Imperial War Museum
From Londonhua WIKI
Imperial War Museum
 Representative Article Image | |
| Imperial War Museum | |
|---|---|
| Attributed to Imperial War Museum | |
| Year | c. 1917 |
| Dimensions | 55.2 cm × 43.8 cm ( 21 3⁄4 in × 17 1⁄4 in) |
| Location | Imperial War Museum, London |
Overview
The Imperial War Museums is series of 5 museums located throughout England which holds a large collection of public and private documents, photographs, videos, and film material, and oral history recordings, an extensive library, a large art collection, and examples of military vehicles and aircraft, equipment, and other artifacts.The London location has a focuses on people's experiences and stories from WWI to current day modern day. It has several permanent exhibits such as the World War I exhibit which focuses on the sacrifices that many countries made while fighting the war, the Holocaust Exhibition, and the Secret War Exhibition.
Contents
- 1 Imperial War Museum
- 2 Overview
- 3 Secret War
- 4 First World War Galleries
- 5 Afghanistan: Reflections on Helmand
- 6 Second World War Galleries
- 7 Nuclear War
- 8 The Holocaust Exhibition
- 9 War on Terror
- 10 Family in Wartime
- 11 Syria: A Conflict Explored
- 12 Lord Ashcroft Gallery
- 13 References
- 14 External Links
- 15 Image Gallery
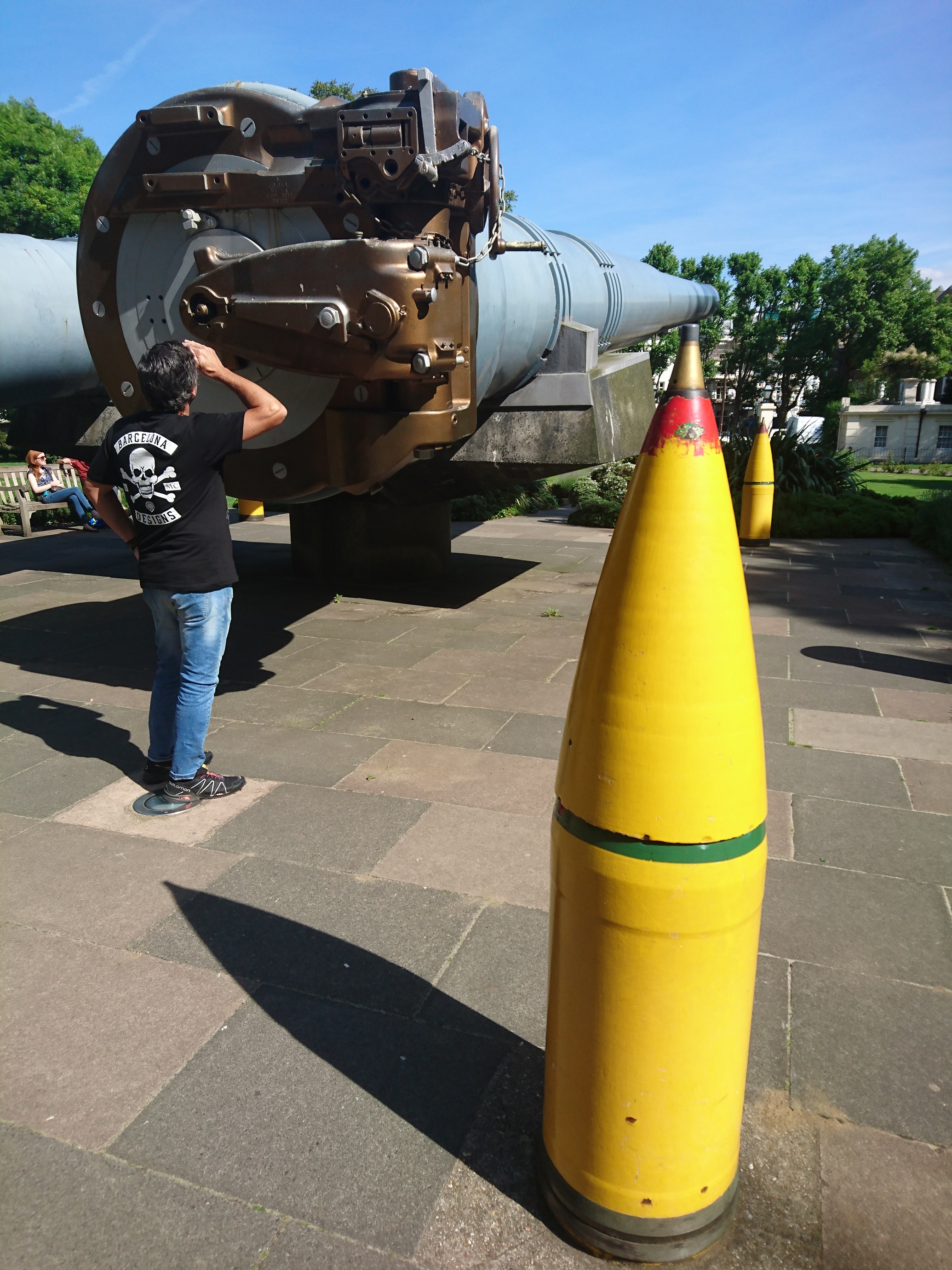
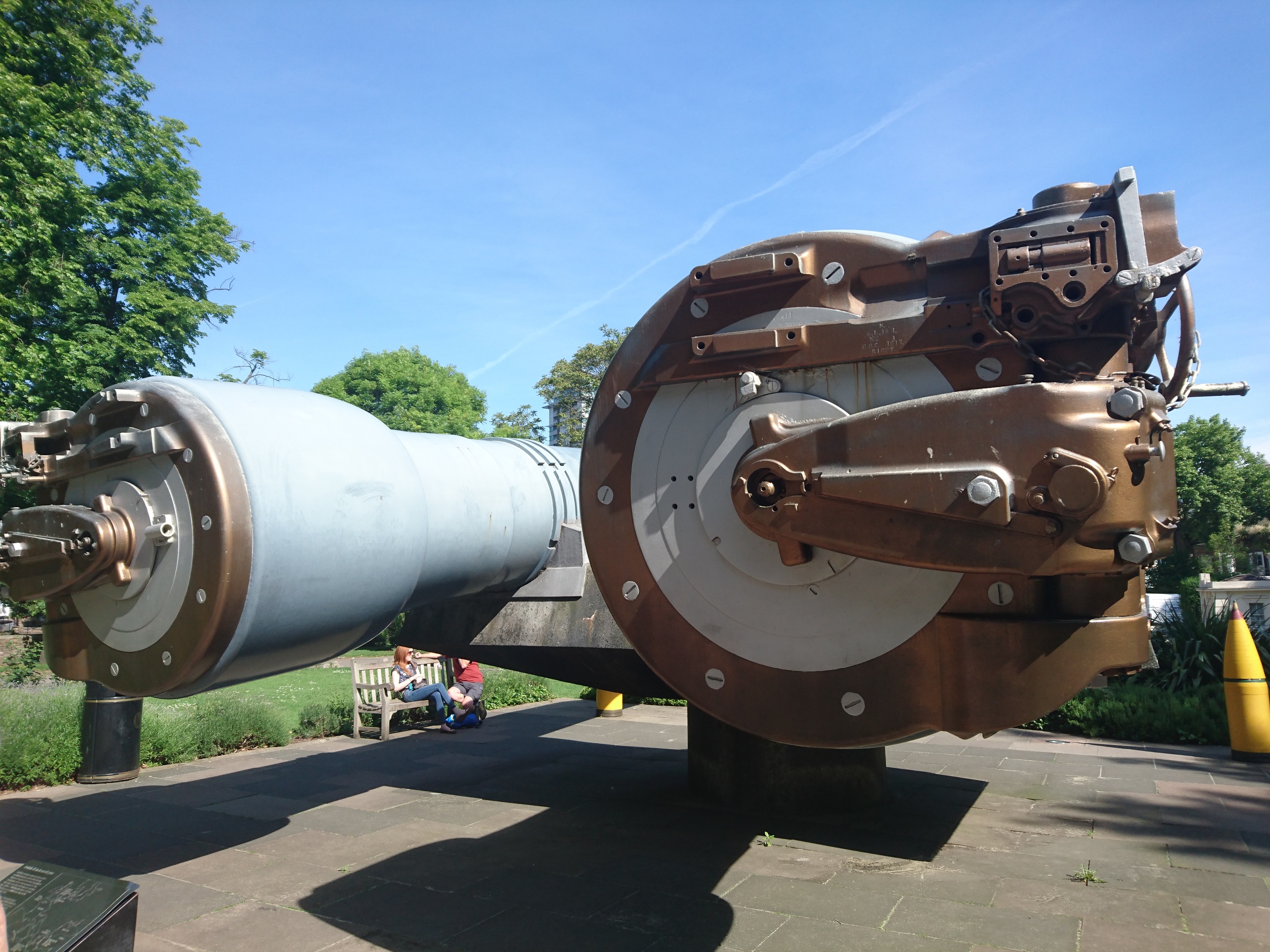
British 15-inch navel guns are on display at the entrance of the war museum. These 15-inch navel guns were the newest, largest and the most powerful guns found in the year, 1914. Each gun weighs approximately one hundred tons and launches 1,938lb shells at a distance of sixteen and a half miles. Both guns on display saw action during the course of their lives participating in the Greco-Turkish War, Invasion of Normandy, and D-Day. The guns were decommissioned in the 1940's and installed in front of Imperial War Museum London in 1968.
Secret War
Secret War is an exhibit revealing the covert operations departments in Britain. These five departments are MI5, MI6, Secret Communications, SOE, and Secret Soldiers, each with their own specialty. Together, they provide critical intelligence to Britain to protect the country and its assets and act on this intelligence.
MI5
Military Intelligence 5 (MI5) or otherwise known as the Security Service protects Britain against espionage, terrorism or other forms of sabotage within the country. While MI5 was established in 1909 it was not until 1989 that its role was formally defined in the Security Service Act. Britain was one of the few European powers going into the twentieth century without a secret service. However, fear of Germany took over and the War Office's Secret Service Bureau was formed. MI5 came from the "home" department of this bureau. Despite being new and small, the department apprehended 12 German spies by the start of World War I. During the war the department was designated as MI5, acquired 21 agents and grew greatly in size. After the war focus shifted to Irish Nationalism, the threat of communism and right wing extremism. MI5 helped carry out surveillance on fascist and communist organizations that were acting as a front for Nazi and Soviet espionage. During World War II they went on the offensive due to the German threat. Sixteen enemy spies were executed and forty-seven others were "turned" into double agents as part of "The Double Cross System". MI5 also collaborated with MI6 and foreign secret services to defend allies against espionage and create a network of double agents. During the Cold War, MI5 worked hard to defend the country against Soviet spies and British citizens under their control. Starting in the 1970s concern over terrorism grew and MI5 expanded to fight that as well.
