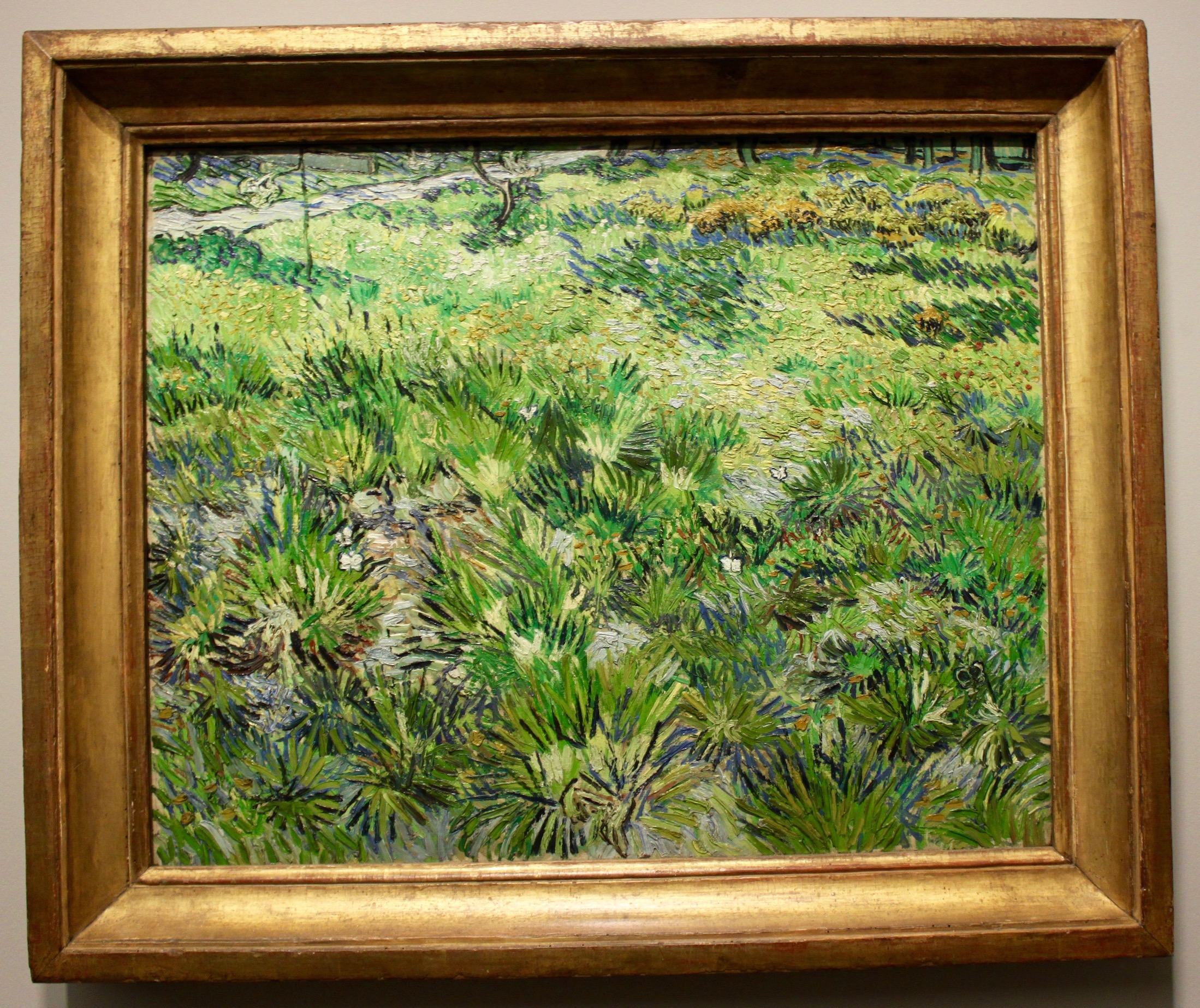
Long Grass with Butterflies
Also created the year he died in 1890, he painted Long Grass with Butterflies from what he observed "the grass grows tall and unkempt" in the garden of the assylum at St.Remy.