MI6
Military Intelligence 6 (MI6), the Secret Intelligence Service, was created in 1909 and formally defined in 1994 in the Intelligence Services Act. Its purpose is to collect intelligence on foreign activity and act on it. MI6 was formed from the other department of the War Office's Secret Service Bureau, the foreign department. Going into World War I the objective was to gain information on German naval construction as well as any plans to invade Britain. During the war the department was designated as MI6. Their purpose was to establish networks of information and to thwart the efforts of Germans in neutral countries. The most successful intelligence network was "La Dame Blanche" consisting of almost 1000 informants. After the war the focus was on monitoring the Soviet Union and fighting the spread of communism. As World War II approached, aerial photographic reconnaissance became important. At the start of the war, MI6 suffered due to a shortage of staff and funds, the kidnapping of two senior officers and the robbery of its communications system by the Germans. They recovered quickly, however, thanks to valuable signals intelligence, an influx of funds and foreign dissidents forming information networks. Post-war, MI6 worked to destabilize the Soviet Union and turn members of the Warsaw Pact. Since the end of the Cold War their goals have changed but the purpose remains to collect intelligence on foreign threats.
Secret Communications
SOE
Secret Soldeirs
First World War Galleries
These galleries are about the First World War The 'Great War', as people called it at the time, lasted for over four years and cost millions of lives. In Britain everyone was affected by the Great War, whether they were fighting or on the home front. In these galleries men, women and children who experienced the war will tell you their stories.
The first thing you see when you go into the Gallery is 3 models of ships. Britain relied on ships such as in food and raw materials and to export its goods. Almost half of the world's merchant shipping was British. For example the ss Nonsuch was a merchant ship. Another model ship was the SS Gloucester Castle, a mail ship. Ships such as this enabled families and businesses to keep in touch across vast distances. As well as carrying post, mail ships carried passengers emigrating from Britain to new lives in the Empire and the United States. But the most important and largest ship was the HMS Hercules.
 The restored HMS Hercules model, shortly before its installation in the First World War Galleries. | |
| Attributed to Imperial War Museum | |
| Location | Imperial War Museum, London |
|---|---|
This model she had been displayed in the Imperial War Museum's Naval Gallery since 1936 but on Friday 31st January 1941 a huge incident happened. A group of workmen in the museum were repairing blast damage from earlier air raids, around midday they stopped for lunch and shortly afterwards a German bomber dropped five bombs in the locality. Had the bombs fallen a few minutes earlier the workmen would have all been killed. However, the Imperial War Museum's Naval Gallery was destroyed. Six showcases of ship's badges had their contents blasted cleaned out of the building being thrown off to the park and events the museum's roof. The bomb blast shattered the Hercules model glass showcase and "turned the ship's masts and other fittings into a mass of tangled wreckage".[1] In 2010, work started to slowly restore the Hercules model so that it could go on display in the museum once again.It is now available for visitors from all around the world to admire in the First World War Galleries of the Imperial War Museum London.
Like many ships of the Grand Fleet, Hercules drew its name from classical mythology. In the Greek myths, Herakles, known to the Romans as Hercules, was a hero of legendary strength who overpowered and outwitted his enemies. Some ships' names, like Hercules, evoked legendary figures known for their combat prowess or martial qualities. Examples include the battleships Bellerophon and Orion, the slayer of monsters and the huntsman respectively, or the light cruiser Bellona, the Roman goddess of war. Others ships took names that suggested perhaps surprising qualities for warships – the light cruisers Comus and Calliope remembered in their names the drunken god of wild partying, and the goddess muse of poetry and eloquence.[2]
Before the War
"England and the Empire were never greater than they are to-day"The Times New Year's Day 1914.
Most Britons were proud of their empire, the greatest the world had ever seen. Every fourth person on Earth owed allegiance to the British Crown. Many had emigrated from Britain, while millions more, notably in India, lived in lands conquered by the British.
Did all Britons feel pride in the Empire?
Most Britons believed that Britain's empire was a force for good. British emigrants who had sailed for new lives in Australia, Canada, New Zealand and South Africa felt pride in both their adopted homelands and the mother country. Yet doubts about the future of the British Empire were growing People living in Britain's overseas possessions increasingly demanded greater freedoms their own affairs. Britain's worldwide empire also aroused the envy of its European neighbours.
Britain was the maritime nation. "Grown by the sea and live by it; if we lose command ofit we starve."- The Riddle of the Sands' 1903. Britain was a hugely wealthy country. The sea was Britain's lifeblood. British merchant ships, guarded by the Royal Navy, traded goods across the globe. British industry generated great riches. London was the financial centre of the world. Did all British people benefit from such wealth? Only the ruling classes really benefited. Millions lived in poverty. Discontent was growing. Industrial workers downed tools in strikes over poor conditions and low pay. Barely two-thirds of men and no women had the right to vote. Suffragettes waged a sometimes violent campaign to change this. British politics was divided over Home Rule for Ireland, war. which was on the verge of civil By 1914 the United Kingdom looked increasingly disunited.
There are always clouds in the international sky. For decades Britain had existed peacefully, if not always harmoniously, with its European neighbours. But from beginning twentieth century. Germany's aggressive attempts to compete as a world power worried Britain, France and Russia. Was Europe sliding towards war? Between 1900 and 1914 several diplomatic crises were triggered by the growing fear and distrust feet by Europe s statesmen. Huge sums of money were spent on armies and navies. By 1907 Europe had split into two main camps: Austria-Hungary Germany, and Italy joined together in and France, Russia and Britain the other. Yet until in the summer of 1914. there seemed no immediate reason for war.
<br.
Why War?
- Distant crisis On 28 June 1914 a Serbian-backed terrorist shot dead Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne.
- War in south-east Europe Austria-Hungary, encouraged by Germany, set out to It war.
- Crisis rapidly spreads. This immediate crisis stirred old tensions and anxieties drawing in allies and supporters on both sides.
- A divided continent Leaders were willing to risk war to defend or extend their own national interests. Germany was determined to support Russia decided to stand reliable up for the Serbs. *Powers prepare Within weeks.Europe's leaders had prepared their armies and navies for war. Europe at war Germany believed it could gain an advantage by striking first. It declared war on Russia and then on Russia's ally in the west, France.
- Will Britain intervene? Some Britons did not want to join the fight. The British government, led by Prime Minister Herbert Asquith, agonised over whether to support Russia and France. But it feared German domination of Europe A victorious and hostile Germany would threaten Britain's security and its position in the world.
- Britain declares war. Germany's invasion of Belgium, to get to France, tipped the balance. Britain had long promised to protect Belgium's right to be neutral On 4 August 1914. Britain with its global empire declared war on Germany.
War Time
Seven million men marched off to war in August 1914. A million of them lay dead by the end of the year. Mainland Europe became a battleground. Both sides wanted to crush their enemies and end the war quickly. n the west, British, French and troops Belgium fought the German invaders. In the east, Germany and Austria-Hungary clashed with Russia and Serbia Neither side achieved a decisive victory The horrific number of casualties caused by modern weapons came as a terrible War crimes against civilians made the horror The British Expeditionary Force (BEF), the core of Britain's small army, was almost destroyed. In 1914 all armies hoped for a swift victory. On the Western Front, Germany planned to defeat France quickly. It would then strike at Russia. The Germans won a series of bloody clashes driven back at the Marne. Yet they still occupied nearly all of Belgium and much of northern France. On the Eastern Front, Russia captured much Austro-Hungarian territory, but its invasion of Germany was a disaster. Austria-Hungary failed miserably in fighting Serbia and Russia Why was there no quick victory in 1914? Modern weapons enormous numbers of casualties. Endless marching and fighting exhausted men and horses. Generals lacked the communications equipment to control huge armies. On both fronts, the war ground to a halt.
By late 1914 the war on the Western Front had become deadlocked Neither side had achieved victory in northern France and Belgium. They now dug trenches to protect themselves from each other's murderous fire. Soon, vast trench networks snaked from the English Channel to Switzerland. The German Army had to defend the rich industrial regions it had seized. Trenches were easier to defend than attack, so the Germans hoped to wear down their enemies by sitting tight. The British and French had to drive the Germans out. They searched desperately for new weapons and new ideas to do just that.
World War
A European war meant a world war. From the very beginning, the overseas empires of the European powers were drawn into the conflict. As the war spread, so did the suffering. Germany hoped to divert Britain's attention away from the Western Front. It struck at Britain's global empire. Britain struck back. There was fighting in Africa, in Asia and in the Middle East. In these far-flung campaigns, more soldiers and civilians became victims of disease than of shells and bullets. The seas were also Both sides tried to starve their enemies. They sank or seized ships carrying vital food and supplies.
Total War
In 1915 Britain faced falling army recruitment and shell shortages at the Front. To win the war, a transformation was needed. A home front' was created to supply the fighting fronts' constant demands for men, weapons, equipment and food. A new government stepped up the effort at home. It built a network of factories for weapons production and recruited an army of men and women to work in them. lt passed laws which controlled people's lives in ways they had never expected. And no longer the government men volunteer From 1916, make them fight it.
As 1916 drew to a close, there was still no sign of victory. New leaders urged their weary citizens to work even harder. Total war on the battlefield meant total war on the home front. Nobody in Britain could escape the impact of war. Women kept the country going, filling jobs usually done by their fathers, brothers and sons. Even children played their part in the war effort. Britain itself was coming under attack. German aircraft bombed people in their homes. German submarines attacked ships bringing food and supplies. There was armed rebellion in Dublin. But America's entry into the war offered new hope for Britain and its allies.