Georges Seurat
Bathers at Asnières
| Artist | Georges Seurat |
|---|---|
| Year | 1884 |
| Location | National Gallery, London |
Dated 1884, Georges Seurat's piece showing a scene next to the Seine river of several people relaxing and bathing. This piece is considered one of his masterpieces, and is one of the most prized paintings at the National Gallery. The painting and Seurat's other works only gained appreciation long after his death, and he has been lauded for its innovative brush techniques, including pointillism. This technique, which was his own invention, involved painting using small dots of color to create patterns that generated an image.
The piece was painted at Seurat's studio, on a canvas the same size as his more famous work, "A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte." When it was released, the painting garnered mixed reviews. However, as time passed, the piece became more respected.
After X-ray imaging, an interesting theory emerged about some of the later additions to this painting. The skiff and ferry boat were added very late to the painting, and the theory suggests that these were added by Seurat to connect Bathers to A Sunday Afternoon.
Carlo Crivelli
This artist was born around 1430 in Venice, Italy and was most likely trained in Squarecione in Padua. He was cast out of Venice in 1457 for adultery and became more of an active artist. He was a master of alter pieces which usually depicted saints and the holy family, but deliberately created them to be artificial to draw the viewer to the fact that the painted pictures mystical. Crivelli had the ability to simulate marble architecture as well as incorporated coloured glass as jewels and guided work. His main influence was Giorgio Schiavone, who was a Croatian born painter who was active in Venice. Crivelli passed away around 1494 AD.
La Madonna della Rondine
This is an alter piece that pictures Mary and Jesus surrounded by St Jerome and St Sebastian. The piece is called rondine (meaning swallow) because of the swallow perched above which is used as a symbol of the resurrection. In the predella, the tier below the alter, is St Jerome of the Wilderness, the Nativity and the Martyrdom of St Sebastian. Next to them are St Catherine, a martyr, and St George, who was in combat with a dragon.
The Immaculate Conception
The painting pictures the Virgin Mary, who miraculously conceived a child by the Holy Spirit. In the painting is a vase with a white lily to symbolize her purity. This piece was made for the Franciscan order's church at Pergola in the Italian Marches.
Francisco de Goya
Francisco de Goya is an artist of the Spanish Golden Age and one of the pioneers of the style of realism. The Golden age was an era of art, literature and science. It was a time of innovations and ideas, such as the idea of no more monarchy. The people of Spain preferred to have elections instead. This lead to wars. These political conditions inspired artists such as Goya. He was a painter for the king, Carlos IV. However, he painted the royal family with a brutal realism because he did not like how the monarchy would harm the people of Spain. In addition to royal portraits, Goya painted places that he visited. Common elements to his paintings include no distinct lines and dark tones.