Machines Against Man
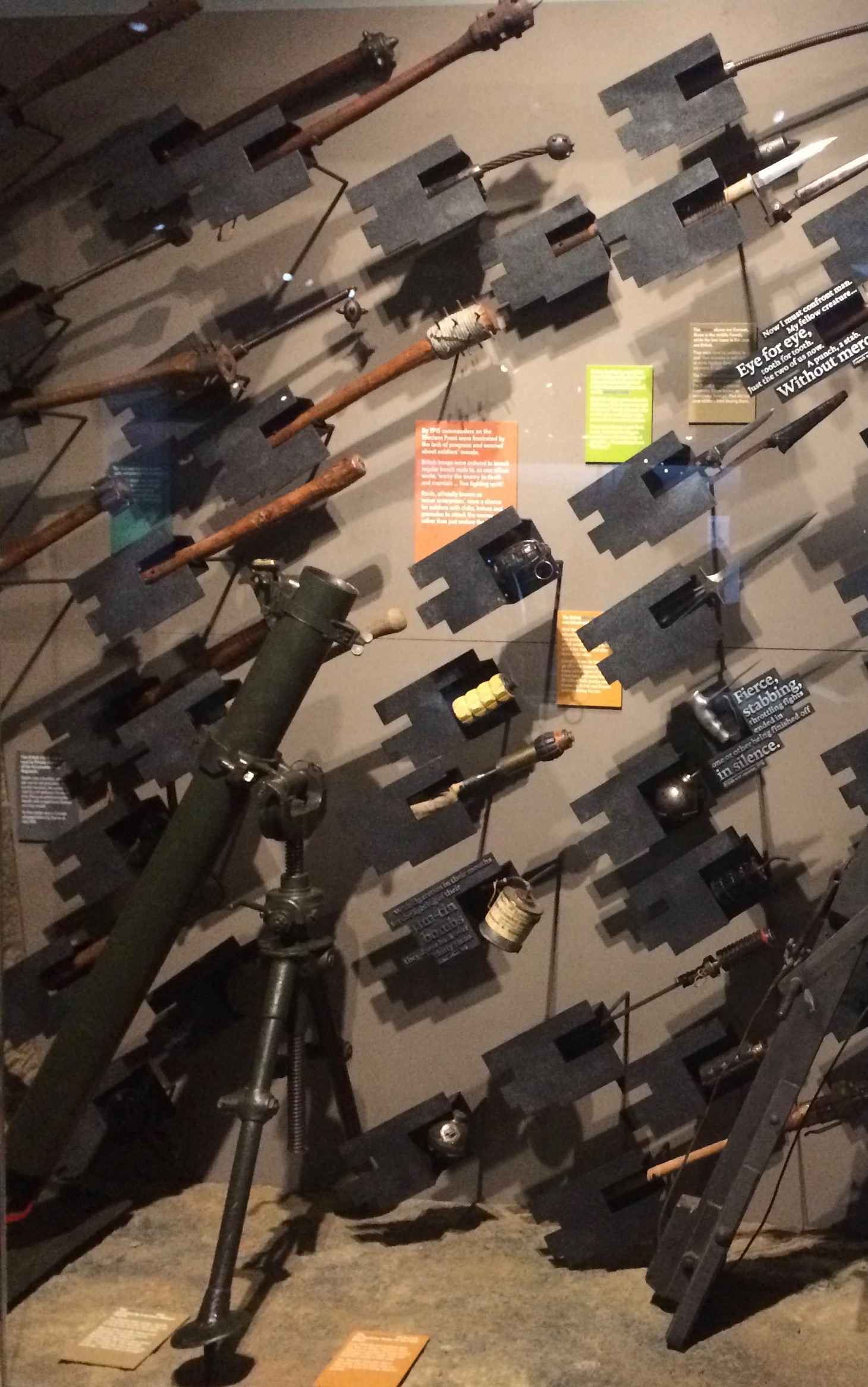
The First World War galleries dedicates a section of the gallery to the changing technology and machinery of WWI. The new machines of the War created a new kind of devastating war and landscape. New technologies and tactics of wartime changed the way that the war was fought. In 1917, British commanders began to truly understand the power of tanks and aircrafts after three years of difficult fighting. Many people described this time by agreeing that the day of the rifleman was over. New weapons could easily locate and destroy enemies and barbed wire fences. However, it was difficult to move large weapons across a battlefield due to the devastations of war and the fact that moving them gave the enemy time to regroup after an attack.
Another defining feature of WWI or the Great War as it was called, is the its unique role as the first "modern" conflict of such immense scale. Newly developed weapons of the era, as a result of lack of intensive field testing, often proved faulty or otherwise unreliable. Early on, The First World War, as a result, was fought with weapons ranging from clubs and daggers to muskets and early machine guns to improvised grenades and shell mortars.
Communication technologies also improved during this time. Also, British soldiers now had the power to have their own machine guns, giving them automatic firepower when they needed it. Guns were becoming increasingly more destructive and the inventions of tanks and new planes forces better teamwork skills among soldiers to be produced. However, the war was not easily won and victory did not come quickly. As weapons became more sophisticated, increases in death and destruction occurred, making it a tough fight for Britain.
The new landscape of war caused the British government to employ men who were artists and soldiers in order to have them capture the new world of war around them. This war art was hugely popular with people everywhere, and the art appeared in museum exhibitions as well as in magazines and on postcards. British people on the home front desired a way to see what the men in their families were going through, which attracted many people to displays of the art.
Breaking Down
By 1917 war was putting ever greater strain on armies and home fronts. Genera A growing number of civilians, politicians and soldiers were looking for a way out. Statesmen thought about negotiating an end to the war. On the battlefield soldiers went on strike and deserted. On home fronts there was hardship and often hunger Public calls for peace became louder. Austria-Hungary and Turkey began to crumble. But Russia, one of Britain's allies, broke first. Gripped by revolution, Russia left the war. By 1918 Germany could concentrate its army on the Western Front. would gamble on one last offensive to defeat Britain and France.
October Revolution
In 1917, the war was entering its final stages, but a new war broke out in the heart of Russia. The Tsar was being overthrown by the people. A revolution was hand during the Great War. Once the Tsar was overthrow, there was a power vacuum in Russia. They had withdrawn from the war, erasing Germany's western front. Their focus was inward on who would end up leading the vast nation. A provisional government was setup in wake of the Tsar abdication, but the government was weak and couldn't last for long. In October, the solution was found with the Bolshevik people. Their leader, Vladimir Lenin, lead the revolution with full force. The revolution had occurred because of the way the Russian people were being treated during the war. They had mass protests about their involvement in the war, but the Tsar wanted to keep Imperial Germany away from Russia's doorstep. Food supplies were being diverted away from the Russia people and to the soldiers on the front lines. Lenin and the Bolshevik's promised "Peace, Bread, and Land" to the people, and they bought into it. At the World War I gallery in the Imperial War Museum, there was a pro-Bolshevik propaganda sign that read "пролетарии всех стран соединяйтесь! в борбе обретеш ты право свое!". When translated into English, the sign reads "The proletarians of all countries unite! In struggle you will find your right!". Lenin and the Bolsheviks were channeling the hatred, anger, and low self worth of the Russian people, and that ultimately lead them to victory during their October Revolution. They had successfully turned Russia from an Empire to a Soviet State, and it would remain a Soviet State through World War II and Cold War before finally collapsing in late 1991.
Rationing Propaganda
In an effort to conserve supplies for those on the front lines, many government propaganda posters were created for both sides of the war.These posters encouraged the consumption of less bread and to growth personal gardens to increase food supplies. Families on both sides also had a form of rationing book and coupons to receive a monitored amount of necessities like milk and sugar. Families with young children and newborns were given a larger supply of supplies such as milk, but it was not significantly more than the standard portion. German rationing had come to the point where the people were making bread containing sawdust, tobacco with tree bark, and coffee made out of barley.
Seizing Victory
Seizing victory 1918 saw the dramatic end of trench warfare as both sides used new tactics and colossal firepower to break the deadlock. The German Army launched gigantic offensives on the Western Front. For the first time since 1914, the Allies feared defeat. They held on, but only just From July, the Allies counterattacked. They had more weapons and more supplies. All along the Front they struck devastating blows against the Germans Germany's army retreated. Its allies crumbled away. Its people began to revolt. Germany's army was defeated. On 11 November 1918 a beaten Germany signed the Armistice. The fighting ended.
The end came rapidly. its allies disintegrated. In October, hoping for lenient terms, Germany approached US President Wilson for an armistice. angry Germans When this became public, wondered why they were still fighting. To avert revolution, to abdicate. the Kaiser was forced On 11 November 1918 Germany signed an armistice which ended the fighting on the Western Front. What was the Armistice? An armistice is usually just a ceasefire. But the 1918 Armistice forced the Germans to leave occupied territory and to surrender weapons, aeroplanes and warships. Beaten in battle, Germany had no bargaining power. For Germany, the Armistice was both a defeat and a bitter humiliation.
Britain and its empire were triumphant, but much changed by four years of war. The Great War gave rise to new ambitions, rivalries and tensions. Old empires had fallen, new nations had been born. Revolutionary ideologies like communism fascism emerged Wars were still being fought The leaders of victorious powers met the They Paris to settle the peace. and were faced with an exhausted shattered world. would had high hopes they create a new, that safer and better one.
Afghanistan: Reflections on Helmand
This temporary exhibition examines the 2006 arrival of British troops in Helmand province, Afghanistan. The exhibition contains artifacts from the conflict, including knives, handguns, a fighter pilot's helmet, and a piece of shrapnel that was stopped by a soldier's armor. Also featured are audio and video interviews with soldiers and commanders, exploring the decisions that shaped the conflict and the lessons learned.
History