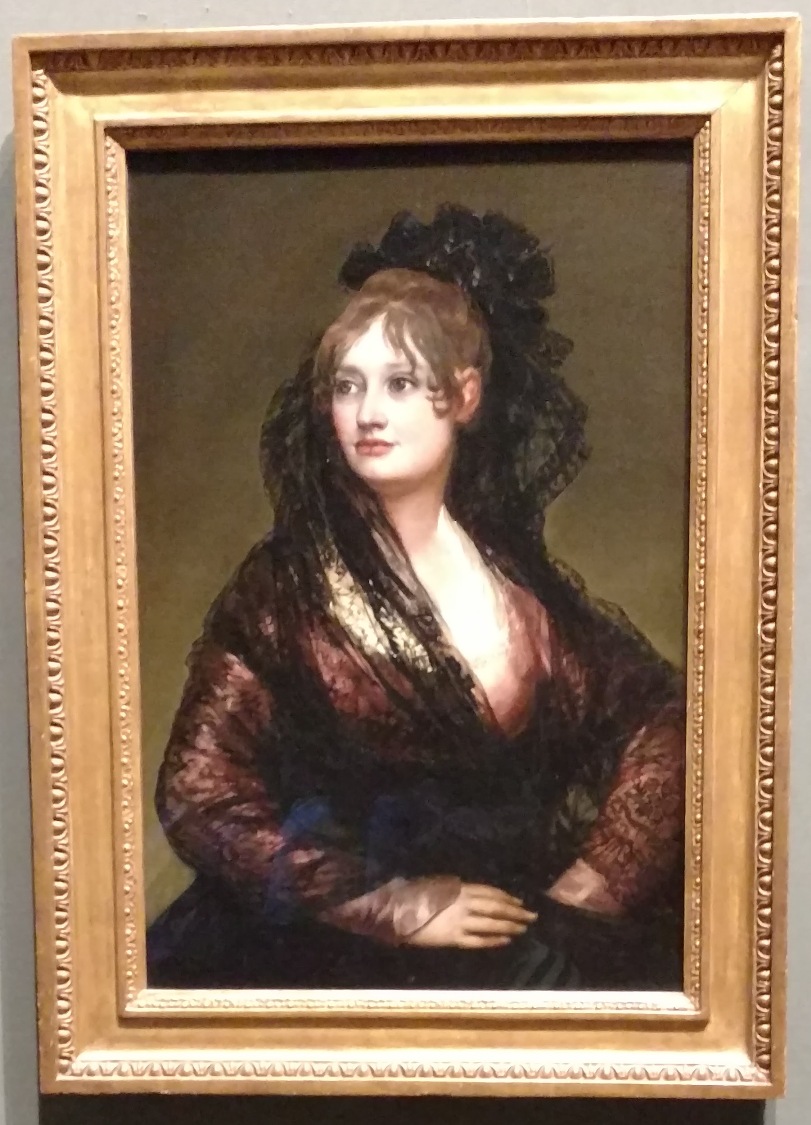
Doña Isabel de Porcel
Doña Isabel is painted wearing the fashion of the time, the lace headdress. However, this portrait has more to it than what meets the eye, literally. Beneath Doña Isabel there is another painting of a man in a waistcoat. Some portions of it can be seen through parts of the portrait of Doña Isabel. While credited to Goya as one of his finest portraits, some scholars question if he painted it.
The National Gallery in Media
The National Gallery is one of the most iconic buildings in London located in Trafalgar Square. Because of its importance the National Gallery can be seen in many television shows and movies. One example is in the popular British television show Doctor Who, where the 50th anniversary special opens in the National Gallery. The National Gallery was also used as a meeting point for James Bond and his quartermaster in the 2012 film Skyfall.
- DoctorGallery.jpg
Clara and The Doctor at The National Gallery
Hidden Art
The purpose of visiting an art gallery is to view all the pieces that they have on display but what about the art that is hidden in plain sight. Most spend so much time looking at the paintings hanging on the walls that the beauty of the surrounding area is missed. In 1831 the National Gallery was constructed at Trafalgar Square comprising of just six rooms with the remaining space used by the Royal Academy of Arts. 31 years laters the Royal Academy moved into it's own building opening up more space for the Gallery. From then on there have been 4 more extensions to the building. This building now has several beautifully designed rooms that can be found on the upper levels. Many of the entrance ways are elaborate pieces of art with corinthian columns surrounding doors and gold plated reliefs just above. The ceilings also can be admired with their many carvings and large windows bringing in much natural light. The floors are also worth a look between the mosaics by the main entrance, the patterned metal air grates, and the different designs made from the hard wood floor.
References
- National Gallery History retrieved from www.nationalgallery.org.uk
- Rembrandt. (n.d.). Retrieved May 10, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/rembrandt
- ↑ Johannes Vermeer. (n.d.). Retrieved May 15, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/johannes-vermeer
- ↑ A Young Woman standing at a Virginal. (n.d.). Retrieved May 15, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/johannes-vermeer-a-young-woman-standing-at-a-virginal
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Claude. (n.d.). Retrieved May 12, 2017, from https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/claude