British forces arrived in Afghanistan in October 2001 as part of an international force, helping to maintain security for the new government. In 2006 British troops were deployed to Helmand province with the plan to create a secure environment at the center of the province. Soon after they arrived, British troops became involved with fighting the Taliban. At present, many of the locations in Helmand secured by British forces have returned to violence. Because of the limited long term gain and the high human and financial costs, the decision to deploy to Helmand is now under contention. As Mark Etherington, Head of the Joint Planning Team for Helmand in 2005 said, "I suspect the overwhelming lesson learnt is never again[3]."
Second World War Galleries
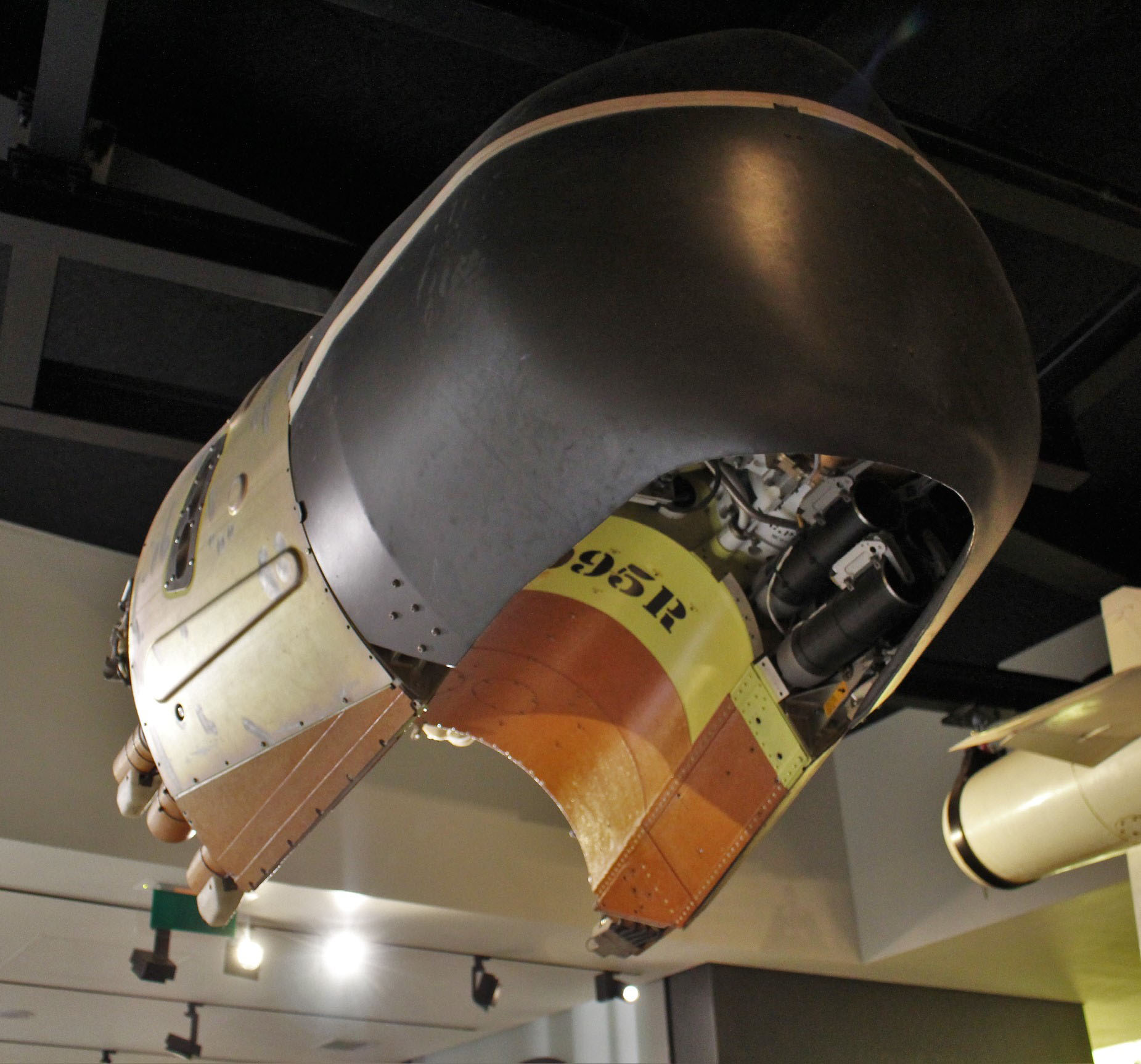
V-2 Rocket
The V-2 Rocket was invented by Germany during the second World War. It is the first long range ballistic missile ever invented. It is the first ship to ever capture footage from space. It was invented by Wernher von Braun who later invented the Saturn V rocket for the United States. (pics will come)
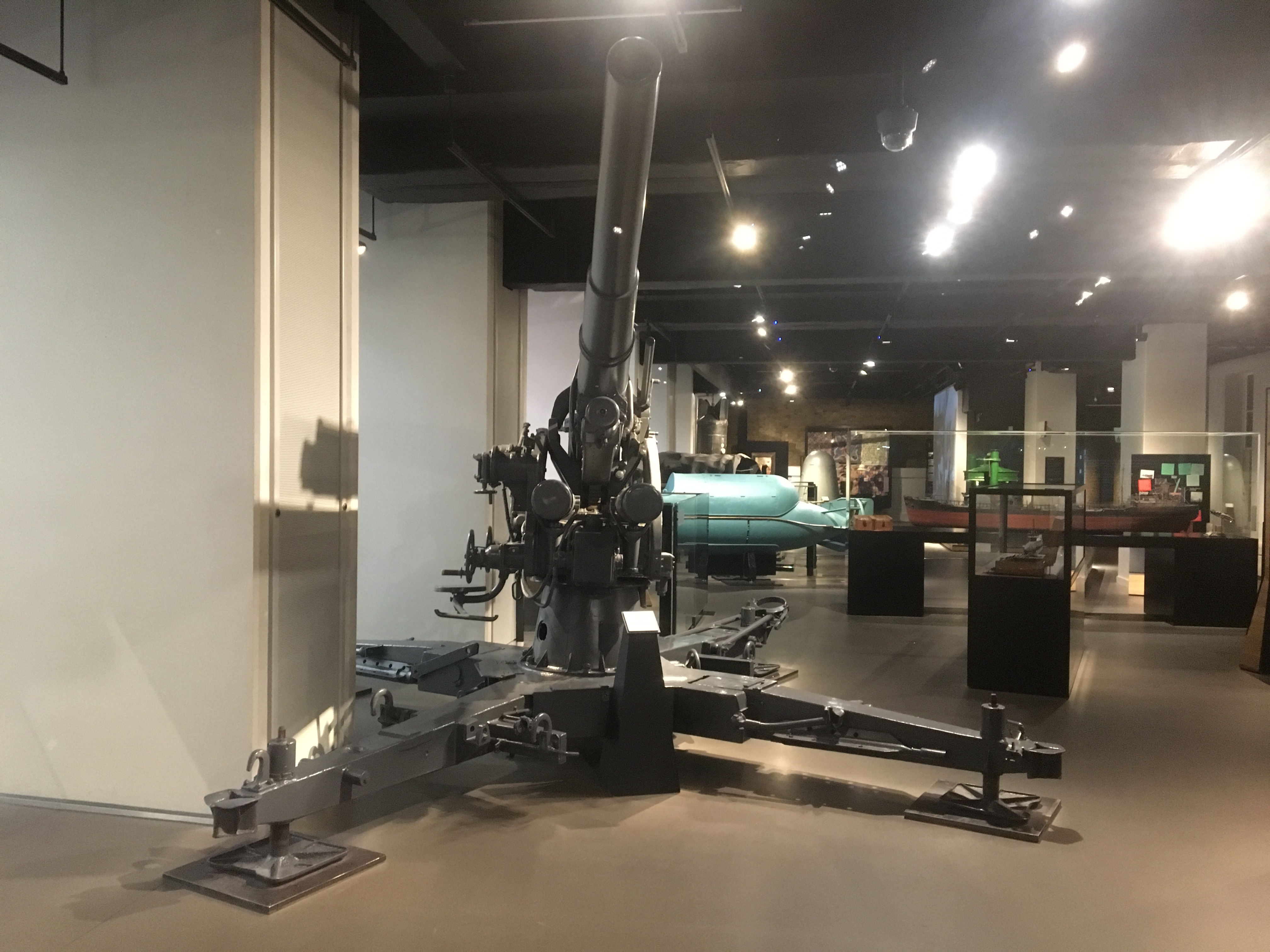
Flak 36
During the second World War when the RAF began flying missions over Germany flak was encountered. One of the main guns behind this was the 3.5 inch Flak 36. These kinds of flak guns caused over one-third of RAF casualties. By 1944 Germany had between 10,000 and 15,000 of these guns protecting it.
Turning Points
The turning points in World War II were outlined in this exhibit. All of the objects were connected and had a story. The second world war changed the world and these are the objects that changed history. To read more about this, click here
Nuclear War
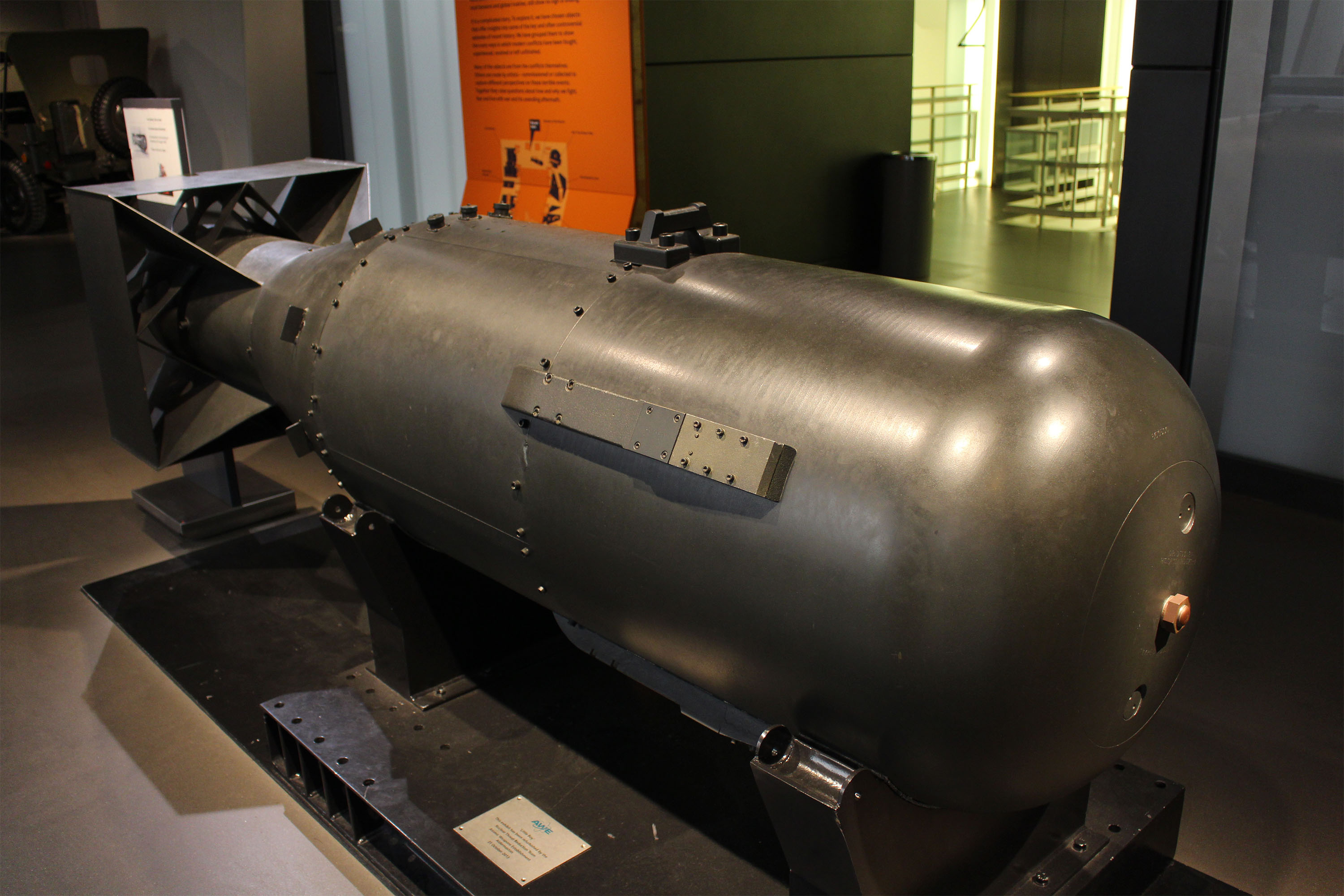
Little Boy
Nuclear Bombs have only been used twice at war, on the towns of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The Imperial War Museum has one of five casings made for the Little Boy bomb, which was dropped on Hiroshima. As a result of the bomb, around 70,000 people were killed. The bomb casing has been placed as close to the center of the museum as possible, in order to symbolize, as stated by the museum curator, Roger Tolson, "not only political power and creative development, but also [...] absolute fear and horror."
Radar Penetration System
As missile technology grew more advanced, so did the defense mechanisms put in place to protect from these. The Penetration Aids Carrier was secretly developed to mask the sonar signal from a nuclear missile so it would be able to bypass Soviet defenses. Of course, this was never ultimately necessary, but the entire logical reasoning behind nuclear weapons was to use Mutually Assured Destruction as a way to keep the other side from launching a missile.
The Holocaust Exhibition
This exhibition goes from the year 1933 to the year 1945 focuses on the Nazi regime and their persecution of Jews in Europe. It examines how and why Hitler rose to power and how it ultimately affected the population of Europe forever. This exhibit has photographs, diaries, clothing, toys, and films of people who experienced this tragedy. The exhibit and the personal accounts of survivors are a painful reminder of the tragedy of war and how it had devastated the lives of many.
War on Terror
Counter-terrorism is the measures deemed necessary by governments and their security forces to neutralize terrorist threats. A lot of the counter-terrorist activity is necessarily conducted in secret, but it is supposed to always be conducted in accordance with the law. Way of interrogating including abduction, detention without trial, and use of torture, go against international law. The works in this exhibit show the most controversial parts of the international terrorist response.
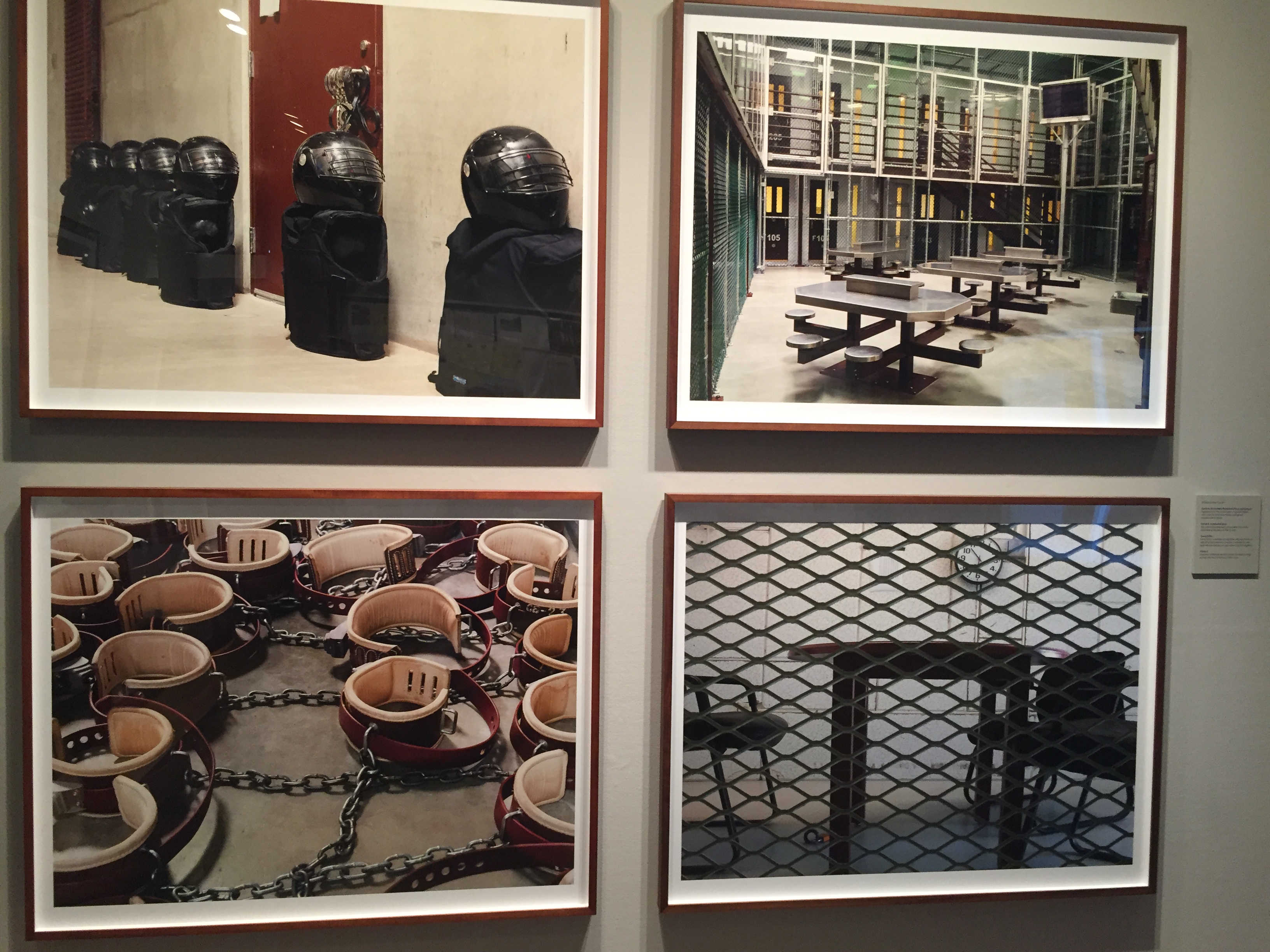
This work is called Guantanamo: If the Light Goes Out (2010)
It is a serious of photographs that are reflecting on an experience of being held at the US military detention facility in Guantanamo Bay. Guantanamo Bay was opened in January of 2002 and its purpose was to detain men suspected of terrorist- related activity and get intelligence. Of the 779 men who have been held at this facility only eight have been convicted, of which four had their convictions overturned. President Obama pledged to have the facility closed, however as of June 2016, 80 men still remained in custody. These photographs which were subject to censorship on site, show the systems of control, and the interrogation experienced by detainees.
Going clock-wise from top left, the first image is of Camp 6, Immediate Response Force Equipment. This is equipment for the small teams of guards that are in charge of coercion and responding to a detainee with force. The next image is the Camp 6 communal area. When the photographer visited, this communal area was not available for use by the detainees. The next image is of Camp Echo, which consisted of individual cells, that have an attached interview area which was used to consult with legal representatives or for supervision and interrogation. The final image is of Camp 6, it is a picture of shackles, which detainees where regularly shackled to rings that are set into the floor when they are out of there cells.
Family in Wartime
This exhibit focuses on how family life was affected primarily during World War II. One of the main focuses of the exhibit is to give visitors a better understanding of how daily life in Britain changed during the war. Things such as air raids, rations, and preparedness plans were all part of life especially in London itself. The exhibit holds many primary documents such as newspapers that brings the war experience a little closer to the visitor. The exhibit also has a continuous rolling film of the war which was described as commonplace to keep citizens up to date and connected to the war effort.
Syria: A Conflict Explored
This is a temporary exhibit that is opened till September 2017.[4] Part of the Conflict Now program, this exhibit explores the beginnings, timeline and the human impact of the things going on in Syria. The conflict in Syria started in 2011 and is still going on today. According to the War museum website, 'The ongoing conflict has already lasted longer than the Second World War. [4] As a result, nearly half a million people have been killed. Almost eleven million – half the pre-war population – have been forced from their homes and much of the country lies in ruins.'[4] This section shows a collection of war objects, and stories of real people that show the devastation that Syria has faced through this.[4]
Sergey Ponomarev: A Lens on Syria
Sergey Ponomarev is an award-winning Russian photographer. Over 60 of his works are featured in "unforgettable color" from two of his recent works. His photos in his work Assad's Syria offer rare insight into what life is like for people living in Government-controlled areas in Syria in 2013-14. His work The Exodus captures the endurance and suffering of people from Syria and elsewhere who were seeking asylum in Europe in 2015-2016.
Lord Ashcroft Gallery
The Lord Ashford Gallery houses largest collection of Victoria Crosses in the world along with a huge collection George Crosses. The Victoria Cross is the highest award given in the British Army and is given to those who have gone above and beyond in the protection of the country. The collection was donated to the Imperial War Museum by Lord Ashcroft, who was a collector of the Victoria Crosses. He is a philanthropist and the gallery was named after him. This gallery not only houses all of these medals but also tell the stories of those awarded with medals. Those given these metals are people of great bravery and deserve to be honored. [5]
Victoria Cross vs George Cross
The Victoria Cross was created on January 29, 1856 to recognize extreme bravery carried out under direct enemy fire. There have been 1,354 award recipients, four of which been from 2000 with one in Iraq and three in Afghanistan. The youngest recipients to ever receive a Victoria Cross are Thomas Flinn in 1857 and Andrew Fitzgibbon in 1860, they were both 15 years 3 months old. The oldest recipient was 69 year old William Raynor who defended an ammunition store in India for five hours in 1857. Two soldiers have earned the Victoria Cross for saving their brother's life including Charles Gough in 1857 and Horace Ramsden in 1899.
George Cross was created on September 24, 1940 to recognize extreme bravery carried out both in peace time and in wartime away from battle. It is the second highest award given out to British arm forces and citizens. There have been 406 given out, one of which is on display at the Museum of London Docklands as it is Richard V Moore's for his bomb disposal efforts during the Second World War.
Joan Daphne Mary Pearson
 | |
| Attributed to | User:Kfconroy |
|---|---|
Joan Daphne Pearson is one of the first women to be awarded the George Cross for bravery during World War II. She was given this award for saving several men from an aircraft crash during the middle of the night. Seeing that Joan Daphne was the first responder to the scene, she decided to try to get medical attention to the seriously injured airmen. There were many bombs aboard the wreckage and she was risking her life trying to save him, but that did not deter her from getting the pilot out of the cockpit. However, after getting him about 30 yards from the wreckage, a 120lb bomb exploded and she immediately used herself as a shield to protect him. When the other rescuers found her, she left to see if anyone else survived. Joan Daphne risked her life for the well-being of others and that’s what made her the award recipient of the George Cross. [6]
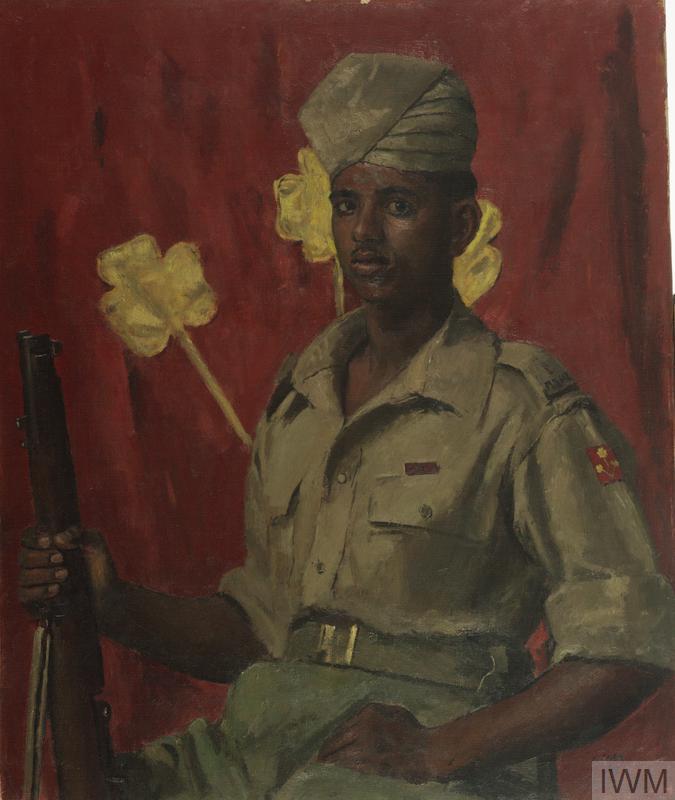
Kamal Ram
 | |
| Attributed to | User:Kfconroy |
|---|---|
Kamal Ram was a Sepoy in the 8th Punjab Regiment of the British Indian Army during World War II. He was only 19 years old when his battalion was assaulted by the German forces. His battalion was held up by heavy machine-gun fire and they needed a volunteer to clear the area. He volunteered and single-handedly killed the first and second machine gunners and then killed the German officer appearing from the trenches. Kamal then proceeded to, by himself, attack and defeat the remaining posts. He and his battalion continued to take over the area, which could not have been done without his bravery and selflessness.[7]
References
- ↑ J. (2016, March 16). HMS Hercules At War And On Display. Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.iwm.org.uk/history/hms-hercules-at-war-and-on-display
- ↑ J. (2016, March 16). HMS Hercules At War And On Display. Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.iwm.org.uk/history/hms-hercules-at-war-and-on-display
- ↑ Afghanistan: Reflections on Helmand. (n.d.). Retrieved May 23, 2017, from http://www.iwm.org.uk/exhibitions/iwm-london/afghanistan-reflections-on-helmand
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 K. (2017, March 31). Syria: A Conflict Explored. Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.iwm.org.uk/exhibitions/iwm-london/syria-a-conflict-explored
- ↑ About the Victoria Cross. (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.lordashcroftmedals.com/about/
- ↑ George Cross & GC. (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.iwm.org.uk/collections/item/object/30009898
- ↑ THE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO THE VICTORIA AND GEORGE CROSS . (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2017, from http://www.victoriacrossonline.co.uk/kamal-ram-vc/4587254429
External Links
If appropriate, add an external links section
Image Gallery
If appropriate, add an image gallery